When installing electrical wiring, the main cable enters the switchboard, and several conductors extend from it. To prevent overheating of the wires and ensure reliable contact, an electrical cross-module is used for wiring in the shield.
Definition and purpose of a cross-module

The cross-module is a device with insulated metal busbars inside. They are designed for connection with screw clamps of outgoing wires of different cross-sections.
The crossbar is made of electrical copper or brass to ensure fire safety. All elements of the device are housed in a protective plastic case. There is a hinged cover for access to the inside.
The use of modular switchgear allows you to avoid unreliable and fire hazardous twisting of cables in the switchboard and greatly simplify installation. The device is small in size and can be compactly installed in the panel itself.
Wiring and wiring takes a few minutes, the bus screw clamp provides reliable contact between the neutral and power cores. This is especially important for industrial enterprises, where dozens of branches can branch off from the switchboard.
Three-phase cross module
The three-phase unit is equipped with 4 metal busbars for connecting the neutral wire and three power phases A, B, C. The number of outgoing connections can be from 7 to 15. Outgoing wires can be used both single-phase for lighting and sockets, and three-phase for connecting industrial motors.
In the presence of a large number of outgoing cables, a cross-module on a DIN rail will help unload the system, the 3 phases of which will be compactly located for ease of assembly. In addition, multiple devices can be placed on a DIN rail.
Advantages of the modular distribution block

The use of cross-modules for wiring installation has a number of advantages over conventional twisting. They are as follows:
- First of all, it is fire safety. Reliable fastening of wires to metal rails prevents sparks from occurring due to loose contact. The presence of a zero phase bus prevents the occurrence of a short.
- Ease of wiring installation. This kind of work can be done even without much experience. The entire installation, wiring and wiring process is fast.
- Possibility of connecting cables of different cross-sections.
- With a large number of connections, several interconnected devices can be installed on one DIN rail.
- No piling up of bundles of twisted wires, an attractive appearance of the switchboard, the ability to visually view the status of all connections.
These qualities contribute to the widespread use of distribution blocks when installing electrical wiring in industrial plants.
The cost of purchasing devices and installing electrical wiring will quickly pay off due to the trouble-free operation of the system over a long period.
Cross-module installation
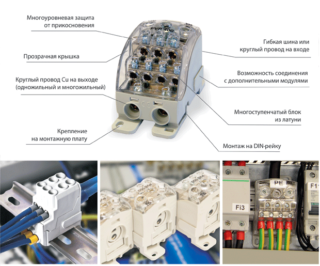
Cross-modules are mounted on the wall in two ways: using screws or on a DIN rail.The first method is used quite rarely when it is necessary to install only a separate unit. When mounting on a rail, several different electrical devices can be installed together at once, connected by wires, which is very convenient and compact.
The installation DIN rail is fixed with self-tapping screws in the place where the unit is supposed to be installed. The length of the rail is cut off based on the number of devices that are planned to be installed. There are special grooves for fastening in the cross-modules, so the installation is quick and reliable.
IEK cross-module

The preliminary diagram of the switchboard is drawn up taking into account the fact that there must be free access to the unit for installation work. The selection is carried out taking into account many factors: the cross-section and the number of wires to be connected, the overall dimensions of the model, the maximum load in amperes and the possibility of installing the unit on a DIN rail along with other electrical devices.
One of the main criteria that you need to pay attention to when choosing a distribution block model is the maximum current load in amperes for which the device is designed. If it exceeds the indicator specified in the technical documentation, the wires will heat up, the cable may catch fire.
To prevent such cases, special protective devices such as MZN or MZT are installed in the system. Additional protection is provided in the IEK cross-module: all buses inside the block are isolated from each other. This makes it possible, with certain skills, to connect wires without even removing the voltage from the unit. Due to this design, the IEK cross-module is considered one of the most used devices.
Design features, varieties of cross-modules

Depending on the number of metal busbars, distribution blocks can be used in single-phase or three-phase networks. They differ in the number of connections and the load value. In addition, there are three types of models for switching wires for different purposes:
- Null. The plastic housing contains one rail with clips. Wire connection with screw clamps.
- Phase. Outwardly it looks like a zero, only the bus is designed for a high load at a voltage of 1000 volts and a current of 500 amperes. The body of such a device is made of heat-resistant plastic.
- Combined type, in which busbars are placed for connecting phases and a neutral wire. For industrial networks with a large number of branches, such a cross-module is the most suitable option.
The industry produces models of distribution blocks for information networks. Used to connect optical fiber and twisted pair.
The use of switchgears allows you to significantly speed up installation work when laying electrical networks. A wide range of manufactured models will satisfy any customer need.








