To create artificial lighting, a conventional incandescent lamp is often used. This element is familiar to everyone since the days of the USSR. Glass bulb, cartridge and spiral are the main visible parts of the product. How an incandescent lamp works from the inside is interesting for both a novice master and a professional.
The history of the invention of the light bulb

The product was designed and refined by many scientists in different periods. The first electric arc was ignited by the scientist V.V. Petrov. in 1802. The invention consisted of two carbon rods that were connected to the poles of a galvanic battery. At the moment of their approach, an electric discharge arose, and a luminous arc was formed above the elements. The use of such a lamp in everyday life was impossible for a number of reasons - the inconvenience of the design, the rapid burnout of the coal rods. But world scientists began to understand what to make a lamp from.
70 years later, in 1872, Lodygin A.N. received a patent for an incandescent lamp. As a spiral, a retort coal rod was used in it, which was placed under a glass cover.
Already in 1880, on May 10, Lodygin's lamp was equipped with street lighting in St. Petersburg on Liteiny Bridge. The life of the light source was only 2 months (until the carbon rod burned out).
In 1880, Thomas Edison introduced an improved Lodygin incandescent lamp in the USA. He managed to achieve the elimination of air from the glass bulb, which ensured a longer burning of the spiral and its brighter glow. Edison also developed a threaded base for screwing the lamp into the socket.
In 1910, it was decided to twist the tungsten filament into a spiral to increase its service life. Thus, the product now works instead of the initial 50-100 hours for a full 1000 hours.
The principle of thermal radiation is also used in the production of fluorescent halogen lamps.
What the lamp consists of
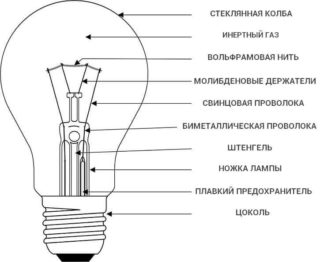
The structure and circuit of an incandescent lamp looks like this:
- glass bulb pear-shaped or round;
- filament body (tungsten or carbon filament) located in it on two hook holders;
- two electrodes;
- fuse;
- leg;
- base (housing) with an insulator;
- its contact (bottom).
Oxidation of the tungsten filament (spiral, filament) is excluded by placing it in a vacuum or gaseous medium. They fill a glass flask.
Electrical parameters
All bulbs are manufactured for different voltages. Since the refractory metal tungsten has a low resistivity, a long wire is needed to construct the light element. Thus, the filament in a light bulb often reaches 50 micrometers. When the light is turned on, a current passes through the filament body, which exceeds the working one by 10-14 times. The more the thread heats up, the more the thread resistance increases and the current decreases.
The principle of operation of an electric incandescent lamp
Having considered what the light bulb consists of, it is important to understand the principle of its operation:
- When the light is turned on, a current flows through the bottom of the base to the filament body.
- The tungsten filament is very hot after closing the electrical circuit, which leads to its glow.
- At this point, the temperature of the thread reaches 570 degrees.
- Thus, the glow spectrum of the bulbs is shifted towards warm temperatures.
For reference: the lower the degree of the tungsten / carbon filament, the lower will be the fraction of energy that goes to the incandescent body and provokes its visible radiation. Retro lamps differ in that they warm up the spiral more slowly and weaker.
Varieties of light elements
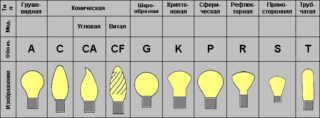
All products are classified according to different parameters. By the type of flask filling, the following lamps are distinguished:
- the simplest vacuum ones (when they are made, all the air is sucked out of the flask);
- filled with argon gas;
- xenon halogen;
- filled with krypton.
By the type of purpose, light bulbs are divided into the following types:
- Decorative. They work according to the usual principle. The flask is made in the form of a candle or a ball.
- General purpose. These are common elements familiar to everyone that are screwed into a chandelier or sconce. Often the master is concerned with the question of how many watts a light bulb consumes. You can buy a product for 40, 60, 90, 100, 120, 150, 200 and more watts. The higher the indicator, the brighter the glow will be.
- Lamps for local lighting. Structurally, they are no different from ordinary elements. But the operating voltage for them is in the range of 12-42 V.
- Light bulbs for illumination. They have a flask painted in bright colors. Working power in the range of 10-25 W.
- Signal. They have extremely low power and are used for light signaling devices. Today, such products are confidently replaced by modern LED lamps.
