LED garlands have replaced the usual ones. They compare favorably with obsolete incandescent lamps by their characteristics - long service life, reliability, efficiency and safety. LED rgb garlands are used in festive illumination, illumination of buildings and trees, in advertising. Garlands differ in their design, characteristics and connection diagram. You can repair the LED garland with your own hands - for this you need to familiarize yourself with the design features of the product.
Types of LED strings

LED electric garland is characterized by such parameters as power, number of LEDs, structure diagram, length.
By design, the product is:
- Traditional. They are a thread on which diodes are fixed. They are 5-12 meters long.
- Light curtains - "rain" or "waterfall". Several luminous threads are fixed at a certain interval on one.
- Fringe. The LED garland-curtain on the window is a type of rain, it differs in shorter length and different levels of threads.
- Light grids. The threads are connected in a network.
- Garlands for trees called clip-light.
- In the form of balls and icicles.
Each of these types is used in different areas.
Garlands can be classified according to the type of food. There are devices that are powered from the mains - they just need to be plugged into an outlet. Products of the second type require connection through a step-down transformer, since they operate on a voltage of 12 V or 24 V. They are safer - even if the insulation is damaged, a person is not in danger.
Garland design and scheme
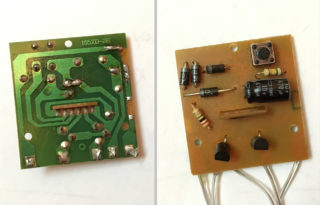
Externally, the LED garland is no different from the usual one. It also has wires, lamps and a control unit, which is the most important element.
The block is a small plastic box with buttons that you can use to change the operating mode. It is usually manufactured in a high-quality case with an IP44 protection level. The level of protection depends on the room in which the garland will be installed. On the street, frost-resistant products will be required. There are soldered wires inside the unit. Also inside there is a board on which the controller, thyristors, resistors, capacitor and diode bridges are soldered. Expensive models may be equipped with a fuse.
LED garland circuit
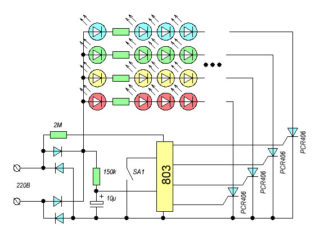
The mains voltage is supplied to the power supply. It passes through the diode bridge and resistors, then it is smoothed by a capacitor, after which the voltage is supplied to the supply controller. When the button is closed, the modes are switched. The controller controls thyristors, the number of which depends on the number of backlight channels. After passing through the thyristors, the voltage is applied to the LEDs.
The variety of illumination colors depends on the number of outputs. If there are only 2 lines, the garlands will work in two modes - dim and light up in turn. More expensive products may have more channels.
The main causes of malfunctions
The microcircuit, which is the main working element, rarely burns out. The most frequent breakdowns include:
- Poor contact on the wires.
- Breakage of one of the LEDs.
- Condenser problem.
- Resistor burned out.
- Problems with diode bridge or thyristors.
The Chinese light bulb festoon circuit can use cheap, substandard components that will have to be replaced.
Poor soldering

If the garland stops working, first of all, the quality of the connections of the supply and outgoing wires is checked. If the contact is weak, the device will not receive voltage. This problem is common in cheap Chinese string lights. They are manufactured using thin strands that break easily at the joints.
To ensure a reliable connection, the contact points must be filled with a thick layer of hot melt glue.
LED burned out

In the garland, the LEDs are connected in series. If one element is burned out, the whole chain will stop working. You need to repair the circuit by replacing the non-working component. You will need a multimeter to identify a broken light bulb. Thin needles should be tied to the ends of the probes with a thread to test the diodes. The tip should protrude 5-8 mm. From above everything needs to be wrapped with a dense layer of electrical tape.
First of all, the garland must be disconnected from the electrical network. The check begins with the last diode, since it is to it that the power wire is directly drawn from the control unit.
The LEDs are soldered, so you won't be able to simply pull them out like a regular light bulb. To check, you will have to pierce the insulation until copper strands appear. The multimeter must be set to dial mode. After that, you need to consistently pierce the supply wires next to each suspicious LED along the entire length of the circuit.
If a 12 or 24 V garland is used, the diode should light up from touching the probes. When powered by 220 V, you need to check the readings obtained with a multimeter. They will be almost the same for the working elements; an open circuit will be recorded on the faulty diode. This method violates the integrity of the insulation. If a street garland has been tested, it can only be used indoors.
Chaotic flashing lights

When the garland is turned on, a situation may occur when the diodes randomly light up with different brightness. Such flickering is not associated with operating modes and factory effect, but is caused precisely by problems in the garland itself.
The likely reason for this effect is the breakdown of the electrolytic capacitor. It can swell up, and this will be clearly visible to the naked eye. The broken component must be replaced with one of the same value. The capacitance value is indicated on the cell body.
If replacing the capacitor did not help, the resistor could burn out. You will need a tester to check it. By marking, you need to find out the nominal resistance, and then check with the measured value. If the parameters do not match, the resistor must be replaced with a new one. After replacing the bulbs should stop flashing.
Part of the garland is off
The failure of one of the channels can be caused by two reasons. These problems are associated with circuit components - breakdown of a thyristor or diode. To check, you need to separate one posting from a non-working channel and connect it to an adjacent one that is known to be working properly. If it also does not work, the fault is with the thyristor or diode. They need to be checked with a multimeter and replaced with new ones.
Low light
The LEDs on a single channel may be dim compared to the others. This is not related to the operation of the controller circuit, the continuity of the components will also not give results. The most likely cause is wires. They should be inspected for breaks and kinks. After finding the problem area, you need to take a soldering iron, disassemble the wires and install new sections. The contact point must be securely insulated with a heat shrink tube.
Making a garland with your own hands
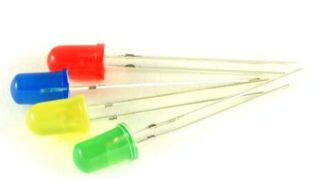
A DIY LED garland can be no worse than a store one. It's easy to create. For this you will need:
- soldering iron;
- insulating tape;
- heat-shrink tubing;
- LEDs;
- resistors;
- Power Supply.

The work algorithm is as follows:
- Determination of the distance between the diodes.
- Marking with a marker on the wire in those places where the lamp will be installed.
- Removal of insulation in marked places.
- Application to areas of solder.
- Fixing LEDs on solder.
- Insulation of connections. You also need to seal it with silicone sealant.
- Connecting the current limiting resistor and power supply.
To check the system, you can connect rechargeable batteries or a power supply from charging a smartphone.








