Self-development of the project and installation of wiring is a rather troublesome business, although it is quite feasible on its own. At the same time, the design and installation of electrical wiring will require the owner of the house to have special knowledge and experience in carrying out such work. If you do not have such skills, it is better to use the services of qualified specialists.
- General design rules
- Wiring diagram
- Choosing the type of wiring
- Power consumption calculation
- Consumer groups
- Recommendations for the selection of wires
- Drafting and approval of the project
- Drawing-project of electrical wiring and a set of documents
- Typical wiring diagrams
- Wiring diagram in the kitchen
- Garage / basement wiring diagram
- General layout of the electrical wiring in the house
- Wiring diagram
- Common design mistakes
General design rules

The wiring of a private house is a set of cables and wires laid inside the building, complete with protective, installation and fastening elements. As a rule, it is laid in accordance with a project agreed and approved in accordance with the established procedure, carried out by a specialized company with an appropriate license. The development is preceded by the familiarization of the designers with the layout of the building and a conversation with its owner. During the conversation, it is determined:
- the number and lifestyle of people living in the house;
- in what capacity the house will be used (main or seasonal housing);
- the estimated composition of energy-consuming equipment.
The main requirements for the wiring of a private house are safety and reliability. As a rule, the source of electricity for buildings of this type is a transformer substation, the voltage from which is supplied to the consumer via an overhead power line or an electric cable laid underground. Therefore, at the first stage of design, the owner of the house needs to accurately calculate the amount of energy consumption. It is on this value that the choice of wires, cables, as well as protective and switching devices depends.
Before starting work on the design of electrical wiring, the owner of the house must conclude a contract for its power supply. After that, the power supply company will branch off the nearest main power line and install an introductory machine and a meter on one of the outer walls of the house. It will also ensure their connection in the future.
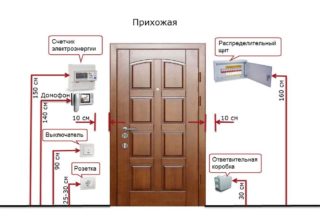
The design of electrical wiring in a private house should be carried out taking into account the requirements specified in the current regulatory and technical documentation (PUE, VSN, SNiP, etc.):
- A switchboard with a protective device must be installed at a height of 150-170 cm from the floor.
- Electric wires and cables are laid parallel or perpendicular to the floor surface.
- Removal of cables and wires from distribution, protective and switching devices should be carried out at an angle of 90 °.
- Rotation / bending of cables and wires during laying should be carried out at a right (90 °) angle. Diagonal placement of cables and wires when laying electrical wiring is prohibited.
- The laid wires and cables must be removed from door and window openings at least 15 cm.
- Socket blocks should be located at a height of 30-40 cm from the floor surface.
- Switches should be installed at a height of 80-90 cm from the floor, while the distance to doorways cannot be less than 15-20 cm.
When designing a wiring diagram, the home owner should not forget about comfort. Near double beds, you can provide power sockets on both sides, and in the kitchen you can install power sockets in the area where kitchen equipment is located.