- Searchlight. The glowing body is laid here in a special way due to its convenient suspension in the flask. As a result, it is possible to achieve better focusing of the glow. The power of such lamps reaches 10-50 kilowatts.
- Mirrored. They have a special coating on the flask. It is partially covered with a film of thermally sprayed aluminum. Thus, it is possible to achieve a narrow directivity of the light beam. Mirrors are used for local lighting devices.
- Transport. These products are characterized by increased strength and vibration resistance. For transport lamps, special caps are used, thanks to which you can quickly replace the lighting element in the cramped conditions of the car. Such elements work from a 6-220 V auto power supply.
- Products for optical devices. Today they are almost never produced. Previously used for film projectors, medical equipment. Lamps of this type have a special shape of the bulb.
- Switching light. They belong to the signal class. They have a small flask size, which allows them to be placed under the buttons of panels of various settings.
By the number of filaments, all elements are:
- Double-stranded. They have one incandescent body for far (strong) light and one for near (weak) light. They are used in auto, aviation, railway traffic lights, in the stars of the Moscow Kremlin.
- Single-stranded. Habitual light bulbs with a tungsten filament.
The heating body of low-inertia products has an extremely thin spiral. They were previously used for optical sound recording systems. There are also heating lamps that are used for drying chambers, electric stoves, office equipment, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
- acceptable cost;
- compact dimensions;
- instant response to on / off;
- lack of flicker, adversely affecting the eyes;
- inertia to voltage surges;
- soft gamma of glow, contributing to relaxation, creating an atmosphere of comfort;
- good color rendering index equal to Ra 90;
- work in any conditions (including high humidity);
- constant availability for the consumer;
- environmental friendliness;
- lack of noise during operation;
- inertness to ionizing radiation.
The disadvantages of incandescent lamps include the following points:
- fragility, sensitivity to mechanical damage;
- relatively short service life;
- low efficiency, not exceeding 5-7% (ratio of consumed power to visible radiation);
- fire hazard due to direct contact of the lamp with combustible substances (textiles, straw, etc.);
- the probability of an explosion due to thermal shock or rupture of the spiral under tension.
Despite all of these shortcomings, the usual light bulbs confidently retain their positions. More than 70% of the CIS population still use them.
Efficiency and durability
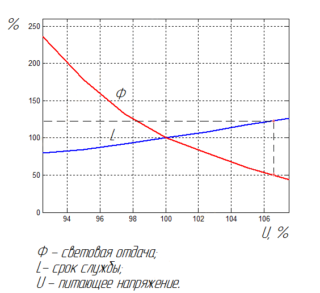
When analyzing how an incandescent lamp works, it is important to understand its efficiency. At a light temperature of 3400 Kelvin, the cell efficiency is 15%. This refers to the ratio of the power consumption to the light radiation visible to the human eye. At a temperature of 2700 K (average normal for an ordinary household lamp), the efficiency is only 5%.
The higher the filament temperature, the greater the efficiency will be. However, the service life of the product is reduced. For example, if the voltage is increased by 20%, the brightness of the lighting will become stronger - the efficiency of the light bulb will increase, but the service life will be reduced by 90-95%. Accordingly, a decrease in voltage leads to a decrease in the efficiency of the product and an increase in its service life.
How to extend the life of an incandescent lamp
On average, an ordinary household incandescent light bulb lasts 700-1000 hours. But in fact, the element burns out much faster. To extend the life of the light bulb, it is necessary to prevent factors provoking the burnout of the spiral.
- Observe voltage range. It is indicated on the flask of the product. As a rule, it is equal to 125-135 W, 220-230 W, 2.3-2.4 kW. If the voltage in the house is exceeded, the product will burn out sooner. For example, in an apartment the maximum voltage is 220 V, and the lamp was purchased with a range of 125-135 V. Here the filament will burn out definitely faster, since the efficiency of the product increases.
- Eliminate the cartridge malfunction. If the lamps burn out often, it is worth inspecting it, rechecking the contacts. Change the cartridge if necessary.
- Eliminate vibrations. They lead to rapid burnout of the tungsten filament. Therefore, it is better to carry out the transfer of mobile lamps with the lamp turned off.
To extend the life of the incandescent lamp, you can reduce the voltage in the network by only 7-8%. In this case, the product will work 3-3.5 times longer with economical energy consumption.












