As electricity tariffs rise, the issue of energy conservation is given more and more attention, with particular importance for private consumers. Among the known methods of saving electricity, there are automatic devices that control the switching on and off of lighting in controlled spaces. The street motion sensor is a special sensitive device that allows you to turn on the light only when absolutely necessary.
Areas of use

The first samples of motion sensors (DD) were used mainly in the protection of objects. With their help, an alarm signal was formed, warning of the entry of unauthorized persons into the territory. Over time, manufacturers decided to expand the protective functions of the sensor, which, after revision, was able to turn on lighting devices.
Since a wide variety of illuminators are installed in open spaces, the field of application of wireless sensors is very wide.
Together with a lighting fixture, they are used in the following situations:
- If necessary, turn on the spotlight in front of your house or outside the garage.
- For security lighting of backyard areas (as part of landscape design systems).
- In order to illuminate the facades of buildings.
- On any objects where it is possible to protect against penetration by suddenly turning on a powerful illuminator.
In addition, outdoor motion sensors are used in hotel and office facilities, as well as in educational institutions, sports facilities, parking lots and shopping areas.
Principles of operation and types of sensors
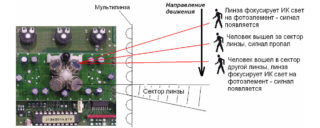
The essence of the functioning of street motion sensors to turn on the light: when a constantly moving object is detected, the sensitive element is triggered and sends a signal to the actuator, which turns on the illuminator for a certain time. After its expiration, the lamp or searchlight turns off until the next operation.
As sensitive sensors in such a system, various devices are used that work in conjunction with lighting equipment. There are four types of motion detectors that differ in the built-in sensor element:
- IR sensors;
- modern ultrasonic devices;
- microwave or microwave elements;
- hybrid sensors that combine the capabilities of several types.
Street infrared DD

Infrared sensors are among the most common types of detectors, the principle of which is based on the detection of movements in the controlled area. They are able to turn on during the transformation of the general physical picture, due to the heat released by a living organism. Any changes in the temperature state or position of the object are recorded by a sensitive device.
Of the two known types of IR sensors (active and passive), only the latter are used in conjunction with illuminators.
Despite the weak sensitivity, shorter range and significant error, passive products are in great demand, which is explained by their relatively low cost.
Ultrasonic

Devices of this class are triggered by the effect of reflection of the sound emitted by them from a moving object.After receiving the reflected signal, the sensor recognizes changes in its spectrum and generates a pulse to turn on the lighting. The frequency of the ultrasound generated by the sensor is in the range of 30-40 kHz and is practically not captured by the human ear.
These frequencies still have a certain physical effect on the human body, and most often they are unsafe for health. Therefore, ultrasonic sensors are recommended for outdoor use only.
Microwave
The operation of these devices is based on the Doppler effect, which extends its action to signals in the microwave range. When any object moves, the frequency of the signal reflected from it changes its value. The magnitude of this change is proportional to the speed of movement of a person who has fallen into the sensor's sensitivity zone. This method also has its drawbacks, which are manifested in the fact that any random obstacles interfere with the operation of the system.
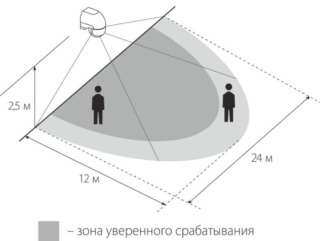
Factors to consider when selecting and configuring
Before choosing a sensor, you need to immediately decide in which place this device will be used, as well as with the following important points:
- fastening method;
- the degree of security;
- the total power of the switched lighting equipment.
There are models on the market with a wide variety of characteristics, differing not only in their appearance, but also in functionality. They are capable of performing protective functions in various visibility conditions and are considered all-weather. These devices differ in the following parameters taken into account when setting them up:
- configuration of the field of view, the correct choice of which determines the reliability of the device (no false alarms);
- the ability to accurately set the moment of switching on and off the light source;
- various viewing angles ranging from 180 to 360 degrees.
Sensors with a viewing angle of 180 degrees are installed in the entry-exit zones and are mounted on the surface of the walls.
Installation of devices
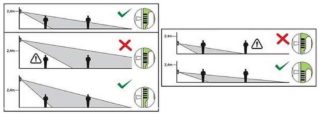
There are usually no special difficulties with mounting sensors. For their installation, a place is selected from which the working element reliably fixes the movements of objects falling within the radius of action. It is chosen so that when the searchlight is turned on, a complete overlap of the controlled space is provided.
A number of DD samples provide for the possibility of using a backup battery that is connected in the event of a power outage.
In this case, when installing the product, you will need to provide a separate place for the battery (if an external battery is used), reliably protected from bad weather.
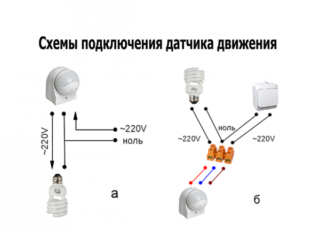
Connection and setup
- direct switching on of the illuminator;
- use of a switch mounted in parallel;
- a combined option, in which several sensors or illuminators are turned on (due to its high cost, it is used very rarely).
In the first case, the lighting can be connected only when a person appears in the sensitivity zone - the light comes on after the DD is triggered. The second option is considered more versatile and allows a choice according to the user's preference. You can leave the device in automatic mode (the switch is locked) or turn on the lighting fixture manually. In the latter case, the circuit is switched in parallel (in one way or another - at choice).

Setting up the system with DD is carried out according to the instructions attached to each device.It assumes the following procedure:
- The correct direction to the emitted or reflected signal is selected to the maximum of its fixation by the receiver.
- The sensor is configured so as not to be triggered by accidental interference.
- At the final stage, they try to combine the two settings until the system is stable in order to get good statistics.
When setting the sensitivity limit, the sensor in open spaces is adjusted to a minimum.
At low illumination of the controlled area, the exact value is selected empirically. At the final stage of the configuration, it is additionally corrected.