When arranging a home electrical network, RCDs and circuit breakers cannot adequately protect the system and residents. The best option for preventing an emergency is grounding in a private house. This line is organized according to several schemes, clearly regulated by regulations.
- What gives grounding
- Do I need grounding in the country and in a wooden house
- Private house grounding systems
- Application of TN-C-S
- Features of the TT system
- Grounding device
- What to make grounding
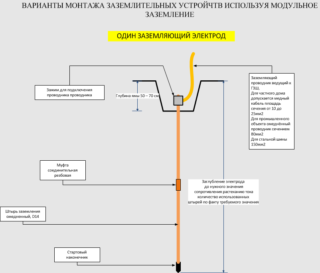
- Modular pin grounding
- Black metal contour
- Driving depth of pins
- What not to do
- How to do it right
- Procedure
- Entering the ground loop into the house
- Why it is impossible to make separate grounding
- Which system to choose
- TN-C-S grounding system
- TT earthing
- Why do you need an RCD in the presence of grounding
- Circuit without grounding and RCD
- RCD in a system without TN-C protective conductor
- Circuit with protective conductor (TN-S and TN-C-S) and RCD
- Gas boiler and RCD
What gives grounding

Particles of electric current (electrons) are directed to positive charges or the contact of grounded devices, if any. If the electrical network is not grounded, electrons begin to accumulate in the cables, damaging the sensitive parts of electrical appliances. When touching the power circuit, a person becomes a point of electron withdrawal. This leads to injury or death.
In a private or country house, it is necessary to make a grounding line in order to:
- elimination of the risks of electric shock;
- automatic power off in the room;
- class 2 equipment insulation;
- equalization of charge potentials;
- protection of power lines, low voltage systems;
- isolation of premises, sites, recreational areas.
Electrical installation rules call grounding an obligatory part of the electrical network.
Do I need grounding in the country and in a wooden house
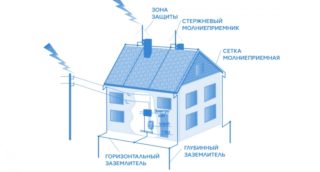
The abundance of household appliances and legislative regulation of electrical safety explain the need to protect wiring from electric current. This is especially true for summer cottages and wooden buildings.
In a holiday village, a wooden or frame house is most often built. The main communications of the site are pipelines on the surface or minimum depth, wells, wells. During thunderstorms, these communications can attract lightning.
If a country cottage is not equipped with a lightning rod or grounding, the risks of fires increase significantly. With no fire department nearby, fire spreads quickly. Owners can lose property or be seriously injured.
The grounding circuit at the dacha is not enough - a lightning rod is needed.
Private house grounding systems
At private construction sites, grounding can be made based on the TN-C-S and TT systems.
Application of TN-C-S

- use of a PEN conductor with mechanical protection;
- reserve grounded posts every 100-200 m.
Implementing TN-C-S in rural areas is problematic.
Features of the TT system
The earth wire is fed to the switchboard from an individual ground loop.The system is resistant to cable breaks, but does not function without an RCD. The last element eliminates the risk of electric shock.
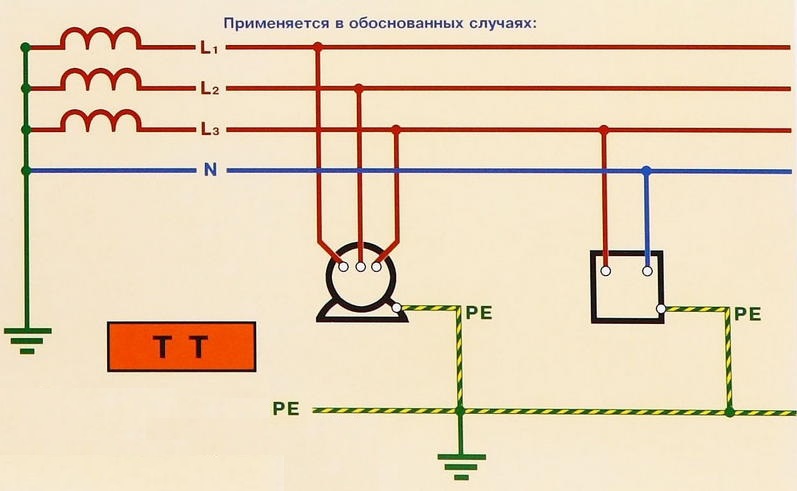
TT is a backup option, which is used in cases of impossibility of organizing TN-C-S.
Grounding device
The home ground loop is a device with an indoor and outdoor subsystem. Two of its tracks are connected in a switchboard, the rest is on the street. It consists of electrodes held together by metal plates and dug into the ground. A metal bus is stretched to the main shield from the structure. The device works on the principle of diverting electric current into the local soil when a person touches equipment.
What to make grounding

