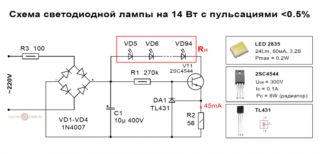
The brightness of LED sources depends on the current flowing, which in turn depends on the supply voltage. In conditions of load fluctuations, luminaires ripple. To prevent it, a special driver is used - a current stabilizer. In case of breakdowns, the element can be made independently.
- Design and principle of operation
- Varieties of current stabilizers
- Resistor stabilizers
- Transistor devices
- Current stabilizers on a field worker
- Linear devices
- Ferroresonant device
- Features of the current mirror circuit
- Compensation voltage stabilizer
- Devices on microcircuits
- Pulse stabilizers
- How to make a current stabilizer for LEDs yourself
- Driver based
- Stabilizer for car lights
- Nuances of calculating the current stabilizer
Design and principle of operation

The stabilizer ensures the constancy of the operating current of the LED diodes when it deviates from the norm. It prevents overheating and burnout of LEDs, maintains a constant flow during voltage drops or battery discharge.
The simplest device consists of a transformer, a rectifier bridge connected to resistors and capacitors. The action of the stabilizer is based on the following principles:
- supplying current to the transformer and changing its limiting frequency to the frequency of the mains - 50 Hz;
- voltage regulation for increase and decrease with subsequent equalization of the frequency to 30 Hz.
High-voltage rectifiers are also involved in the conversion process. They determine the polarity. The stabilization of the electric current is carried out using capacitors. Resistors are used to reduce interference.
Varieties of current stabilizers
The LED lights up when the current threshold is reached. For low-power devices, this figure is 20 mA, for super-bright devices - from 350 mA. The spread of the threshold voltage explains the presence of different types of stabilizers.
Resistor stabilizers
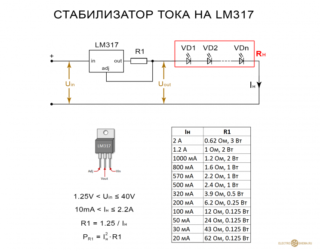
For an adjustable stabilizer of current parameters for low-power LEDs, the KREN circuit is used. It provides for the presence of elements KR142EN12 or LM317. The equalization process is carried out at a current strength of 1.5 A and an input voltage of 40 V. Under normal thermal conditions, the resistors dissipate power up to 10 tons. Their own power consumption is about 8 mA.
The LM317 node maintains a constant voltage value across the main resistor, regulated by a trimmer. The main, or current-distributing element can stabilize the current passed through it. For this reason, stabilizers on KREN are used to charge batteries.
The value of 8 mA does not change even with fluctuations in current and voltage at the input.
Transistor devices
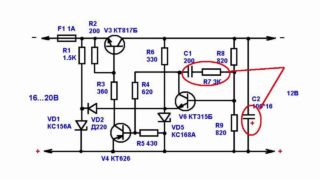
The transistor regulator provides for the use of one or two elements. Despite the simplicity of the circuit, with voltage fluctuations, there is not always a stable load current. With its increase on one transistor, the voltage of the resistor rises to 0.5-0.6 V. after that, the second transistor begins to work. At the moment of its opening, the first element closes, and the strength and magnitude of the current passing through it decreases.
The second transistor must be bipolar.
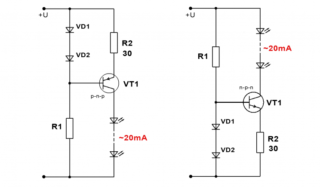
For implementation withchemistry with replacing zener diodes apply:
- diodes VD1 and VD2;
- resistor R1;
- resistor R2.
The supply of current through the LED element is set by the resistor R2. Resistor R1 is used to reach the linear section of the I - V characteristic diodes with reference to the current of the base transistor. In order for the transistor to remain stable, the supply voltage should not be less than the total voltage of the diodes + 2-2.5 V.