Wiring diagram
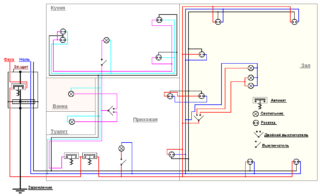
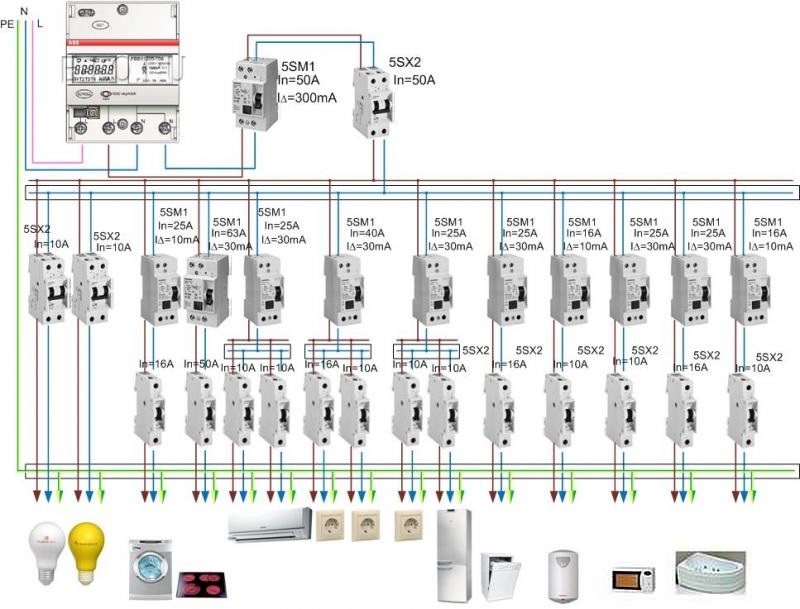
A modern private house is equipped with a large number of various electrical appliances, some of which are quite powerful. This imposes certain requirements on the choice of cabling and wiring products, protection devices and other necessary equipment. It is recommended to divide the wiring into a number of circuits, connecting each of them to a separate protection device (circuit breaker).
The design of electrical wiring begins with the development of a wiring diagram. In this case, it is advisable to at least roughly imagine where the main consumers of electricity will be located (washing machine, microwave oven, water heater, etc.), which in turn will allow for the location of outlets in the immediate vicinity of these devices.
Having drawn a sketch of the electrical wiring, the owner of the house can easily:
- calculate the maximum electrical load for each room;
- calculate the total power consumption;
- make a list of required materials and components;
- select the cross-section of wires and cables.
Choosing the type of wiring

Electrical wiring in a private house can be done in two ways - outdoor (open) or hidden.
The outdoor method of laying wires is used in wooden houses or when decorating the interior of a house in the "Retro" style. In this case, the project should provide for the laying of wires in plastic boxes or with fastening on porcelain insulators. The latter will require the use of a special cable. You will also need outdoor sockets and switches.
When laying the cable outside on the diagram, in addition to the route of its wiring, you will also need to indicate the installation locations of the insulators.
In modern buildings, as a rule, a hidden method of wiring is used. It is somewhat more complicated, since the owner will have to make grooves in the walls, where the cable will then be laid. The laid wires will then have to be fixed with alabaster or plaster mortar. Sockets and switches must be of internal design. For them, the project should provide for the installation of special socket boxes.
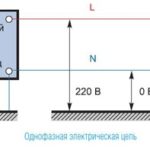
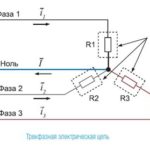
Starting to design electrical wiring, you need to decide on the type of connection of the house to the electrical network - it can be single-phase or three-phase. If it is possible to connect the house to a three-phase network (~ 380 V), it is better to use it, since most powerful household appliances are designed to be connected to just such an electrical network. Their operation from a single-phase network is considered only as a compromise option. If there is no possibility of connecting to a three-phase network, there is only one option - a single-phase ~ 220 V.
The presence of a three-phase input will require you to take care of the uniform load of each phase, otherwise in case of poor contact or complete burnout of "0", the voltages on the phase wires will start to differ from each other. At the same time, due to increased (~ 250 ... 280 V) or low (~ 180 ... 150 V) voltage, household appliances operating at the level of single-phase ~ 220 V power supply may fail. Power consumption of devices that are insensitive to such voltage imbalance will significantly increase. To avoid these negative phenomena, it is necessary to distribute electrical appliances into groups in such a way that the load on the network and each phase separately is optimal.
Power consumption calculation
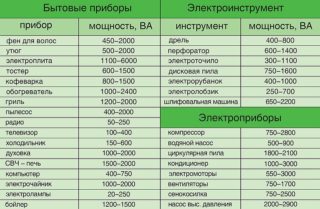
The development of a wiring project is impossible without determining the total power consumption. It is determined by summing up the power consumption of all electrical appliances that are supposed to be used in a house, garage, basement, workshop and in a personal plot. Then the resulting value is multiplied by the coefficient of simultaneity of switching on the devices, which is usually taken equal to 0.7.
