For electrical work related to the arrangement of power lines or the formation of branches of an air cable from the main line, it is supposed to use connecting adapters. Electrical walnut is one of the varieties of such connectors that provide high-quality transition contact and its reliable protection from external influences. To understand the principle of operation of the branch clamp called "nut", you will need to familiarize yourself with its design and application features.
Design and installation features

The electrical connecting nut got its name due to its external resemblance to the known fruit, which is directly related to the configuration of its body part.
In the official and working documentation, this type of intermediate connectors is called a branch clamp or, more simply, a clamp.
Outside, the wire connection nut is protected by a durable and lightweight polycarbonate casing in two halves. When assembled, these parts of the structure snap into place easily, forming a shape similar to a nut. Inside the structural element there is a core consisting of 2 steel dies and a spacer plate. To obtain reliable contact, they are compressed together with the plate by means of special tightening bolts.
Purpose and advantages of connectors
The nut clip for electrical wires is especially in demand in situations where it is necessary to prepare a branch from the main wire without the need to cut it. An illustrative example of the use of this connector is the use in storey driveways, from which electricity is supplied to apartments along branches from the main cable line. When registering the next branch to the dwelling, the main wire at each site is laid in an unbreakable way. Food is supplied to individual apartments due to the arrangement of the branch with the use of electrical "nuts".
In the event of a break in the trunk cable and the design of taps on the site using conventional terminal blocks, the reliability of power supply to individual consumers is sharply reduced.
With such an organization, the loss of contact on the second floor of a building, for example, will lead to the simultaneous disappearance of power in all apartments located in its upper floors.
Nuts for wires can be installed in power supply lines with an operating voltage of up to 660 Volts, within which it is possible to obtain a reliable connection of the outgoing wire to the main cable route. Thanks to the use of these electrical components, much less time is spent on the corresponding installation work. At the same time, no special skills and efforts are required from the installer.
Nuts for connecting wires do not guarantee absolute tightness, as dust or moisture can enter them under certain conditions. To avoid this nuisance, experts advise, after the formation of the connection, to wrap the nut compression body with insulating tape.
The indisputable advantages of this type of clamps include:
- With their help, it is possible to connect branches without breaking the cable.
- To work with these connecting elements, no special training and high qualifications are required.
- By means of nuts for connecting electrical wires, it is possible to combine dissimilar materials (copper and aluminum, in particular).
The latter advantage is especially important when installing conductive lines, since in this case oxidation of the contacts and the possibility of a complete interruption of the supply of electricity to the consumer are excluded.
Application example and assembly order
As an example of the application of products of the "nut" type, a three-phase cable is usually considered, from which a wiring with a cross section of 1.5 mm2 is taken off. The correct approach to arranging such a branch involves the following procedure:
- On a cable line with a cross-section of 6 mm2, at the point of the outlet, the insulation is removed for the length of the clamping plate of the connector.
- The preparation of the nut itself is carried out, for which a screwdriver is taken and with its help, first pry off, and then the retaining ring on the body is removed.
- The halves of the product are separated.
- It is necessary to unscrew the clamping bolts from the contact plates.
- The protective insulation is also removed from the outlet conductor with a smaller cross-section to a length corresponding to the size of the pressure plate.
At the final stage of work, the bare parts are first tucked into the grooves for the connector dies, and then tightened with screws with effort.
Between the plates, it is necessary to install a brass gasket, which makes it possible to obtain a large connection area and to exclude contact of dissimilar metals.
When tightening the screws, do not use too much force that could damage the threads of the grips. Upon completion of this operation, proceed to the assembly of the walnut body. In doing so, it is important to distinguish between the two halves in which there are four target holes. One of them is simply sealed, the other is intended for the output of the outgoing wire, and two more are for wiring the trunk cable. Parts of the assembled body are securely fixed with special retaining rings.
Combining tires from different materials

Connecting wires using electrical nuts is allowed to be done with more than one branching method. Due to the simplicity of the design and the reliability of the resulting connection, these elements are used in any areas of existing power grids, including junction boxes. When using them inside installation products, it is necessary to take into account the dimensions of the clamps themselves and select boxes of appropriate dimensions.
If it is necessary to connect aluminum and copper conductors, clamps for wires "nuts" electrical installation are simply irreplaceable. The need for them is due to the following reasons:
- With direct contact of aluminum and copper wires, the metals in the connection area oxidize over time.
- With prolonged use of the twist, it gradually collapses and can weaken so much that the circuit through which the load current flows is finally broken.
- As a result of this destruction, the power supply to the object connected to it is completely cut off.
When forming nut-type connections, first copper and aluminum wires are freed from insulation to the width of the plate. After that, the fasteners are first loosened, and the corresponding wires are inserted into the vacated grooves. At the final stage of assembly, they are tightened with previously loosened screws. Due to the fact that a brass plate is placed between the copper and aluminum wires in the nut, no direct contact is formed between them.
Branch from the high-voltage line pole

According to the provisions of the current regulatory documentation, work on connecting the cable stretched from the power line pole to entering the house is carried out by specialized organizations. This is due to the fact that the open part of the common electricity supply route is very important from the point of view of its correct arrangement.
Such work can only be performed by specialists who, during installation, use special methods of laying lines, including the design of branches from a typical SIP cable.
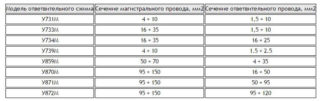
According to the requirements of the PUE, with the air supply method, the following types of conductive material can be used:
- Copper veins with a cross section of 4 mm square with a distance from the post to the house of about 10 meters;
- the same cable, but with copper conductors with a cross section of 6 mm square - at distances from 10 to 15 meters;
- aluminum wires with a cross section of at least 16 mm in diameter - in all cases when, in order to save money, their copper substitute is not used.
Arrangement of a branch from a pole located on the street near the house is just the case when a nut-type end-to-end connection is required. When using this connecting element, it will be possible to ensure reliable contact of the conductors of the aluminum cable of the high-voltage line with the copper outlet towards the residential building.
Nut clamps for 220V wires are very popular among specialists in the installation of high-voltage lines. They are used wherever there is enough space to place them, and guarantee a reliable connection of wires without direct contact.














