Conductors are zero protective and zero working, each of them has its own purpose, method of connection and permissible functional loads in the electrical circuit. Before starting work on the creation of a protective circuit, it is important to obtain the minimum, but necessary knowledge.
Purpose of conductors

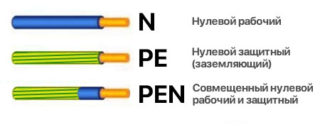
The zero working conductor has another name - the network conductor. A load current flows through it. On the diagram, it is denoted by the Latin letter "N".
The main task of the neutral protective conductor is to ensure safety. In systems with a zero terminal of a solid-grounded transformer, it commutes the conductive parts of electrical receivers and the zero point of the supply transformer. In emergency or abnormal situations, they are under attack.
The following electrical elements are subject to protection against indirect contact (according to PUE 1.7.76):
- enclosures made of metal for portable and mobile devices;
- metal structures of transformers, electrical machines and lighting devices;
- metal cases of various designs with electrical equipment, cable sleeves, trays and various distribution devices;
- steel cases of floor, apartment boards, distribution boards.
As a protection, the switching of these devices with a dead-grounded neutral is used in TN or TT, IT systems. The last two are grounded.
Schematically, the neutral protective conductor is designated "PE". When the electrical circuit is operating normally, no current flows through the PE.
In the diagrams, the combination "PE" means a neutral protective conductor, as well as all protective segments of the circuit, for example, laid buses and conductors, grounding conductors, individual cores in cables, as well as a wire in the equipotential bonding system.
The difference between zero protective and working conductors
Before starting work, it is important to familiarize yourself with the features and characteristics of conductors, to conduct a comparative analysis.
| Name | Description |
| N - neutral working wire | Together with the phase conductor, it takes part in the continuous and unhindered supply of power to household appliances and other electrical appliances. A working current constantly flows through it. |
| PE - neutral protective conductor | Does not take part in the provision of electrical appliances and household appliances with electricity. The main task is to protect against indirect interaction in networks with a solidly grounded neutral. |
Designation of a neutral protective conductor
Most often, the marking of zero protective conductors has a yellow-green color. The PUE establishes the basic rules for choosing the cross-section of the current-carrying wire.
PE has its own ground loop, or its main tasks can be assigned and combined with a neutral wire, in this case everything depends on the installed grounding system in the building structure. The combination of two conductors is called PEN, its cross-sectional area must be at least the parameters of the cross-section of the working wire N.
Laying rules
- There must be no devices in the line that could cause disconnection, loss of continuity, such as removable plugs, switches, circuit breakers and fuses.
- All equipment and live parts are directly connected to protective earth.
- It is forbidden to connect several electrical devices according to the loop principle.
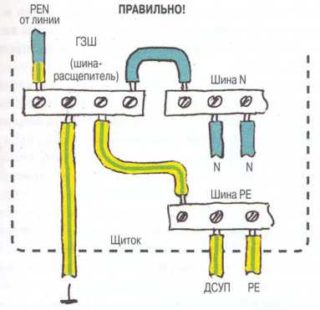
- A separate terminal (clamp) is allocated on the PE distribution bus. It is forbidden to simultaneously connect the zero protective and working wires to the same terminal.
- If RCD residual current equipment is installed in a switchboard, N and the protective conductor must not have contacts on the same line. If you neglect this rule, the RCD will have a lot of false positives.
- For working wires, the cross-sectional area must be larger than the cross-section of the protective ground.
- The zero protective conductor must be laid near the working wires.
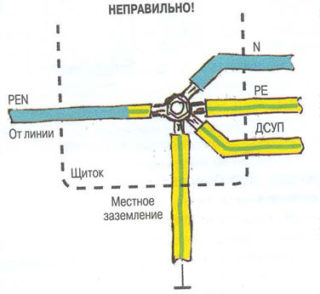
- For grounding, you cannot use objects and communications that are not intended for this. Most often, in this case, fittings in the walls, piping and heating batteries are used for other purposes.
- It is forbidden to connect PE to independent grounding buses, if such are provided in the electrical circuit.
The resistance of the PE insulating layer should not be less than that specified in the regulatory document.
Types of grounding
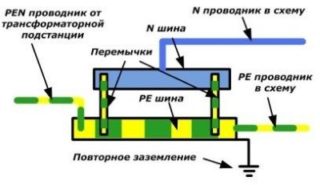
Depending on the functions of PE, grounding is divided into several types.
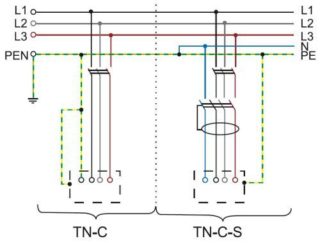
Old grounding systems are characterized by the integration of the neutral and protective working conductors throughout the network, therefore they are not equipped with separate PE. According to the regulation of the PUE, since 2017, it is prohibited to operate such systems. When building new structures, they resort to safer and improved grounding systems.
A characteristic feature of the new types is the implementation of separate circuits for protective and working grounding. It also provides access to private networks, it is carried out taking into account all the requirements for the independence of N and PE. If we are talking about the TN-C-S system, it is allowed to combine these conductors in private networks.
Electric current carries a potential threat to human health and life. If the relevant knowledge and experience is not available, it is recommended to consult a professional electrician. You can find a suitable candidate in the housing office, the city management company or any construction organization. If it is decided to do all the work independently, before exposing the wires, you need to turn off the power supply to the apartment house, and check the voltage at the output using a special screwdriver equipped with an indicator.