With your own hands, you can make grounding from metal rods 16 mm in diameter. One end of the element is sharpened to a sharp state, and a flat platform is attached to the other by welding.
They also use a metal corner with ledges in the form of shelves 50 mm long, which are quickly hammered into soft soil with a sledgehammer.
Tubes with a flattened or welded edge are also suitable for arranging protection. You will need to make holes 50 cm from the edge in order for the system to function in dry soil conditions. To restore work, a solution of salt and water is poured into the elements. The lack of technology is the need to dig or drill a well.
Grounding cannot be made of reinforcement - the hardened layer changes the direction of the current and quickly splits in the soil.
Modular pin grounding
Assembly and installation are carried out sequentially:
- The pin is treated with an anti-corrosion agent.
- A nozzle-tip is installed on the upper part for convenient work with a vibratory hammer.
- A pointed tip is put on the other end of the rod and covered with an anti-corrosion agent.
- A flat pad is put on top of the pin.
- A recess is dug in the ground.
- The earthing set in the assembly is placed in the pit and screwed in to the maximum depth.
- With a vibrating hammer, the structure is immersed in the soil, leaving 20 cm for attaching another rod.
The finished modular device occupies a small area and does not require welding. All parts of the structure are prefabricated, so they can be assembled without effort.
Black metal contour
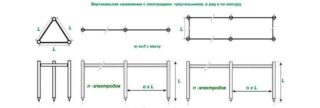
A popular option for making a protective circuit is in the form of a triangle, where the electrodes are the tops. The pins are connected with metal strips, a similar element is pulled to the switchboard. Depending on the resistance of the soil, the rods are installed at a distance of 1.2 - 3 m.
IEC 60364.5.54 notes that in conditions of sandstone, alkaline soils with low GWL, galvanized black metal pins can be used.
Driving depth of pins
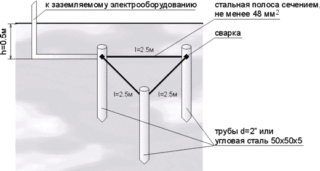
Driving of metal rods to a depth is allowed:
- from 80 to 100 cm, but not less than 60 cm below the level of soil freezing;
- from 100 to 200 cm in the presence of plastic, mobile soils on the site;
- with a 1/3 protrusion in wet soils.
Frozen or dry top layer increases soil resistance by 10 times.
What not to do

In order to safely ground the site and the house, it is worth paying attention to the prohibitions of the PUE. According to the document, you cannot:
- use corroded metal - there are risks of short circuits;
- use fittings as a ground electrode and a conductor - the current destroys the hardened layer and the rod quickly rusts;
- lay the circuit at a distance of no more than 1 m from a residential building - the system will be ineffective;
- use pipes for heating or water supply as a circuit - the system will not be integral;
- combine the PE-conductor with a working zero behind the separation section - the circuit breaker will start to operate constantly;
- set the jumper to zero and the PE-conductor of the socket - in case of a zero break, a phase will be supplied to the housing of household appliances.
Detailed recommendations are given in the Electrical Installation Code.
How to do it right