Next, they proceed to the distribution of electrical appliances into groups, based on the fact that the total power consumption of one group should not exceed 4.5 kW.
Consumer groups
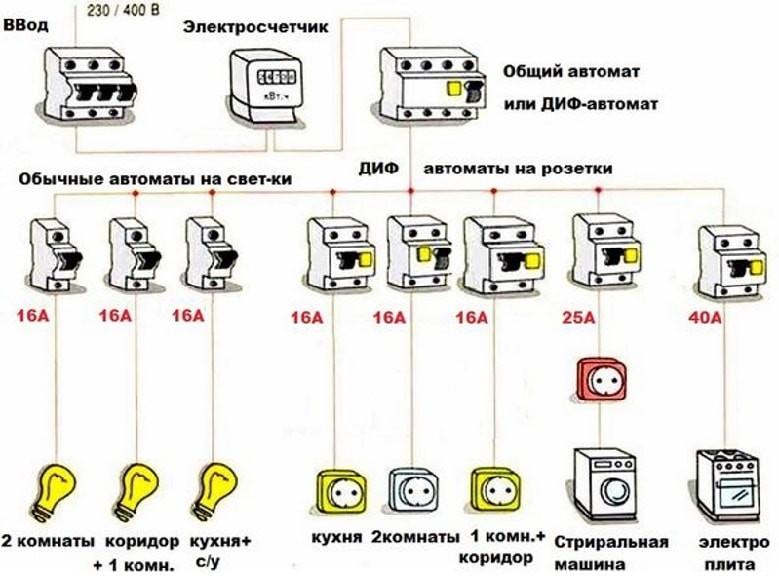
Given the large number of various electrical appliances that are used in the house, it is better to divide cable lines into several groups:
- outlet (low-power household appliances);
- lighting;
- separate power lines for household appliances such as an electric stove, water heater, washing machine, air conditioner, etc.
According to the requirements of VSN 59-88 (clause 7.2), the sockets installed in the kitchen and in living rooms must belong to different groups. In this case, the rated power of the circuit breakers of these group lines should not exceed 16 A (clause 9.6).
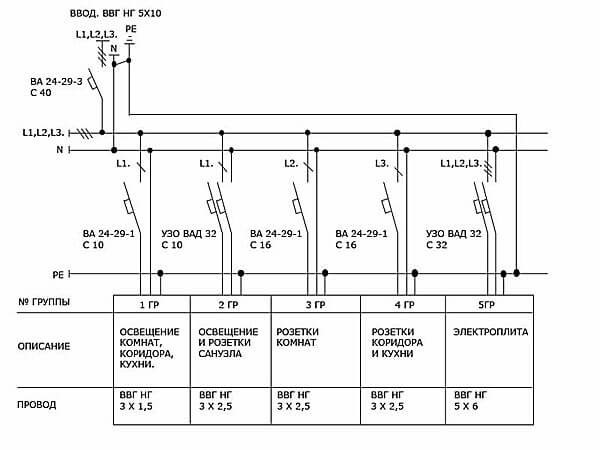
The first group includes general lighting devices connected to the L1 phase through a 10 ampere circuit breaker with a leakage current of 10 mA. The second group includes energy consumers installed in the bathroom and toilet. Given the high humidity of these rooms, electrical appliances of this group are connected to phase L1 through a residual current device (RCD) with a rated leakage current of 30 mA (requirement of the PUE). Power supply to room outlets (third group) and sockets installed in the kitchen and corridor (fourth group) is supplied from phase conductors L2 and L3 through 16 amp circuit breakers. The electric stove (fifth group) is connected to a three-phase network (L1, L2, L3, neutral wire + ground) through an RCD designed for a current of 32A.
