The concept of "load" in electrical networks is inextricably linked with the need to protect them from overcurrent and short circuit. To solve the problems associated with the operation of power lines, switching circuits provide for special protective devices. One of these devices is a circuit breaker, the rating of which is selected depending on the operating mode of the load and the parameters of the supply line itself. To choose an automatic machine according to the cable section, you will need to familiarize yourself with the functions that it performs on the network.
Circuit breaker functions

According to the PUE, the main function of automatic disconnecting devices is to protect the power supply from short-circuit and overloads. This device disconnects the consumer from the line when the current exceeds the specified nominal value (setpoint). At the same time, it should not work with the current load permissible for it (when the iron and the hob are turned on at the same time, for example).
The function of the line fuse also manifests itself in protecting the power cable from thermal destruction due to the ignition of its sheath and the subsequent fire. Such situations are quite possible, since under short-circuit conditions, the currents in the line reach thousands of amperes. None of the well-known brands of cable products will be able to withstand even a few minutes under the specified loads. Not to mention ordinary products with a cross section of 2.5 sq. mm, traditionally used for arranging electrical wiring in private houses and city apartments.
Competent calculation of the protective circuit breaker is of great importance to ensure the safety of the operation of the local electrical network. The correct approach to the selection of the ratings of the machines for the cable cross-section plays a paramount role in this matter.
Factors influencing the choice of the required denomination
The calculation of the operating parameters of the wire and the machine is permissible only if all the nuances related to the features of the operation of the electrical network are taken into account. This approach will help to avoid possible mistakes when choosing a protective device.
Determination of the total power consumption
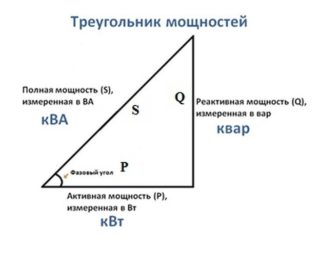
Known category of loads, which include capacitive and inductive elements. They are called reactive and do not take part in the formation of the total power consumption - during operation they simply pump energy from the network and vice versa. However, from the point of view of choosing an automatic machine over a cable cross-section, this component of the current must be taken into account.
Sometimes the full or nominal power, taking into account the active and reactive components, is also indicated in the passport.The current flowing in the load circuit is calculated in this case, based on its value (it is divided by the effective voltage of 220 or 380 volts).
Increased starting currents
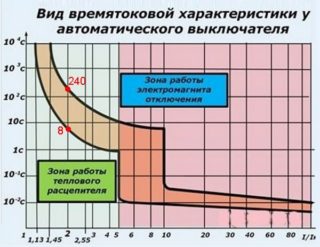
However, its electromagnetic part, which is responsible for short-circuit overcurrents, in real conditions often triggers and turns off the device. Very often this happens in dedicated three-phase power lines with machine equipment connected to them (in private houses). In this case, it is necessary to determine the size of the starting pulse and provide for the use of a class "D" machine.
Demand factor accounting

For circuits with loads of equal energy intensity connected to them, the concept of "demand factor" is introduced, denoted as "ks". The meaning of its application is that all devices are never connected to the network at the same time and a simple summation of their powers will give an overestimated indicator. The coefficient used for this purpose takes on a value equal to one or slightly less.
Taking it into account, the design power (Pr) for all serviced devices is found by the formula:
Pr = ks x Swhere S - its total value before the introduction of the amendment.
It makes sense to use this coefficient in office and retail premises with a large volume of office equipment and other equipment.
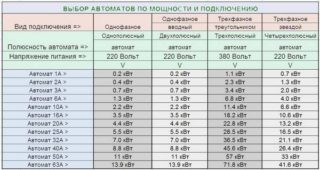
For modern one-room apartments with a limited number of consumers, it is usually not taken into account. When the total power of all consumers is determined, you can proceed to the procedure for selecting the machine for the maximum current load. Its working or nominal value is determined by Ohm's law:
I = S / 220 Volts - for one phase.
I = S / (1.73x380) - for a three-phase network.
The factor 1.73 takes into account the inductive nature of the load.
Calculation of the parameters of the machine
For any mains supply connected to a local distribution cabinet, the following inequality must be fulfilled:
In <= Ip / 1.45
Here In corresponds to the rated current of the machine, and Ip is its maximum allowable value for the wiring itself. Compliance with the requirements of this inequality is the main condition for the correct choice of the “machine - cable” pair, which excludes overheating and emergency ignition of the electrical wiring.
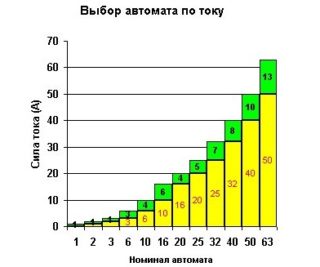
You can calculate the rated current either by the known total load, or by the cross-section of the conductors of the existing wiring.
If the sketch of the wiring in the apartment has already been drawn, and it has not yet come to laying, the procedure looks like this:
- The total current of all devices connected to the mains is calculated (according to the diagram).
- An automatic machine with a nominal value of a suitable value is selected.
- According to the table of correspondence of cross-sections and currents, the cable of the required brand and type is selected.
When the electrical wiring has already been laid, the necessary operations will be greatly simplified. According to the known cross-section of the cable laid in a certain way, the limiting current is determined according to the correspondence tables. After that, according to the formula given earlier, the value of the nominal value of the machine is calculated.
Choosing between multiple options
When using several stages of protection, the circuit breakers should be chosen so that the value of the rating of the upper level exceeds the same indicator for devices of a lower status.On the other hand, the choice of a lower value is advantageous in that in this case the thermal release will trip faster when the current exceeds the permissible value.
You can carry out the calculations of the machine for the cable cross-section online. For this, there are many sources presented on the Internet.