Distribution panels are installed in buildings supplied with electricity. The electrical box organizes, isolates the distribution and protective equipment: circuit breakers, RCDs, difavtomats, voltage limiters, meters, as well as adjacent cables from the influence of the environment, mechanical damage, outside interference in the distribution system.
Types of equipment in accordance with GOST

Shields are classified as low-voltage complete devices, therefore, the general rules for their construction, installations are described in GOST R 51321.1-2007. The requirements for the equipment of industrial, public and residential buildings are different. GOST 32395-2013 standardizes domestic use, and GOST R 51778-2001 - industrial and public. Shields must correspond to electrical installations of buildings under construction and already operated with TN-S, TN-C, TN-C-S grounding systems.
The GOST 32395-2013 standard applies to multi-apartment buildings of mass development and individual plans, cottages, rural and garden single-family houses. Nominal connection parameters: voltage 230 V or 230/400 V, frequency of three-phase alternating current 50-60 Hz. Access to the panel panels is available to unqualified users to turn on and off the power supply to the internal electrical system, but there are lockable boxes with the possibility of sealing. To protect a person, grounding elements, working or double, reinforced insulation are used in electrical panels.
Shield box design

The electric box for automatic machines is represented by the product lines of domestic and foreign brands. A simple model can be assembled on your own if you have the ability to handle metal. There are several main structural elements.
Housing made of metal or refractory (insulating) plastic.
The metal body is made of steel sheets 0.5–1.5 mm thick, coated with powder paint to prevent corrosion and environmental influences. Such performance is more expensive. Plastic - made of polymers that can withstand high temperatures and overheating. More aesthetic if they fit into the interior. There are miniature versions for 2-6 modules.
The degree of resistance to electrical, thermal and mechanical influences is determined by the IP ** marking, where the first * is expressed by a number from the range 0-6 and shows the level of protection of a person from contact with electricity and equipment from the ingress of solid particles and dust, the second * is protection from moisture (0-8).
When installed outdoors, the switchgear enclosures must be protected from water by at least 3. For this, use sealed models with a rubberized lid perimeter. The degree of protection of the shell and the operational one often diverge, therefore two values are indicated.
Electromagnetic processes affect the quality of plastic and rubber parts - they lose their properties under the influence of thermal loads. The insulating material that touches the conductive parts withstands the hot wire test up to 960 ° C. For other prefabricated elements, 650 ° C is sufficient.
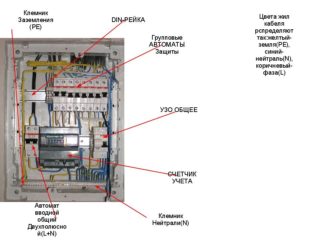
The junction box for the meter and metering and distribution units has an insulated or non-insulated window through which the readings are visually controlled. Plastic models are produced with a transparent lid. Input / output of wiring to / from the case is carried out through technical holes.After the installation is complete, they are closed with special plugs.
Other elements of the electrical box:
- Internal flap for wiring insulation. Required if access to the control panel is not limited to qualified personnel. A widespread screen with a slot for access to readings of accounting equipment, switches and switches. If necessary, the partition is equipped with a special lock, sealed so that only employees of the electrical service organization have access to the wires.
- Mounting plate, rail for modular elements or combination. The classic option for fixing devices is a plate with mounting holes. Most modern boxes are equipped with a 35 mm metal profile (din-rail) for fixing modular equipment. The casings accommodate one or more fastening strips, depending on the estimated or actual number of machines inside. One module on the rail is allocated 17.5 mm, the distance between the centers of two adjacent elements is 18 mm. The difference is due to the need to leave air gaps between pieces of equipment. It should be understood that the size of one module is equal to a single-pole switch. For a two-pole - 2 modules, a single-phase RCD - 3, a three-phase RCD - 5, an electric meter - 6-8. I expect the standard indentation in rows of vertical profiles - 125 mm.
- Busbars for withdrawal of zero (N), grounding (PE), common conductor (PEN). Fixed with screws to the case, some models - on a din-rail.
- Self-tapping screws for fixing built-in and wall boxes.
- Partitions and compartments are sometimes present inside the shells.
- The complete set of expensive models can be supplemented by clients, jumpers, and have removable sides of the box.
The size of the boxes is directly related to the wiring diagram. The more lines, protective equipment, the larger the case. For an apartment panel without a meter, a box for 12-24 modules is usually sufficient.
Types of LVCD
It is worth choosing a model according to climatic performance: U1, UZ, UHL3, UHL4. Decoding of markings:
- U - temperate climate;
- UHL - temperate and cold climate;
- 1 - street,
- 3 - closed rooms with natural ventilation,
- 4 - spaces with artificial ventilation, full or partial air conditioning, laboratories.
Contents and location of shields:
- apartment group and accounting-group are installed in individual dwellings, organize the connection of group circuits, differ in the presence of a meter in the second version;
- storey distribution, accounting and distribution and accounting-distribution-group - are located on the walls of storey corridors and staircases, separate the line through apartment-group nodes, contain apartment-based accounting equipment and connection of circuits.
According to the method of installation, the electrical box can be hinged, mounted in a niche or a floor cabinet. The mortise box is less knocked out of the situation, but for it you need to cut the wall, which is not always acceptable. With an open wiring, this installation method is not relevant. Hinged ones are fixed to a vertical surface using a self-tapping screw. The cupboards are screwed to the floor. The collection of electronic "filling" can be carried out both before and after fixing the body.
By the presence of protection against electric shock - I or II class. I - presence of grounding of non-live parts, II - double or reinforced insulation.
According to the number of phases - one- or three-phase. This affects the size and number of technical holes.
The shields are equipped with a low-current compartment for laying telephone, cable, local networks, security and fire alarms or video surveillance, as well as an introductory device, a riser cutter (supply circuit), and remote control.
Basic rules and procedure for assembling a shield
Installation steps:
- The inlet plugs are removed.
- A door or external screen is displayed.
- Rails and grounding buses, neutrals are mounted.
- A box is tried on at an equipped place.
- Attaching electrical equipment is easier on the desktop.
- Last but not least, the door returns to its place.
Before purchasing and installing a shield, it is worth carefully designing the circuit, determining the environmental conditions and budget.