Loop grounding is installed to protect buildings from fires, and people from electric shocks. When performing work, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of the PUE, correctly calculate, mount the circuit and check the level of its resistance.
- The device and principle of operation of grounding
- Varieties of ground loops
- Traditional grounding systems
- Deep grounding systems
- Calculation of the protective contour
- Objects requiring equipment with a contour
- Connection diagrams
- Ground loop inside the facility
- Installing the ground loop
- Preparing for installation
- Mounting the protective device
- Measuring the resistance of the protective device
- Loop resistance check
- The most common mistakes
The device and principle of grounding
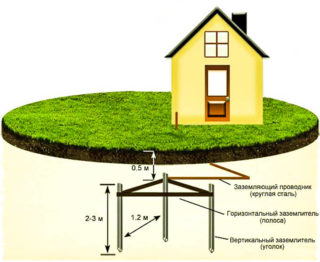
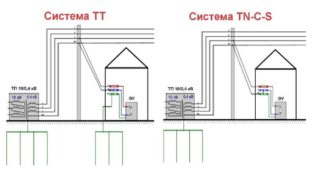
In residential premises, a TN system is often installed, the neutral of which is solidly grounded. The ground wire connects all electrical consumers to the protective circuit. The latter has a low resistance, and the current always flows in the circuit where the resistance is lower. Compared to a grounding device, the human body is distinguished by high resistance, therefore, the circuit allows you to solve the tasks assigned to it.
Contour grounding is a system in the form of an equilateral triangle, rectangle or square, assembled from vertical ground electrodes - steel rods or corners, which are connected by welding at the upper points with horizontal steel strips. It is connected to the equipment to be grounded with a cable. The most common type of construction is triangular.
The outer contour is buried in the ground. The level of resistance to the spreading of currents of the protective device differs depending on the type of soil, its structure.
The best indicators are recorded when installing a ground loop in peaty, loamy and clayey soil. In the latter case, provided that groundwater is close to the surface. If the soil consists of dense rocky inclusions, the performance deteriorates.
You can assemble the circuit yourself or use a ready-made kit.
Varieties of ground loops
There are several types of structures used for grounding.
Traditional grounding systems
A system of this type consists of a minimum number of elements: two vertical electrodes made of metal reinforcement and one horizontal strip-like one that connects the previous two. The sections and dimensions of the elements must comply with the standards. It is recommended to install grounding on the northern shaded side of the site, in a humid place. However, due to the fact that the circuit is often made of steel and cannot be painted with paint, it quickly corrodes. Also, the resistance of such a device is influenced by the temperature and moisture level of the soil, since the circuit is placed in the upper layers.
Deep grounding systems
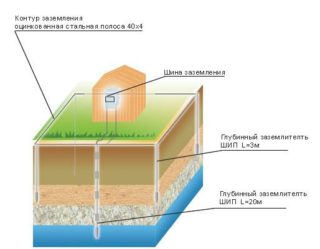
Such a system is manufactured using a modular pin method. Compared to the previous version, it differs:
- long service life;
- simple calculations;
- unaffected by the influence of the environment;
- lack of need for maintenance;
- ease of installation.
The resistance measurement of the installed equipment must be carried out by specialists.
The outer ground loop consists of vertical electrodes and horizontal grounding elements. It is made of four strips with a thickness of 40-50 mm and is installed at a distance of at least 1 m from the building.The horizontal strip should be located at a depth of 50 to 70 cm from the surface.
Calculation of the protective contour
To perform an accurate calculation of the ground loop, you must consider:
- soil moisture;
- average temperature in winter and summer in the area of installation;
- soil resistance and salinity;
- cross-section and length of grounding conductors and electrodes;
- the distance from the house to the contour.
The calculation is made according to the formulas, this procedure is difficult for a person who does not have an engineering education. However, even if correct calculations are made, the real loop resistance will differ from the calculated one due to a large number of influencing dynamic factors.
In fact, many take into account only the remoteness of the contour from the foundation, and then adjust the resistance by measuring this indicator of the already mounted structure.
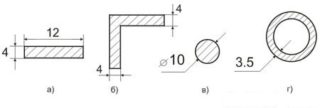
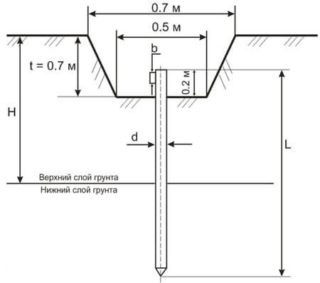
Recommended sizes of earthing switches:
- strips - width - 40-50 mm, thickness - 4-5 mm, at least 2.5 m in length;
- corners - shelf thickness - 4-5 mm, shelf width 40-50 mm, at least 2.5 m long;
- rods (necessarily smooth) - section 16-20 mm, not less than 2.5 m long;
- pipe - wall thickness 3.5 mm, diameter not less than 32 mm, length - not less than 2.5 m.
Accurate calculations taking into account all parameters must be carried out if large commercial and industrial buildings need to be grounded.
Objects requiring equipment with a contour

