Concrete, metal or wooden piles are buried in an inclined position or placed vertically. The racks are mounted in the soil at the foundations of structures to perceive the shear, pulling or pressure load from the house to the ground and transfer it to the stable underlying layers. The methods of driving piles differ and depend on the type of soil, the environment, and the structure of the support bar.
Varieties of piles

Driven species go deep into the ground without preliminary excavation using hammers (hammers), vibration installations by screwing or indenting. The shell piles are mounted with vibratory hammers, while the soil for the installation is developed in advance.
Bored types represent the immersion of the casing, followed by concreting and installation of reinforcement. Screw varieties are equipped with blades for sequentially screwing the rod into the earth.
Wooden
Racks made of wood are immersed in hammering, placed under low static loads from the aboveground part, used in individual housing construction and partially in industrial construction of structures.
Wooden pillars are performed according to the technological scheme:
- placed one by one;
- make composite sections;
- apply batch layout.
The material is long coniferous logs, sometimes oak is used. The products have a cross-section of 22 - 34 cm, a length of 700 - 800 mm, while maintaining the natural taper of the trunk. Wooden piles are buried with a steam-air, mechanical hammer, a vibratory pile driver is used.
Bored

They are shell pipes that are buried in the ground and subsequently concreted. The execution technology depends on the characteristics of the soil and above-ground loads.
Types of stuffed casings:
- passages in which no casing is placed, but concreted and reinforced in the excavation;
- wells with a metal pipe shell;
- screw method with simultaneous earth excavation and mortar injection.
The casing is not placed in dry soils, as the passage walls are stable. The casings are used in eroded soils and quicksands.
Reinforced concrete
Made using heavy concrete and reinforcement. Reinforced concrete elements with a section of 35x35 and 40x40 cm are produced with a length of 16 m, and a size of 30x30 cm has a length of up to 12 m. To increase the height, composite piles are used.
The type of load is distinguished:
- pillars-piles, which with a tip rest on stable layers (rocky, little compressible);
- hanging elements that transfer the load by lateral friction against the ground and the fifth.
For deepening, a pile driver based on hydraulics or a diesel installation is used. The bearing capacity is determined by calculation according to the formula or checked by static research by test vibratory driving of reinforced concrete piles until conditional readiness.
Concrete

Such racks are clogged with pneumatic impact devices. Concrete piles are cone-shaped steel pipes that are filled with concrete mix using special pumps. They are used in urban environments when there is a large overcrowding of neighboring buildings.Heavy equipment is not used in such conditions due to the complexity of the situation.
The dimensions of the pneumatic impact device allow it to be used in proximity to the existing foundations of other buildings. Concrete racks are placed on sandy soils, wet soils, used to build foundations at the bottom of reservoirs.
Sheet piling

Piles are made of wood, reinforced concrete and metal, tongue-and-groove types are placed in the construction of embankments, bridges, the construction of special hydraulic structures, fences. When mounted close to each other, a wall is obtained through which water does not penetrate.
Structures prevent the movement of soil from the fenced area to an adjacent area, for example, when excavating at great depths. When piles are vibrated, parts of embankments, slopes, slopes may fall, therefore, with the help of sheet piles, landslides are prevented.
Ground-melted
The piles are placed in wells, where the thermal strengthening of the soil has been previously done. The procedure changes the structure of the soil, mechanical and physical properties. During plasma heating, high temperatures, magnetic waves and electrostatic fields act on the earth.
The process consists of transformational stages:
- dehydration (moisture removal);
- heating of mineral components;
- burning;
- melting;
- degassing, heating of the melt;
- hardening with gradual cooling.
The new bonds in the soil impart positive physical characteristics to the massif, making the soil suitable for carrying heavy loads.
Dive features and sequence

