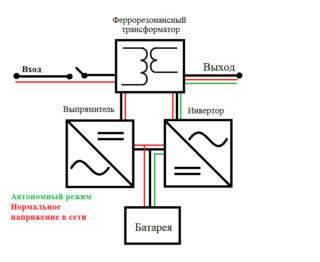
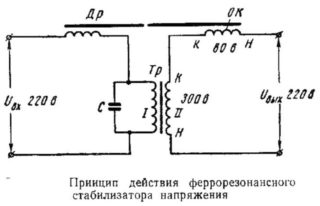
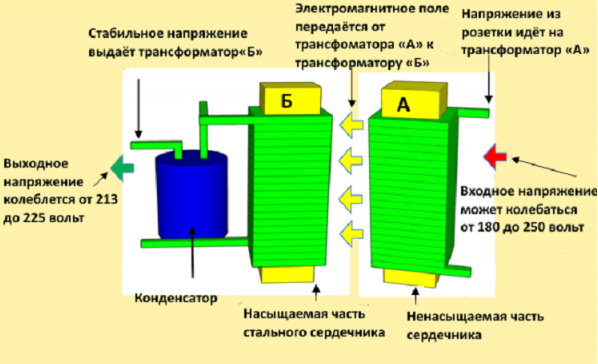
The ferroresonant voltage stabilizer has long been actively used not only in everyday life, but also in industry. Devices of this class allow you to equalize the AC voltage. The principle of operation is based on the effect of electromagnetic resonance in the oscillatory circuit. Such normalizers have many advantages, but they also have their disadvantages.
- Ferroresonance phenomena in electrical networks
- Ferroresonance in a voltage transformer
- Ferroresonant stabilizers
- The influence of the stabilizer on the technique
- Operating modes
- The principle of operation of ferroresonant stabilizers
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Selection Tips
- DIY ferroresonant voltage regulator
Ferroresonance phenomena in electrical networks
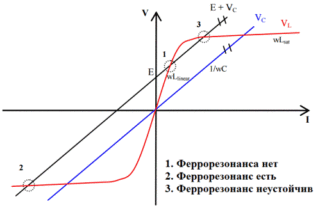
This phenomenon is of 2 types: resonance of currents and voltages.
Ferroresonance of voltages is possible when there is inductance in the network, characterized by a nonlinear volt-ampere property. This characteristic is inherent in inductors, where the cores are made from ferromagnetic components. This is especially true of rectifiers of the NKF line. This negative phenomenon is due to a small indicator of resistances of ohmic and inductive types in relation to power transformers.
Ferroresonance in a voltage transformer
At the end of a certain time period, the voltage on the inductive element becomes peak, the magnetic circuit is powered, and the voltage on the capacitive type component continues to rise. Ferroresonance in a voltage transformer occurs when the voltage of the inductor and the capacitive element becomes equal.
The rapid transition of the applied voltage from the active-inductive type to the active-capacitive type is referred to as "phase reversal". This effect is dangerous for electrical appliances.
Ferroresonant stabilizers

Ferroresonant rectifiers are not equipped with a built-in voltmeter, which makes it difficult to measure the output voltage of the mains. It will not work to adjust the voltage value with your own hands. Ferroresonant stabilizers partially distort real readings, the error value is up to 12%.
Those who use such devices for a long time should remember that they are capable of emitting a magnetic field that can disrupt the proper functioning of household electrical appliances. Stabilizers of this class are adjusted at the factory; they do not require any additional adjustments in everyday life.
The influence of the stabilizer on the technique
Ferroresonant voltage regulator, the principle of which is not simple, affects household appliances as follows:
- Radio receiver - the sensitivity of signal reception can be reduced, the output power indicator is significantly reduced.
- Music center - the output power of such a technique can be significantly reduced, erasing and writing new discs is significantly impaired.
- TV - when connected to the stabilizer, you can observe a significant decrease in the quality of the picture on the TV, some colors are not transmitted correctly.
The electrical circuit of modern ferroresonant type normalizers has been improved, which allows them to withstand heavy loads. Such devices can guarantee accurate line voltage regulation. The correction procedure is performed by a transformer.
Operating modes
The operating modes of the stabilizers depend on a number of factors. The power indicator and the class of the device have a direct influence. The power characteristics of the device can be different, they must be chosen taking into account the type of electrical equipment to be connected.
The modes of operation of the rectifier depend on the following types of load:
- inductive;
- active;
- capacitive.
An active load in a pure form is extremely rare. It is only needed in circuits where the variable value of the device is not limited. Capacitive loads can only be used for those rectifiers that have low power.
The principle of operation of ferroresonant stabilizers
The output voltage is generated at the terminals of the secondary winding. A load is connected to this winding, which is on the core, has a small cross-section and is in a saturated state. In case of anomalies in the mains voltage and magnetic flux, its value is not actually modified, and the EMF indicator remains unchanged. During the increase in the magnetic flux, some of it will be closed on the magnetic shunt.
The magnetic flux takes a sinusoidal shape and when it approaches the amplitude indicator, its separate section goes into saturation mode. In this case, the increase in magnetic flux stops. The closure of the flux along the magnetic shunt will be carried out only when the magnetic flux indicator is compared with the amplitude one.
The presence of a capacitor allows the ferroresonant stabilizer to operate with an increased power factor. The stabilization index depends on the level of the slope of the horizontal type curve with respect to the abscissa. The slope of this section is significant, so it is impossible to obtain a high level of stabilization without auxiliary equipment.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the key advantages of ferroresonant rectifiers are:
- overload resistance;
- wide range of operational values;
- speed of adjustment;
- the current takes the form of a sine;
- high leveling accuracy.
But with all these advantages, devices of this class have their own disadvantages:
- The quality of functioning depends on the load indicator.
- During operation, external electromagnetic interference is generated.
- Unstable operation at light loads.
- High indicators of weight and dimensions.
- Noise during operation.
Most modern models are devoid of such disadvantages, but they stand out for a considerable cost, sometimes higher than the price of a UPS. Also, the devices are not equipped with a voltmeter, which makes it impossible to adjust them.
Selection Tips
The design of the rectifiers is constantly being modernized, the quality of their circuits is improving, which makes it possible to transfer significant ferroresonant overvoltages. Modern models are distinguished by a high level of performance, tuning accuracy and a long service life.Modes are set by the power characteristics of the device and its type.
The main condition for choosing a ferroresonant stabilizer is the place of its connection. Usually it is installed at the entrance of the electrical network to the room or near household appliances. If a rectifier is installed for all equipment, it is necessary to select devices with a high power level and connect them immediately behind the switchboard.
DIY ferroresonant voltage regulator
The ferroresonant circuit is the simplest one for hand-made production. Its functioning is based on the effect of magnetic resonance.
The design of a fairly powerful ferroresonant type rectifier can be assembled from three elements:
- primary choke;
- secondary choke;
- capacitor.
Moreover, the simplicity of this option is accompanied by a whole set of inconveniences. A powerful normalizer made according to the ferroresonant scheme turns out to be massive, cumbersome and heavy.