The operation of electrical appliances is impossible without certain network parameters. They are composed of many factors. One of them is the resistance of conductors to electric current. Taking into account the cross-section when choosing wires or cables, it is necessary to take into account the voltage drop.
Basic concepts

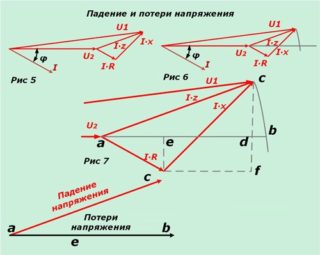
The voltage drop is the magnitude reflected in the change in potential in different parts of the conductor. The current flowing from the source towards the load changes its parameters due to the resistance of the wires, but its direction remains unchanged. You can measure the voltage using a voltmeter:
- two devices at the beginning and end of the line;
- alternate measurement in several places;
- a voltmeter connected in parallel with the cable.
The simplest circuit is a power supply, a conductor, a load. An example would be an incandescent lamp plugged into a 220 V. If you measure the voltage across the lamp with the device, it will be slightly lower. The fall occurred on the resistance of the lamp.
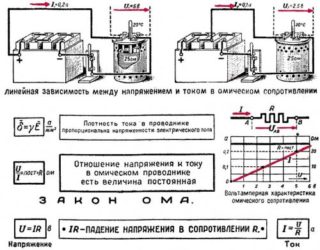
The voltage or voltage drop across a section of the circuit can be calculated using Ohm's law, according to the formula U = IRwhere:
- U - electrical voltage (volts);
- I - current in the conductor (ampere);
- R - resistance of the circuit or its elements (ohms).
Knowing any two values, you can calculate the third. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the type of current - alternating or direct. If there are several parallel connected resistances in the circuit, the calculation becomes somewhat more complicated.
Undervoltage result
According to the regulations, losses from the transformer to the most remote area should be no more than 9%. The result of the deviation of the parameters from the norm may be as follows:
- failure of volatile installations and equipment, lighting devices;
- failure of electrical appliances at low input voltages;
- decrease in torque when starting an electric motor or compressor unit;
- starting current leads to overheating and shutdown of the motor;
- uneven current load at the beginning of the line and at the remote end;
- lighting devices are working half-heartedly;
- loss of electricity, underutilization of current power.
The characteristics and parameters of the operation of electrical devices are changing. For example, due to low power, the time for heating water by a boiler increases. A drop in voltage leads to malfunctions in the electronics.
In the operating mode, the voltage loss in the cable can be up to 5%. This value is acceptable for networks in the power industry, since high power currents are delivered over long distances. Increased requirements are imposed on such lines. Therefore, in case of losses in everyday life, attention should be paid to secondary power distribution networks.
Causes of voltage drop
First of all, you need to understand: this is the fault of the electricity supplier or consumer. Network problems arise for the following reasons:
- wear of power lines;
- insufficient power of transformers;
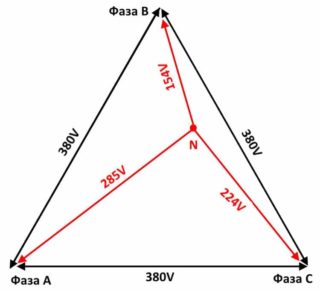
- power imbalance or phase imbalance.
These problems are vendor-related and cannot be resolved on your own.To understand whether the high-voltage lines are working correctly or not, you will have to call the representatives of the power supply. They will take measurements and draw up a conclusion.
You can make sure that the fault of the fall is not related to the supplier. First of all, it is worth asking your neighbors if they have similar problems. A multimeter is suitable for measuring voltage at home. Its cost is up to 1000 rubles. If the device at the entrance to the apartment shows normal voltage, the cause must be looked for in the home network.
The voltage may drop due to the long length of the wiring. When the length of the network exceeds 100 meters, and the cross-section of the conductors is 16 mm, the vibrations will become regular. To remedy the situation, you will have to change the wiring.
Weak contacts are additional resistance to current. It reaches the instruments in insufficient quantities. In addition, faulty contacts can cause a short circuit and lead to a fire. To normalize the indicators, it is necessary to replace the emergency section of the chain and burnt contacts.
The culprit may be the wrong connection of the wires going from the power line to the house. Sometimes, contrary to safety requirements, copper wires are connected with aluminum or copper conductors are connected instead of terminals by twisting. Terminals and clamps are made of poor quality materials, or their expiration date has expired.
Perhaps the malfunction lies in the introductory apparatus itself. In this case, it should be replaced.
How to calculate losses
When calculating the electric line, the voltage deviations should not exceed the regulated norms. Permissible fluctuations for household single-phase networks are 209-231V, for a three-phase network, the voltage can vary from 361 to 399 V.
Fluctuations in the current strength and power consumption lead to a change in voltage in the current-carrying conductors near the consumer. Therefore, when drawing up the wiring diagram, it is necessary to take into account the permissible losses.
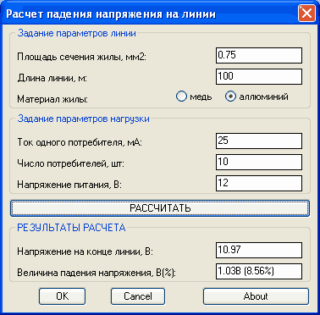
There are two wires in a single-phase network, so the voltage drop can be found using the following formula: U = I * R, in turn, R = (r * 2i) / S.
- Where r - resistivity, which is equal to the resistance of a wire with a cross section of 1 mm2 and a length of 1 m;
- i - denoted as the length of the conductor;
- S - cable cross-section.
In a three-phase network, the powers on the phase wires compensate each other, and the length of the neutral conductor is not taken into account, since no current flows through it. If the phase load is uneven, the calculation is performed as for a single-phase network. For long lines, capacitive and inductive resistance are additionally taken into account.
The fall calculation can be performed using an online calculator, there are also special tables. They show the permissible current loads for different types of cables. When calculating the cable cross-section, the following data must be taken into account:
- material for the manufacture of conductors;
- hidden or open line laying;
- current load;
- environmental conditions.
When current flows through a cable, wire or bus, they are heated. This process changes the physical properties of the conductors. The insulation melts, the contacts overheat, and the wire burns out. Reliability and uninterrupted operation of the power grid depends on the correct selection of the cable.
How to reduce voltage drop and reduce cable losses
You can reduce the amount of losses by reducing the resistance throughout the entire power grid. Savings come from a way of re-grounding the zero at each transmission tower.
The cost of power supply with a long line, selected according to the allowable voltage drop, is higher than the choice made for heating the cable. There is still an opportunity to reduce these costs.
- Strengthen the initial potential of the supply cable by connecting it to a separate transformer.
- It is possible to achieve constant voltage values in the network by installing a stabilizer near the load.
- Consumers with low loads of 12–36 V are connected via a transformer or power supply unit.
The longer the power line cable, the more resistance arises when current flows through it. Obviously, the voltage loss is also higher. You can reduce them by combining methods with each other.
- Reduce costs by increasing the cross-section of the supply cable. But this method will require large financial investments.
- When designing power lines, the shortest path should be chosen, since a straight line is always shorter than a broken line.
- As the temperature drops, the resistance of metals decreases. Vented cable trays and other designs reduce line losses.
- Reducing the load is possible if there are many power supplies and consumers.
Saving is provided by the proper maintenance and prevention of power grids - checking the density and strength of contacts, using reliable terminal blocks.
Energy conservation should be approached with full responsibility. The problem of voltage loss can damage expensive devices and tools. Safety measures should not be neglected, they will neutralize power surges and protect household appliances and equipment at the enterprise.