Most often, a pile driver is used to deepen the supporting elements - an installation for mounting racks in the design position. Diesel hammer is a machine for driving racks into the ground. The rods are immersed in clay and sand using a vibratory pile driver.
The hydraulic hammer works on the basis of excavators, block breakers, manipulators, pile drivers. The equipment is used for breaking rocks, rocky soil, permafrost. Pile-pressing devices and drilling units of universal action are used.
Inspection of piles before work
The technology of vibrating piles provides for checking the compliance of the brand of rods and the actual dimensions of the support. The drawings indicate the modification of the element, the dimensions and the elevation of the deepening into the ground. In the conditions of the construction site, static and dynamic tests of the racks are carried out in case of doubt about the design solutions.
Failures are measured on control specimens - at the end of the dive, a stopping point is set when its value approaches the calculated indicator, and the deepening is stopped. A mortgage control of the dive is made, the results are recorded in the inspection log. This is how at least 10% of the supports on the object are checked and inspected.
Support immersion methods

Before work, they ensure the safety of nearby buildings, examine them. Such a survey influences the choice of the method of driving metal piles, concrete racks, casing pipes. Sometimes they strengthen existing foundations, strengthen the soil. The piles are delivered to the site, already prepared for installation.
The methods of deepening are used:
- blow, hammering;
- casing concreting;
- vibration immersion;
- indentation;
- screw way.
The effectiveness of the dive depends on the correct choice of the material of the struts and the soil.
Shock
Translational energy is transferred to the pile, while the stand is buried in the ground, and part of the soil is forced out. The work is carried out using shock units of self-propelled or rail movement. The pile is held in a vertical position by pile drivers with arrows.
The initial immersion is slow and the tilt of the rod is controlled. A cap is put on the top of the element so that the impact force does not destroy the body of the pile.The rack is deepened until the design mark is reached. The impact method is used on different types of soil, while the work is fast. The rods compact the soil around them at a distance of up to two meters.
Bored
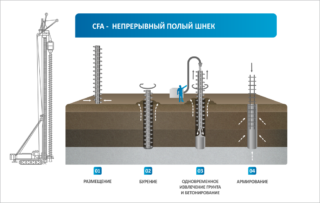
The shells are concreted with compositions of grade M 100 and above, while longitudinal steel rods are installed inside the structure. The readiness of the pile for loading occurs in 28 days, when the reinforced concrete gains the specified strength.
Reusable sectional type pipes are used. The sections are lowered into the well and removed after filling the next pass. Sections are fastened together by welding or technological connections are made. Wells are drilled by percussion method, rotation, vibration, jacks are used. During concreting, the mixture is continuously compacted.
Vibrating
Vibrators reduce lateral friction and soil resistance, so less stress is required. Vibration additionally compacts the ground at a distance of 1.5 - 3.0 cross-sections of the pile and increases the bearing properties of the soil.
Vibrators transmit automatic vibrations to the rack through the headrest, and the piles are driven under the influence of the weight. Heavy rods are immersed at low frequencies, while for light rods, high-frequency exposure is sufficient. The method works when installing in moisture-saturated and sandy soils, dense layers, clay and loamy rocks.
Indentation

It is used in very hard and dense layers (with the exception of rocky soils). Solid pile elements and non-extended tubular specimens (3 - 3 meters) are buried by pressing. The rack is fixed in an upright position, the barrel is secured with pneumatic clamps. The headgear is worn to transmit pressure after a 1 meter dive.
If the rod cannot reach the design mark, it is lifted with special equipment, lowered again and pressed into the ground.
Screwing
This is how the screw pile rods are buried, which include a tip with blade elements in the structure to facilitate entry into the soil. The pile itself is a reinforced concrete or metal trunk. The method is used when immersed in loose and flooded lands. Screw elements are used as a basis for the installation of power lines, the construction of overpasses, bridges and other objects with significant loads.
Screwing is used in densely built regions, for example, in cities, where shock loads will destroy adjacent foundations. Special units fix the pile in the inventory formwork and transmit the torque through the transmission to the submerged element. The holders unclench the rack after reaching the required depth.
Combination
A combination of shock and vibration is more often used, easy entry is provided by the simultaneous action of frequency vibrations, own weight and plugging. The combination is used on dense soils where individual methods are ineffective.
The units for operation have two support frames - on one they put the percussion unit, the second supports the boom vibrator. This is how elements up to six meters high are buried. The piles are protected with a cap after a slight immersion in the ground (0.7 - 1.0 m).