For the correct installation on the protective grounding site and its entry into the house, it is worth choosing the material and shape of the grounding conductors.
The structure is made of steel or copper metal elements:
- vertical rods from 16 mm;
- horizontal rods from 10 mm;
- steel products with a thickness of 4 mm;
- steel pipes with a diameter of 32 mm.
The shape of the ground electrode can be in the form of an equilateral triangle with pin-tops. The second option is a line with 3 elements located exactly. The third method is a contour, in which the rods are hammered in with a step of 1 m and connected by metal bonds.
A step of 1 m is suitable for buildings with a square of 100 m2 or more.
Procedure

Installation of grounding should be considered using the example of a triangle. They work according to the following scheme:
- Marking is done in the form of triangles with an indent from the beginning of the blind area to the installation site of at least 150 cm.
- Dig trenches in the form of a triangle. The size of the sides is 300 cm, the depth of the grooves is 70 cm, the width is from 50 to 60 cm.
- The top closer to the structure is connected by a trench 50 cm deep.
- Elements (round pin or corner) 3 m long are hammered at the tips of the tops.
- The earthing switch is lowered below the soil level by 50-60 cm.Above the bottom surface, it rises by 10 cm.
- Metal bonds are welded to the visible parts of the elements - strips of 40x4 mm.
- The triangle is brought to the house using metal strips or round conductors with a cross section of 10 to 16 mm2 and welded.
- Remove slag from the connection points, cover the structure with an anti-corrosion agent.
- Check the resistance (should be up to 4 ohms) and fill the grooves with soil without large impurities. Each layer is tamped.
- At the entrance to the house, a bolt with an insulated copper conductor with a cross section of 4 mm2 is welded to the strip.
- Throw in the grounding in the shield. The connection is made to a special node covered with a grease.
- The earth is connected to each line wired around the house.
According to the PUE, it is impossible to separate the "ground" with one conductor - only in a common cable.
Entering the ground loop into the house

