Modern LED lamps guarantee a high level of illumination and consume very little energy. The advantages of the illuminators are indisputable, but you should find out if the LED bulbs get hot during long-term operation. To do this, you will need to understand the design of the devices, and then draw the appropriate conclusions about the procedure for use.
Features of the design of LED lamps
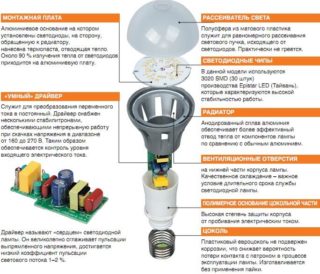
The design of the products is based on the principle of using a large number of LED chips placed on a special heat-dissipating substrate. All components are securely covered under a matte, light-transmitting hemisphere. In addition to the base, which serves as a radiator, the light bulb includes the following mandatory components and elements:
- light diffuser (cap);
- printed circuit board with a set of point LED emitters;
- a radiator that removes heat from diode crystals;
- electronic control unit - driver;
- lamp base.
To get acquainted with the internal parts of the LED lighting fixture, you will need to completely disassemble it, separating the hemispheres of the cap, held together by reliable latches.
Where does heat energy come from and where is it spent
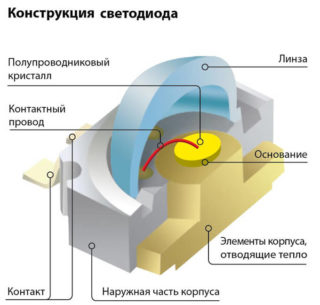
Their work is based on physical principles that are very different from those processes that are observed in fluorescent or conventional incandescent lamps. LED bulbs do not heat up in the truest sense of the word. They do not dissipate thermal energy into the surrounding space, since they spend it on heating the inner crystal of the emitter.
If you do not purposefully remove heat from the semiconductor junction, the crystal of the element under certain conditions runs the risk of overheating and then completely burning out. Therefore, devices that are part of high-power LED products require special heat removal. The design of LED luminaires with separate bulbs placed in them provides for a special substrate that performs this function. This technique makes it possible with a high degree of probability to keep the LEDs intact and extend their service life.
How much the LED crystal heats up
- the temperature to which the air around the light bulb naturally warms up;
- the material of the radiator used to remove heat energy;
- passport power of one light bulb.
The possibility of overheating the crystal depends on the manufacturer that produced the LED, as well as on the quality of its assembly.
The average temperature in the area of the lens of the light bulb ranges from 65 to 70 degrees on the standard Celsius scale.
Which light bulb does not heat up

Lamps that do not produce heat do not exist in nature. This is explained by the physical principle of the formation of light radiation. From the point of view of the classical science of physics, any light bulb is a converter of electrical energy into its variety. In this case, no more than 40 percent of the power taken from the current source is converted into light radiation. Its residues are dissipated in the form of heat into the environment, the more, the lower the efficiency of this light element.
Three different options are considered and compared as an example:
- The upper area of the bulb near an incandescent lamp, for example, with one hundred watts of power, heats up to almost 280 ° C, the base temperature reaches 70 ° C.
- In a compact fluorescent illuminator with a power of 15 W, its base overheats most of all - the place where the spiral is located. Its temperature sometimes reaches 130 ° C. At the same time, the heating of the basement part in the area of the electronic ballast does not exceed 60 ° C.
- In LED lamps, the metal-plastic base of the body heats up the most. For this reason, it is in this place that a radiator is installed, which allows heat to be removed from the LEDs and prevents the light bulb from warming up above the permissible rate.
If we consider the issue of the heat output of lamps by their heating of the surrounding space, LEDs do not belong to "cold" lamps, which in certain situations are allowed to be touched by hands.
Advantages of a gentle temperature regime
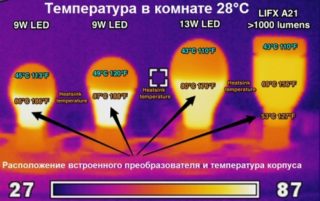
Features of heat removal from LED lamps, which prevent the possibility of heating its working parts above 65-70 degrees, emphasize their advantages over other emitting products. The absence of mercury vapors harmful to the inhabitants of the apartment, as is observed in fluorescent devices, as well as the service life incomparable with other models of lighting fixtures, turn these lamps into a real gift for the user.
The advantage of LED products is that, despite internal heat losses, they still guarantee tangible energy savings.
LED lamps perform best in well-ventilated areas with artificial (forced) ventilation. And placing such lamps in hot and space-limited places that do not have free access and circulation of air masses means endangering the products.
Modern lighting fixtures based on LED lamps belong to the category of relatively new products that need constant monitoring and conditioning. As long as this process continues, each user has the opportunity to try out this original novelty and test it in various modes of operation.
Questions about why some of the energy of the lamps is spent on heat, and whether LED lamps are heated for the home, cannot be answered unequivocally. It all depends on the approach to evaluating the process, which in this case mainly occurs inside the LEDs and only partially extends to the surrounding space.

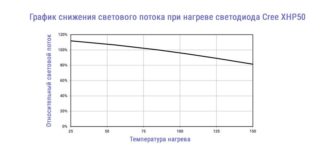








If there is an active resistance, then there will definitely be heating