To obtain a current of 30 mA through 3 series-connected diodes with a voltage of 3.1 V, 12 V is supplied in a straight line. The resistor resistance should be equal to 20 Ohm with a dissipation power of 18 mW.
The circuit normalizes the operating mode of the elements, reduces current ripple.
The disadvantage of the circuit is the voltage drop with increasing current strength. It can be eliminated by replacing the bipolar transistor with a low impedance MOSFET. The powerful diode is replaced by a 12 A IRF7210 or a 3.7 A IRLML6402.
Current stabilizers on a field worker
The field element features a shorted source and gate, and an embedded channel. When using a field controller (IRLZ 24) with 3 pins, a voltage of 50 V is applied to the input, the output is 15.7 V.
The ground potential is used to supply voltage. Output current parameters depend on the initial drain current, and are not tied to the source.
Linear devices
The stabilizer, or constant current divider, accepts an unstable voltage. At the output, the linear device aligns it. It operates on the principle of constantly changing the resistance parameters to equalize the supply at the output.
The advantages of operation include the minimum number of parts, no interference. The disadvantage is the low efficiency with the difference in power supply at the input and output.
Ferroresonant device
Stabilizer for alternating current of an outdated model, the circuit of which is represented by a capacitor and two coils - with an unsaturated and a saturated core. A constant voltage is applied to the saturated (inductive) core, independent of the current parameters. This facilitates the selection of data for the second coil and the capacitive range of the power supply stabilization.
The device works on the principle of a swing, which is difficult to stop at once or swing harder. The voltage is supplied by inertia, so there may be a drop in the load or an open circuit in the power supply.
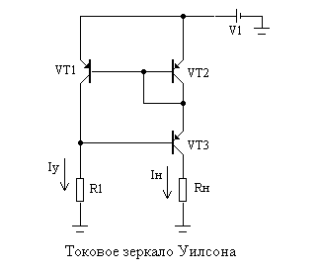
Features of the current mirror circuit
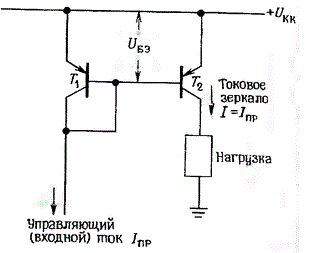
The current mirror, or reflector, is built on a pair of matched type transistors, i.e. with the same parameters. For their production, one LED semiconductor crystal is used.
Scheme of a current mirror according to the Ebers-Moll equation.The principle of operation is that the transistor bases are combined, and the emitters are thrown onto one power bus. As a result, the parameters of the transient voltage of the base-transistor-emitter coupling are equal.
The advantages of the circuit are equal stability range and no voltage drop across the emitter resistor. The parameters are easier to set using the current. The disadvantage is the Earley effect - the binding of the output voltage to the collector voltage and its fluctuations.
- Transistors # 1 and # 1 are switched on according to the principle of a standard current mirror.
- Transistor # 3 fixes the collector potential of element # 1 to twice the diode voltage drop parameter.
- It will be less than the supply voltage, which suppresses the Earley effect.
- The collector of transistor # 1 is used to set the circuit mode.
- The output current depends on transistor # 2.
- Transistor # 3 converts the output current into an AC load.
Transistor No. 3 may not be matched with the others.
Compensation voltage stabilizer
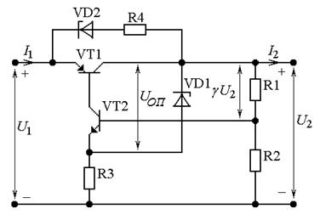
The rectifier works on the principle of voltage feedback. Full or partial stress equates to a support. As a result, the regulator generates error voltage parameters, eliminating brightness fluctuations for LEDs. The device consists of the following elements:
- A regulating element or transistor, which together with the load resistance forms a voltage divider. The emitter index of the transistor must exceed the load current by 1.2 times.
- Amplifier - controls the OM, is performed on the basis of transistor # 2. A low-power element is consistent with a powerful one according to a composite principle.