To enter the circuit into the house, it is worth using a steel strip of 24x4 mm, copper wire with a cross section of 10 mm2, aluminum wire with a cross section of 16 mm2:
- Insulated conductors. A bolt should be welded to the circuit, and a sleeve with a round non-contact pad should be put on the end of the conductor. Next, assemble the device by screwing a nut onto the bolt, a washer on it, then a cable, a washer and tighten everything with a nut.
- Steel strip. A bus or conductor is brought into the room. To ensure the accuracy of execution, a copper bus is carried out with a small size.
- Transition from a metal bus to a copper wire. Two bolts are welded onto the bus with a distance of 5-10 cm. A conductor is twisted around the elements, the bolts are pressed with washers.
The latter method is more convenient for routing through a wall.
Why it is impossible to make separate grounding
Installation of separate groundings will not ensure the efficiency of household appliances. Electric current can cause injury to a person. If the house has 2 or more sockets with separate grounds, the equipment may be damaged. The reason lies in the dependence of the resistance of the contours on the state of the soil in a separate area.A potential difference may appear between the structures, which will disable the equipment or cause electrical injury.
Which system to choose
In the private sector, today only two schemes are used - TN-C-S and TT. Most often, a two-core conductor for 220 V or a four-core conductor for 380 V is supplied to the structure.
TN-C-S grounding system
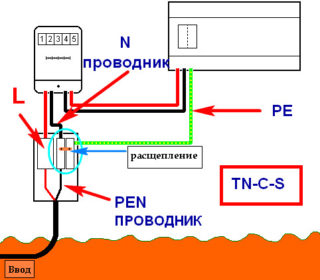
The TN-C-S grounding scheme will provide high-quality protection only in the presence of a difavtomat and an RCD. All systems based on current conductors (water supply, foundation reinforcement, sewage, heating) must be connected to the earth bus with separate wires:
- Selection of busbars for routing the PEN cable. You will need a ground (PE) with a metal base, a neutral (N) with a dielectric base and a 4-point splitter.
- Connecting the metal bus to the metal housing of the shield to form contacts. The paint on the attachment points is removed completely.
- Mounting the zero bus on a DIN rail.
- Checking the location of the tires - they do not overlap.
- Placing a PEN conductor on the release.
- Connection to the ground loop release.
- Installation of a jumper on the ground bus from one socket using a copper wire with a cross section of 10 mm2.
- Installation of a jumper from a free socket to a zero or neutral bus - a similar copper wire is used.
Consumers are connected according to the principle of pulling a phase from the input wire, zero - from the neutral bus, ground - from the PE bus.
TT earthing
The TN-C system in old houses can be converted to TT. The phase cable from the pole is used as a phase, and the protective cable is fixed to the zero bus and remains neutral. The conductor from the finished circuit is immediately brought out to the ground bus.
The disadvantage of the TT system is to protect only the equipment thrown onto the ground wire. Remaining two-wire devices will be energized. In the case of grounding the enclosures with additional conductors, the voltage during surges remains zero, and the machine can break the phase.
Why do you need an RCD in the presence of grounding
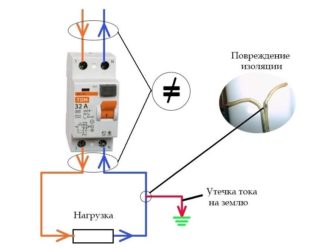
The residual current device is necessary to equalize the phase and zero current. If there is a likelihood of leakage, the RCD will de-energize the line and even when it touches the body of the device, the electricity will go into the ground.
Circuit without grounding and RCD
If there is no grounding in the house, the installation of the protective device is carried out in two ways.
At the entrance.The appliance is the only means of protection for all household wiring. The voltage will be supplied through the input cable to the switchboard, then to the two-pole circuit breaker, and then to the RCD. After that, the machines can be connected to the outgoing lines.
The scheme requires practically no financial costs, it provides a compact arrangement of all devices. Its minus is the operation of the device in the current leakage mode and the de-energization of the entire building.
Inlet and outlet lines.The introductory device is mounted at the entrance, and the auxiliary ones are mounted near the automatic machines of the outlet lines. The number of RCDs is determined by the branching of the power network. It is allowed to connect boilers, washing machines, electric stoves and dishwashers to the protection. By this principle, it is convenient to connect a garage, cellar or outbuildings.
At the moment of current leakage, a specific device is triggered, one type of equipment stops, the rest work in standard mode. The disadvantage of the system is that the grounding is installed for a long time in the dimensional panel, which is not cheap.
RCD in a system without TN-C protective conductor
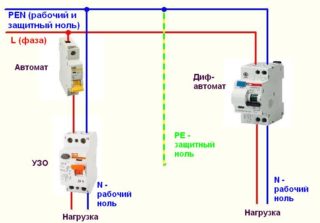
The system includes three-phase (4 pcs.) Or single-phase (2 pcs.) Wire. The first ones consist of 3 phases and one zero, the second - of 2 phases and one zero. In cases of damage to the insulation layer, the device does not immediately react, since no leakage current appears.
When touching the damaged equipment, part of the stress will enter the human body. Only then will the RCD start to work.A lot can happen in 1 / 10th of a second - from unpleasant tingling sensations to electric burns.
Circuit with protective conductor (TN-S and TN-C-S) and RCD
When equipment connected through an RCD with a ground loop comes into contact, a current leak immediately occurs. It occurs when a phase is closed on the equipment case. The machine is activated, breaks the connection, the current is diverted into the ground.
Gas boiler and RCD
It is imperative to ground the gas boiler at the same time as installing the RCD. The need for work is due to the formation of surface stress on the boiler body during operation. Grounding in this case will prevent equipment failure, eliminate the risk of ignition from static electricity. Arrangement of the line will also provide additional fire protection, since the gas is explosive.
Grounding the power grid is a universal way to protect human life, prevent insulation breakdowns, breakdowns of household appliances. Electric lines without grounding are fire hazardous, but it is worth installing a protective system in accordance with the connection diagram of the neutral, phase, earth.