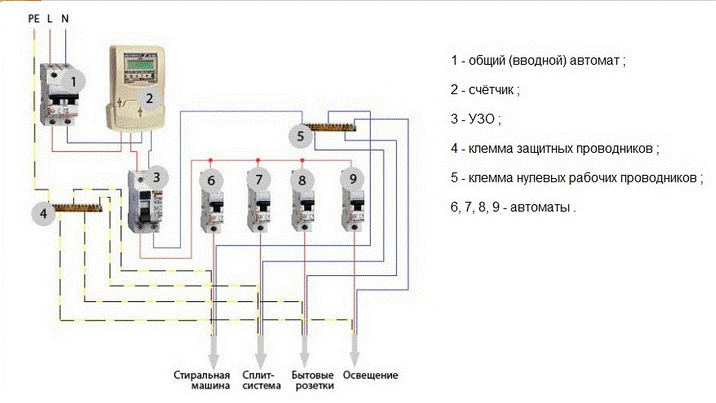
Recommendations for the selection of wires
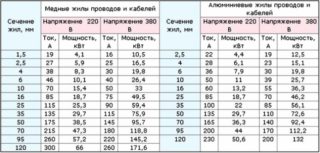
The choice of cables and wires, as well as the calculation of the cross-section of their conductive cores, is one of the main stages in the design of electrical wiring. Missing switches and sockets can be installed later, incorrectly selected machines can be easily replaced, but removing wires from the walls is not an easy job. The durability and reliability of the wiring depends on the correct calculation. Ensuring fire safety is equally important.
When choosing the brands of wires, it is necessary to take into account the requirements of the PUE 7 "Electrical Installation Rules".
- In residential buildings, only wires and cables with copper conductors are used (clause 7.1.34). In this case, the lines of group networks must have a cross section of at least 1.5 mm, and the lines going to the settlement meter - at least 2.5 mm.
- All lines laid from group shields to sockets and general lighting fixtures must be three-wire - phase L, zero working N, zero protective PE (clause 7.1.36).
There are several methods for calculating the cross-section of conductive conductors. Their diameter is calculated according to the following indicators:
- power consumed by all consumers;
- total current value;
- required length of the line to be laid.
However, all these calculations can be omitted, and the cross-section of the conductive conductors can be determined based on the nominal parameters of the group machines. In this case, the method of laying must also be taken into account, since the heat transfer from wires laid in an open or closed way is different.
In the general case, the required cross-section of conductive conductors can be selected using table 1.3.4 (clause 1.3.10 of the PUE 7). However, for lines of powerful devices, it is still desirable to calculate the cross-section of current-carrying conductors separately.
When determining the brands of wires for electrical wiring, it is better to include cable products in the project. The cable differs from wires by improved insulation, which makes it safer to use. As a rule, non-combustible cables of the VVGng or VVGng-LS type are used for electrical wiring inside the house.
Drafting and approval of the project
An individual wiring project for a private house is required in such cases:
- the electrical wiring in the building is being installed for the first time;
- a large-scale reconstruction of the house is planned with a change in the existing wiring diagram and places for installing powerful electrical equipment;
- a significant increase in power consumption is required.
For private property, in which the total power consumption is less than 10 kW - it is allowed to develop a simplified drawing-project for laying electrical wiring; more than 10 kW - it is necessary to develop a full-fledged electrical project.
The development of project documentation begins after receiving technical specifications (TU) from the organization that contains the power line on the balance sheet, from which it is supposed to receive electricity. For the project developer, the fulfillment of the requirements and recommendations set out in the TU is mandatory.
The developed project documentation must be agreed with the organization that issued the technical specifications and the local authority for state energy supervision.