Must be grounded without fail:
- rooms where machines, devices and light sources with metal housings and casings operate;
- complete transformer substations, as well as buildings housing electrical equipment with steel housings;
- secondary winding of the measuring transformer;
- metal pipelines for cables, rooms where metal structures and cables are located at the same time, wires.
It is not required to ground devices that are installed on already grounded equipment, circuit breakers in electrical panels, electrical measuring devices.
Connection diagrams
The most common connection schemes are closed triangular and linear. A closed system is more stable in operation, because even if one of the horizontal earthing switches is damaged, it will continue to perform its function. Linear in this sense loses to a closed design. It stops working if the jumper is damaged.
In addition to linear and triangular designs, oval and rectangular protectors can be made, but these are less popular.
Ground loop inside the facility
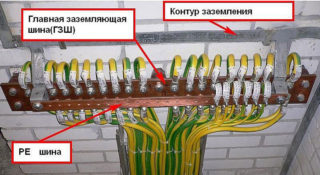
The ground loop is located both outside and inside the premises. When creating it indoors, you must follow the rules:
- Do not use central heating, sewerage and similar pipelines, carrying cables, metal sleeves, armored wires as zero protective conductors.
- Grounding and neutral conductors are laid in an open way, since they must be accessible for inspection, and painted in yellow-green stripes.
- Passages through walls and ceilings are made using non-metallic fireproof pipes.
- Steel tires are painted, welded joints are treated with oil paint.
- In damp rooms, the conductors are welded to the supports.
These are the basic rules, but there are others that are relevant when laying the internal circuit in rooms with an aggressive environment, in the workshops of industrial enterprises.
Installing the ground loop

According to the classical procedure for installing the ground loop, first preparatory work is performed, then the device is installed directly and the resistance is measured.
Preparing for installation
For installation, you need to prepare tools:
- shovel;
- grinder or hacksaw for metal;
- welding inverter;
- puncher;
- wrenches for 8, 10;
- meters of current, voltage, resistance.

Materials required:
- Angles made of corrosion-resistant steel, 40 × 40 × 4/50 × 50 × 5 cm and a length of at least 2.5 m. Or steel round rods with a diameter of 20 mm.
- Three metal strips 250 cm long, 40 to 60 mm wide and about 5 mm thick. The greater the distance between the electrodes, the better the spreading of currents, since the electromagnetic fields interact less with each other. Ideally, the distance between the electrodes should correspond to their length or increase in multiples of this parameter.
- Stainless steel strip for connecting the circuit to the foundation 40 × 4 or 50 × 5 mm or power cable.
- Bolts М8, М10.
- Copper conductor.
The location for the installation of the circuit should be located near the foundation and the switchboard.
Mounting the protective device

The first step is to make trenches about 80 cm deep under the ground loop and a strip connecting the system to the foundation. The trench configuration must match the shape of the ground loop. In this case, grounding is performed in the form of a triangle with sides of 2.5 m each.
The metal corners should be sharpened to make it easier for them to enter the ground. They are driven into the soil, rather than digging holes. The electrodes must go into the ground tightly. The jumpers are welded to the electrodes. Weld seams are treated with bitumen mastic for corrosion protection. The cable is led through the trench into the house, to the switchboard. To do this, using bolts and nuts, the cable packed in the end contact is fixed to the vertical earthing switch. To do this, use tires made of copper (10mm2), aluminum (16mm2) or metal (75mm2). The contour is covered first with sand, then with earth.
Measuring the resistance of the protective device

To check the device's performance, it is recommended to measure its resistance to current spreading according to all the rules. It is better to carry out work in winter or summer, when the soil resistance is maximum. The norm of resistance of the protective circuit is taken as indicators of 15, 30, 60 Ohm or 2, 4 and 8 Ohm when measured with natural ground electrodes and repeated ground electrodes of outgoing lines for the network 660-380, 380-220 or 220-127 V, respectively.
Loop resistance check
To measure the grounding correctly, special measuring devices - "MS-08" or "MS-416" and test electrodes must be used. The technique is as follows:
- A potential electrode is placed between the circuit and the house at a distance of at least 20 m. Another in a straight line with the first and protective device, at a distance of no more than 40 m.
- After connecting the voltage, measure the resistance.
- The grounding measurement is carried out several times, gradually bringing the remote electrode closer, but not closer than 5 m.
Determination of the resistance value is performed according to the worst result obtained.
The most common mistakes

When installing a grounding device, the following mistakes are most often made:
- The circuit is connected to the wrong point in the electrical installation, for example, directly to the equipment. It must be connected to the main ground bus.
- Instead of a circuit, a water supply, heating or other pipe is used. They can be grounding structures with some reservations and not always.
- Lack of connection of the neutral conductor in the grounding device, as well as the installation of separate circuit breakers in the neutral conductor.
- Use as earthing switches of fittings, buried metal objects, working zero, fences.
- Use of ground loops made of small section elements.
- Weld seam less than 10 cm.
- Welded seams are not treated against corrosion with bituminous mastics.
- The outline strip that has come out of the ground is not colored. It should be painted with black or yellow-green paint.
- Insufficient length of horizontal and vertical ground electrodes.
- Insufficient penetration of horizontal elements.
- They establish a ground loop, but do not ground the main communications, consisting of metal elements: water supply, heating, gas supply, sewerage.
It must be possible to disconnect the grounding device from the electrical installation for measurements, that is, the strip that comes out of the grounding device must be disconnected. This possibility is provided by the bolted connection of the elements.
If the installation is made in accordance with all the rules, it was possible to properly measure the resistance and the indicators correspond to the norm, the building is reliably protected from short circuits and its consequences.








