Any modern three-phase transformer is a special electrical device that provides the consumer with the required type and quality of electricity. Like any transformer converter, it contains primary and secondary windings, of which there are three pairs. At high-voltage substations, thanks to this device, it is possible to obtain a voltage of the required magnitude, and then transmit it along a line with a dead-grounded neutral.
Purpose and types

The classic station three-phase power transformer is used to convert high-voltage energy into a consumer-friendly form. A high voltage (6.3-10 kilovolts) is supplied to its primary windings, and 220 volts, more convenient for use in everyday life, are obtained at the output. This value is measured between the phases and the neutral conductor of the transformer, called neutral. It is customary to denote it as phase voltage, in contrast to linear 380 volts, measured between each of the phases.
Three-phase step-down transformers of this class provide the transmission of current from the local substation via an underground cable or power line directly to the end user. For these purposes, a special 4-core cable in an armored core is used, or an air wire of the SIP brand. Through them, electrical energy is delivered directly to its intended purpose - to the input distribution devices of the serviced territories and facilities.
According to their functional purpose, 3-phase transformers are divided into the following classes:
- linear (station) devices;
- special converting units.
Of particular note are the three-phase isolation transformers used to decouple electrical circuits and power circuits.

Special devices are divided into the following types:
- Test transformers. It is customary to refer to them as three-phase autotransformer systems.
- Devices used to power special equipment: welding units, in particular.
- Balancing transformer units.
The first two types are used for research purposes. Three-phase balancing transformers are used to eliminate phase imbalance that occurs in electrical networks due to uneven distribution of loads.
In electrical engineering, there are also options for two-phase transformers, often used in electronic circuits and automation devices. They are designed so that the two output voltages are shifted relative to each other by 90 electrical degrees. Most often, such electrical solutions are used in welding equipment.
Transformer device
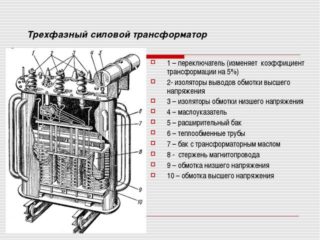
By their design, three-phase transformers are a prefabricated structure consisting of the following units:
- base made in the form of a durable plastic frame;
- magnetic circuit placed in frame sections;
- set of primary and secondary coils with wire windings;
- distribution (soldering) panel with terminal blocks;
- cooling system required to remove heat from the working area.
Each of the known versions of such devices in one form or another contains all the designated nodes. At the same time, they differ in the method of connecting the windings, as well as the type of magnetic circuit used in them.The design features of individual models are reflected in their performance characteristics, in particular, the magnitude of losses in the magnetic circuit and the efficiency.
An exception is the panel for desoldering the transformer windings, thanks to which it is possible to combine groups of connections to obtain the desired configuration.
Winding connection methods
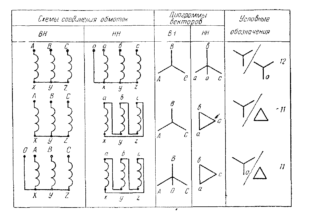
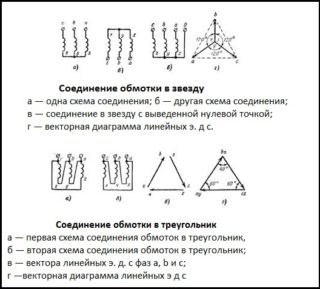
The main difference between various transformer circuits is the configurations used when switching them on (methods of connecting the windings). When organizing centralized power supply, two classic schemes are traditionally used, called "triangle" and "star". The first option involves the sequential connection of the primary and secondary phase windings: the end of one coil is connected to the beginning of the next).
When using the "star" scheme, the beginning of all phase conductors of the primary and secondary windings are combined at one point, called neutral, and their ends are connected to a 3-wire load line. In this case, a cable containing four cores is required to transmit electricity. When connected to the line of the secondary transformer windings, connected in a "triangle", only three cores are used. There is another option for their inclusion, which is called "interconnected star". However, due to the rarity of its use, it is not considered.
Configuration options
When organizing power supply systems, several combinations of switching on the primary and secondary windings of a three-phase transformer are possible. The set of switching actions performed in this case:
- The primary winding is designed as a "star", and the secondary - in the form of a "triangle".
- The second approach uses the reverse order of inclusion.
- In the third case, the already considered combination of the "star" - "star" type or the variant with two triangles (another name is delta-delta) is used.
To take into account all methods of switching on the primary and secondary windings and the subsequent calculation of the parameters of the transformer in electrical engineering, special identification tables are used. They provide possible combinations and combinations to be used if you want to connect a transformer in the line and get the most out of it. The efficiency of the entire power supply system depends on the correct choice of this combination in each specific case.
Parallel connection
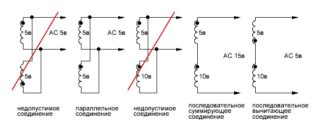
Parallel connection of the same secondary windings allows you to increase the power (current) at the output of the device. In this way, it is possible to increase the efficiency and load capacity of the served line.
When using this approach, you will need to take into account one important detail related to the order of connection of the secondary windings. To obtain the expected results, the windings must be switched in phase, which means the connection of the same type of ends of all three coils at one point. If this rule is violated, the voltage at the output of two non-in-phase windings connected will be close to zero (the substitution principle applies). When this error is made when the transformer is turned on, its power and efficiency are significantly reduced. If a secondary check reveals that the voltage has not changed compared to a single turn-on, then the coils are in-phase.
A converter device, defined as a 220 to 380 Volt 3-phase transformer, can be obtained by applying a special circuit with an increase in the output voltage. Its feature is the presence of one primary and three secondary windings, connected in a "star" or "triangle".