Drawing-project of electrical wiring and a set of documents
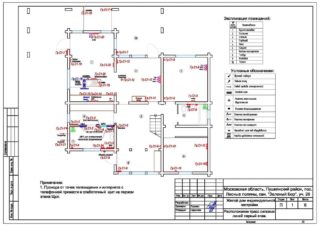
In the general case, the project drawing should, along with the external and internal power supply diagram, contain reliable data on the following factors:
- type and place of installation of circuit breakers;
- brands and sections of wires and cables used;
- the value of the calculated current load;
- electricity metering devices;
- method of connecting electrical wiring to the mains.
In addition, the documentation set should include:
- situational layout of electrical equipment, laying of cable products, as well as grounding and neutralizing conductors;
- lists of required materials, components and electrical equipment;
- explanatory note (if necessary).

A complete set of design documentation is being developed for a private house in which the total electrical power of electrical equipment exceeds 10 kW. Must contain:
- external and internal power supply schemes;
- internal wiring diagram with an indication of the brands of cable and wire products and the method of their laying;
- input device diagram;
- grounding and / or grounding scheme (if necessary);
- calculation of electrical loads;
- calculations confirming the correctness of the selected machines and RCDs;
- calculation of electricity metering.
You can clarify information about the documents in the energy supplying organization.
Typical wiring diagrams
When developing design documentation for electrical wiring for a private house, designers recommend using standard wiring schemes for different types of premises. All these schemes have the same structure, which is based on the division of the wiring into a number of circuits, with each of them connected to a separate machine.
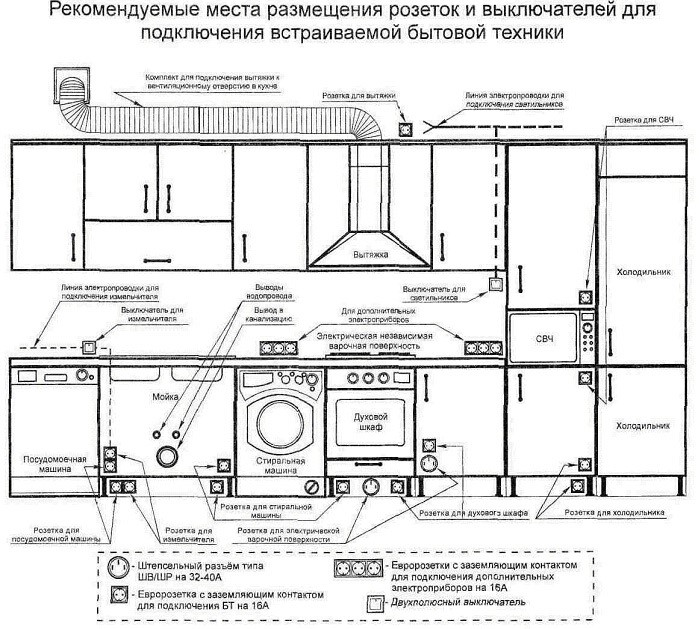
Wiring diagram in the kitchen
The peculiarity of the wiring in the kitchen room is distinguished by the presence of a large number of sufficiently powerful electrical appliances, for which it is advisable to allocate separate lines with their own circuit breakers. The main task of the designer in this case is the optimal location of the sockets - they must be placed next to electrical appliances, providing for the possibility of free access to them for repairs or for rearranging / disconnecting household appliances. In this case, on the diagram, you need to display not only the location of electrical appliances, but also the arrangement of kitchen furniture.
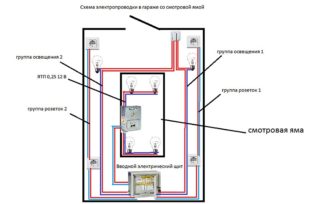
Garage / basement wiring diagram
Quite often, the owner also uses the garage as a workshop. Therefore, when wiring, it is necessary to provide for the possibility of connecting an electric tool, a compressor, or even metal or woodworking machines. This is possible only if there is a three-phase power supply. Depending on which network is brought into the garage, the wiring diagram also depends. In this case, automatic machines must be installed on the switchboard for each group of wires and RCDs.
Taking into account the high humidity in the basements and the garage inspection pit, experts recommend using safety lamps designed for a voltage of 12 V when organizing lighting in them. To connect the wiring leading to such lamps, you will need a step-down transformer.