- Support voltage source - a parametric type stabilizer is used in the circuit. It equalizes the voltage of the zener diode and the resistor.
- Additional sources.
- Capacitors - for smoothing ripple, eliminating parasitic excitation.
Compensation voltage stabilizers work on the principle of increasing the input voltage with a further increase in currents. Turning off the first transistor increases the resistance and voltage of the collector-emitter zone. After the load is applied, it is leveled to the nominal value.
Devices on microcircuits

For stabilizing devices, a 142EN5 or LM317 microcircuit is used. It allows you to equalize the voltage by receiving a feedback signal from a sensor connected to the load current network.
It uses a resistance as a sensor, at which the regulator can maintain a constant voltage and load current. The sensor resistance will be less than the load resistance. The circuit is used for chargers, and the LED lamp is designed according to it.
Pulse stabilizers
The impulse device is characterized by high efficiency and creates a high voltage of consumers at minimum parameters of the input voltage. For assembly, a MAX 771 microcircuit is used.
One or two converters will regulate the current strength. A rectifier-type divider equalizes the magnetic field, lowering the permissible voltage frequency. To supply current to the winding, the LED element transmits a signal to the transistors. Output stabilization is carried out by means of a secondary winding.
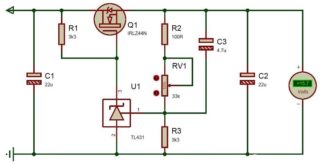
How to make a current stabilizer for LEDs yourself
Making a stabilizer for LEDs with your own hands is carried out in several ways. It is advisable for a beginner to work with simple schemes.
Driver based
The assembly is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- Solder the wires to the middle and end terminal of the resistor.
- Place the multimeter in resistance mode.
- Measure the parameters of the resistor - they should be equal to 500 ohms.
- Check the connections for continuity and reassemble the chain.
The output will be a module with a power of 1.5 A. To increase the current to 10 A, you can add a field operator.
Stabilizer for car lights
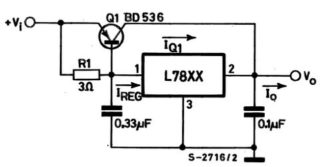
To work, you need a linear device in the form of an L7812 microcircuit, two terminals, a 100n capacitor (1-2 pcs.), Textolite material and a heat-shrinkable tube. Manufacturing is done step by step:
- Choosing a circuit for L7805 from the datasheet.
- Cut a piece of the required size from the PCB.
- Mark the tracks, making notches with a screwdriver.
- Solder the elements so that the input is on the left and the output is on the right.
- Make a body from a thermotube.
The stabilizing device can withstand up to 1.5 A of load and is mounted on a radiator.
The body of the car is used as a radiator due to the connection of the central outlet of the body with a minus.
Nuances of calculating the current stabilizer
The stabilizer is calculated on the basis of the stabilization voltage U and the current (average) I. For example, the voltage of the input divider is 25 V, at the output you need to get 9 V. The calculations include:
- Selection according to the reference book of the Zener diode.They are guided by the stabilization voltage: D814V.
- Search for the average current I according to the table. It is equal to 5 mA.
- Calculation of the supply voltage as the difference between the stable voltage of the input and output: UR1 = Uinx - Uout, or 25-9 = 16 V.
- Dividing the obtained value according to Ohm's law by the stabilization current according to the formula R1 = UR1 / Ist, or 16 / 0.005 = 3200 Ohm, or 3.2 kOhm. The element rating will be 3.3 kΩ.
- Calculation of the maximum power according to the formula PR1 = UR1 * Ist, or 16x0.005 = 0.08.
The zener diode current and the output pass through the resistor, so its power must be 2 times greater (0.16 kW). Based on the table, this rating corresponds to 0.25 kW.
Self-assembly of the stabilizer for LED devices is possible only with knowledge of the circuit. Beginners are advised to use simple algorithms. You can calculate an element by power based on formulas from a school physics course.