Residential, office and other structures are filled with a huge amount of electrical household appliances, appliances and equipment. Energized devices pose a potential danger to human life and health. To determine its degree, such a concept as a class of protection against electric shock (SC) has been developed. It includes a list of insulating materials, fuses and a designation system that are applied to the service information plates for the product. Knowing and understanding the meanings of the symbols will help you make the right choice when buying, operating and maintaining electrical equipment.
Consolidation of standards
The classification of products according to the level of consumer protection from the damaging factors of electricity is standardized and determined by the provisions of GOST R IEC 61140-2000.
The electrical protection class of devices is indicated as follows:
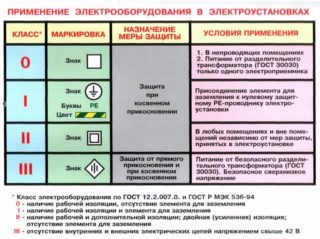
- 0 - complete absence, in the presence of working isolation of communications;
- 00 - indication of the presence of current;
- 000 - presence of an emergency shutdown relay;
- 0I - grounding is provided;
- I - grounding is installed during manufacture;
- I + - in addition to grounding, there is an RCD;
- II - double reinforced insulation;
- II + - RCD and double reinforced insulation;
- III - absence of high voltage, dangerous for living organisms.
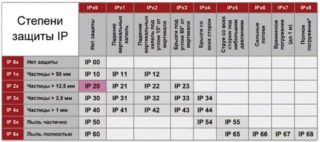
There is a classification according to the degree of protection of electrical equipment from penetration of water and solid objects into live lines and nodes (IP).
- 0 - no;
- 1 - by hand;
- 2 - from the finger;
- 3 - from a screwdriver;
- 4 - from the wire;
- 5 - from splashes;
- 6 - from all external factors.
Using the short circuit marking, the manufacturer provides the user with information about the conditions under which the product can be used.
Operating principle
When determining the KZ, the following factors are taken into account:
- mains voltage;
- current strength;
- power consumed by the consumer;
- ambient temperature;
- air humidity;
- installation of a conductor or ground terminal;
- body tightness;
- the presence of forced cooling;
- structural stability;
- body strength;
- the presence of fencing devices.
The conclusion about the assignment of a particular short circuit to a product is made on the basis of a study of its design and the degree of risks for each technical parameter.
Application of the standard
Zero grade products can be used in dry rooms, provided that there is no contact with water or fumes. In this case, the possibility of accidental damage to the case or the supply cable is excluded in advance.
Class I handheld and stationary equipment can only be used for production purposes, it cannot be sold on the free market. You need to work with such equipment using a special belt, with gloves, on an insulating mat, with the door closed.
Portable tools and luminaires are manufactured in a protective version corresponding to II-III classes.At the same time, for work in a humid environment, products are manufactured that operate on direct current up to 50 V or on alternating current 220 V, but in a sealed design.
Modern household appliances and tools comply with the II KZ. All types of products are equipped with a three-core cable and a socket with a grounding terminal. In its absence, safety is guaranteed by reinforced insulation, relays and fuses.
Household networks
Almost all residential buildings built in the last century are equipped with two-core cables with phase and zero. To make grounding, it is necessary to change the sockets and pull an additional conductor to the shield. Since it is difficult and expensive, most of the tenants refused to do so. Because of this, household networks pose a certain danger and are classified as 0 KZ.
In new buildings, three-core cables are laid, immediately connected to the ground loop. Depending on the type of insulation and the presence of a signal indicator, such lines correspond to I or II short circuit.
Device design
Electrical devices belonging to the categories of safety class have a standard device:
- Power cable. Equipped with insulation of the appropriate short-circuit quality.
- Contacts. These are the connection points of the cable with the working equipment.
- Live parts. The part of the product to which current is supplied after switching on.
- Non-conductive parts. Parts of the device accessible to touch, which may be energized in case of an accident.
- Housing. Designed to protect the working part of the product from mechanical stress and moisture.
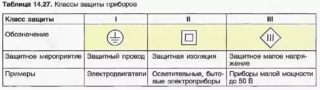
Protection classes
Devices of this category can be used in everyday life, educational institutions, offices and catering establishments with practically no restrictions. Do not install them in wet areas such as saunas and showers.
If the first short circuit provides a relative guarantee of safety, then the second class guarantees protection due to the installation of reinforced insulation, which prevents electric shock to a person. All hand tools, street lighting and electric vehicles are equipped with such devices.
The third short circuit initially excludes the very possibility of undesirable voltage-related phenomena. Reduced direct current can only cause discomfort. Such devices include cell phones, watches, flashlights, radios.
Networks and connectors
When connecting products, the following types of connections are used:
- plug;
- terminal block;
- bolts and nuts;
- clamps.
The choice is determined by the operating instructions for the device.
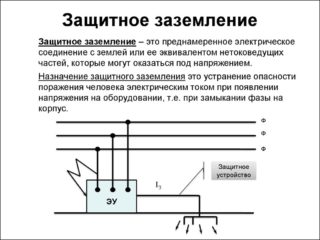
Grounding in electrical installations is a guarantee against human injury from high voltage current. This can occur when the integrity of the insulation is broken, the device breaks down or accidentally touches the live part. For grounding, a powerful copper cable with a cross section of at least 5 mm is used.
EB for children

To protect children from electric shock, the following measures are taken:
- preventive work (lectures, educational films, safety corner);
- installation of plugs on sockets;
- use of high-class safety equipment EB.
If possible, all devices should be installed out of the reach of children.
Interesting Facts
Safety standards are constantly being raised.As a result, in European countries, the use of class 0 products in the home is prohibited.
To ensure complete safety of travel in trolleybuses, modern models are equipped with conductive wheels that provide reliable grounding.
Even new generation TVs have exposed live parts: connectors and sockets.
It should be remembered that in the USSR, heaters with an open spiral were popular - the most dangerous products that were awarded a quality mark.