Grounding is a set of measures aimed at connecting live parts of electrical devices to the ground electrode. This hassle-free process allows you to provide ground potential on the housings of household appliances to prevent electric shock from touching the housings of appliances and other parts of damaged equipment. The connection to the ground bus is made with a cable or wire.
What is a grounding wire for, the principle of operation

The main purpose of grounding is to prevent electric shock to humans or animals. A serviceable electrical device has an integral housing with reliably insulated live parts. If household appliances fail, live parts can touch the case and this will lead to the fact that it will also be energized. Having touched such a device, a person will inevitably be electrocuted.
In this case, the operation of the circuit breaker is impractical, since the current flowing through the human body will not be enough to turn off the power supply. But this force, unfortunately, is enough to deprive a person of health or even life.
To eliminate the likelihood of such events developing, you need to ground all electrical devices through conductors. Grounding household appliances at home is possible only if the house is equipped with a ground loop. Unfortunately, the houses of old buildings are not equipped with such innovations. This is due to the fact that decades ago people in their homes practically did not have household appliances, therefore, the load on the network was minimal.
Now another core is added to the two-phase wiring - a ground wire. As a result, the wiring is already three-phase - two wires are zero and a phase, and the third is protective ground. Thus, by connecting the plug of household appliances to the socket, the metal body of the appliance is automatically connected to the protective earth.
Criteria for selecting a grounding cable
Before choosing a grounding conductor, there are several important points to understand.
Owners of private houses and country buildings in 1998 and earlier are forced to independently conduct grounding. Modern structures are equipped with a ready-made system even during the construction process.
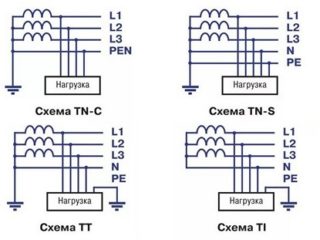
To choose the right ground wire and its cross-section, you need to find out which system is installed in the house. According to the Rules for the Arrangement of Electrical Installations, 4 types of them can be used:
- TN-S - in the AC system, ground is additionally made using a neutral and a separate wire.
- TN-C is characterized by the combination of the neutral and ground wires, the neutral is displayed separately. The most widespread method of protection, which was used in Europe several decades ago.
- TT - equipping electrical equipment with direct protective earthing.
- IT - work directly with the enclosures of household appliances through the complete insulation of all conductive cables and the enclosure itself.
The earthing diagram used must always be marked. In Russia, you can find two of them:
- PE - grounding;
- PEN - zero and ground are combined in one cable.
The next important selection criterion is the type of grounding used. Depending on the purpose, they are divided into two types - portable and stationary. In domestic conditions, a stationary type is sufficient, which allows the operation of both single-core and three-core cables.
Many uninformed people in these surveys have difficulties in what color the ground wire is. According to the requirements of the PUE, the wire must be made in a yellow-green insulation color.
After determining the type of cable and material of the system, you can proceed to the next main step - the selection of a suitable section.
How to choose the right cross-section of the grounding conductor
To connect the protection system, not only natural grounding conductors can be used, but also artificial ones. Selection rules in each case differ from each other and have their own technical features.
Artificial networks are equipped with a capacity of more than 1 kW, in other cases, the operation of natural ones is permissible.
The artificial segment is made of galvanized alloys, steel and copper. The cross-section is selected according to the Rules for the Installation of Electrical Equipment in special tables.
| Material | Section profile | Diameter (mm) / cross-sectional area (mm.kv) |
| Copper |
|
|
| Cink Steel |
|
|
| Black steel |
|
|
One simple but important rule is that the conductor must have a cross-section that is equal to the cross-section of the phase conductor, provided that the conductor is at least 16 mm square. In other cases, the cross section is calculated using the table given in the PUE.
| Section of phase conductors, mm.kv. | The smallest section of protected conductors, mm.kv. |
| S> 35 | S / 2 |
| 35> S> 16 | 16 |
| S <16 | S |
In an ordinary apartment, which is equipped with all the necessary equipment, it is enough to install a protection system with a single-core wire with yellow-green insulation.
Wire marking
Ground wires have another characteristic feature - marking.
Ground color
In the switchboard, it is connected to the bus, the housing and the switchboard door made of metal. In the box, the connection tends to the ground wires. The grounding conductor must not be connected to a residual current device.
Symbols on electrical diagrams: for direct current, standard ground, to the body of electrical equipment, clean and protective.
Neutral color

The zero conductor is strictly blue in color. In the switchboard, it must be connected to the neutral bus, which is designated by the letter N. All remaining blue conductors are connected to it. Through an electric meter or directly without installing the machine, the bus is connected to the input. In the junction box, all wires, with the exception of blue, should not be used for switching. Neutral conductors in sockets are connected to the contact designated N - located on the back side of it.
Phase color
In the junction box, the phase that leaves the consumer is connected to the contact of the automatic switch located at the very bottom, or the residual current equipment.The switches carry out phase switching.
Self-labeling of wires
Periodically, there are conductors with unusual colors. Such solutions do not meet the standards set out in the PUE. To facilitate this task, it is recommended to independently mark the wires with the necessary colors. Colored electrical tape is used for this, as well as heat shrink tubing.
Another task of the wizard is to write down the color values separately on a piece of paper.
Main brands of grounding cable
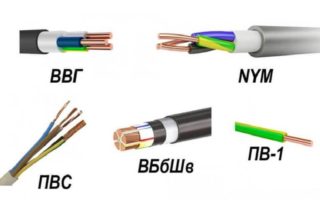
When choosing a brand of cable, it is necessary to study its type: mobile or stationary use. Stationary is designed to protect equipment, switchboards and structures. The best option is multicore stranded cables (VVG, PVG) and single-wire modifications (NYM). If the earth cable is colorless, the earth is pointing towards the conductor.
- NYM cable - sheath is painted in accordance with all rules and regulations, inside is equipped with copper conductors. It also has an intermediate additional sheath, which increases the operational life of the cable, even with prolonged use. Easy to install.
- VVg - equipped with conductors made of copper of the first and second class of twisting. Has an unusual coloration worth paying attention to. The ground is yellow-green and zero is blue. The outer sheath and insulation is made of polyvinyl chloride, thanks to which the cable will not burn even in the event of a fire.
- PV-6 - copper wire, sheath is made of transparent PVC. There is an opportunity to contemplate the work of a conductive core. Working temperature range -40 - +50 degrees Celsius, very flexible material.
- ESUY has one standard application - system short circuit protection. Capable of withstanding enormous loads, often used in junction boxes and on railways.
- PV-3 can be produced in 11 colors, consists of a large number of copper threads, which are placed in a polyvinyl chloride sheath. The peculiarity of the outer shell is fragility when stored or used improperly.
The issue of choosing a grounding cable is extremely important, since an incorrectly selected core will be unable to fulfill all the technical tasks assigned to it. If you have difficulties in making your own choice, it is better to consult with a specialist.