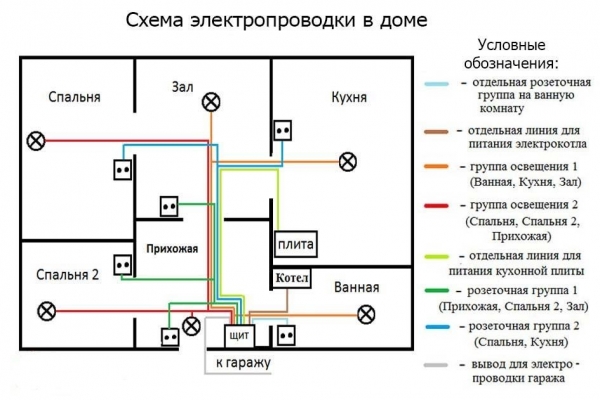
General layout of the electrical wiring in the house
In some cases, before the wiring diagram is drawn up, it is recommended to develop a preliminary diagram listing all the devices intended for installation in the house. Such a scheme will facilitate the calculation of the total number of lines supplied to the switchboard and the total number of circuit breakers and RCDs. It also indicates the type of power supply, which allows you to select the appropriate cable, the type of protection device and the model of the electricity meter.
The explanatory note to the plan indicates that the input device and the electricity meter are installed on one of the outer walls of the house, and the general electrical distribution board is located in the corridor or in some separate room, for example, in a nearby garage. In order not to create difficulties for yourself in maintenance later, in houses with 2 or 3 floors, it is recommended to provide intermediate distribution switchboards on each of them, connected to a common switchboard.
In a similar way, an electrical plan is being developed for a small one-story house.
Wiring diagram
Based on the previously drawn up plans, it is possible to develop a general wiring diagram for wiring wiring, using which, it is easy to calculate the required number of switches and sockets and additional equipment and materials, as well as the footage of cabling and wiring products.
Develop a wiring diagram using a copy of the house plan, which indicates:
- the point of entry of the field line;
- places of installation of the electrical panel, junction boxes, electrical appliances, sockets, switches and lighting lamps.
If it is planned to install high-power electrical appliances in the house, they must also be shown in the diagram, since the power supply for them must be supplied through separate lines.
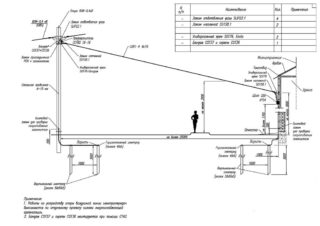
If the project of a private house provides for free-standing outbuildings, the wiring in them must also be displayed on the wiring diagram.
To facilitate the procedure for calculating the required number of cables and wires, it is better to draw the connecting lines of each circuit in a different color.
It is also recommended to designate conductors of the same cross-section on the plan in one color. This will simplify the determination of the nomenclature of the required cabling and wiring products and simplify the process of its installation.
Common design mistakes

The desire for savings often forces the owners of private houses under construction or reconstructed to independently develop a wiring project.However, behind the seeming simplicity of this work lies a sufficient number of problems, ignoring which leads to errors that can disrupt the regular operation of the house electrical network. In this case, the residents may be injured by electric shock, and in some cases, the electrical wiring may also catch fire.
When designing a wiring diagram in a private house, the contractor needs to avoid repeating common mistakes:
- use of materials and components without labeling, often not certified for use in the country;
- the use of cables and wires with aluminum conductors;
- inclusion in the project estimate of sockets that are not intended for connecting electric stoves, electric boilers, water heaters, etc.;
- introduction into the project of the electrical wiring of a wooden house, laying of wires in a closed way;
- switching power cables in one distribution box with low-power lines;
- use instead of special terminals twisted wire connection;
- the location of the junction boxes at the height of human height.
It is forbidden to ground electrical appliances to metal pipes: sewer, gas, water supply, etc.