For the arrangement of the power supply, draft drawings are required. To understand the drawing and read it, you need to know the legend. The circuit breaker on the diagram is indicated in different ways, which often leads to misunderstandings, errors in the assembly of electrical panels and wiring.
Symbols of electrical elements and types of circuits

The initial question that every electrician usually faces is the design documentation of the room or facility that needs to be electrified. Before proceeding with the installation of the equipment, a qualified technician should familiarize himself with the accompanying documents.
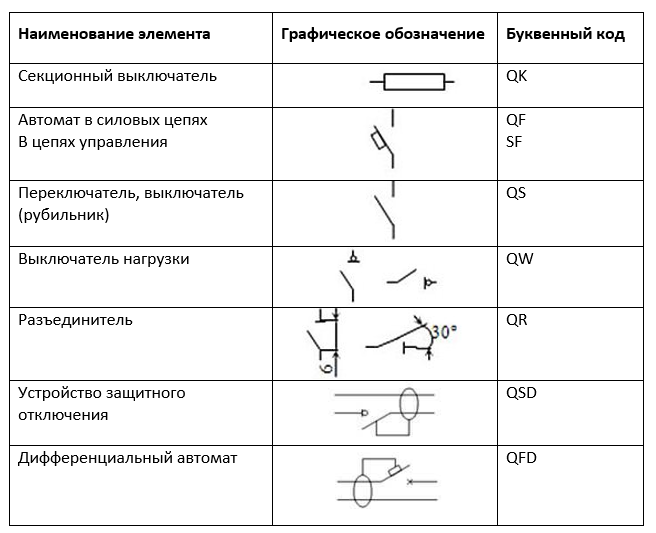
Equipment and elements in the diagram can be designated both by letter and graphic. Drawings are developed in accordance with GOSTs and the rules for marking equipment and elements on drawings and plans. A detailed description and requirements for electrical circuits are given in GOST 2.702-2011 ESKD. In addition to graphic and letter designations, nominal dimensions are affixed to the diagrams.
There are many types of different schemes. In electrics, three main types are most often used. Functional displays the main components of the device, without detailed detail. They look like a set of separate blocks connected in a certain way. The diagram gives an overview of the operation of the facility.
The schematic diagram contains detailed instructions for each element, its contacts and connections. It can describe both a single device and an electrical network. Single-line diagrams indicate power circuits. The method of management and control is described on a separate sheet. If the device is not complex, everything is placed on one document.
The wiring diagrams indicate the elements and their exact location. If this is a wiring in an apartment or house, they indicate the place of installation of switches, lamps, sockets. Distances and ratings are also put down. Indicate the position of the parts, the order and method of their connection.
The residual current device (RCD) and the difavtomat in the diagram do not have a specific geometric outline. For their graphical implementation, the image of blocks and dynamic blocks is used. Each device on the diagram is assigned a letter marking and a positional number.
In addition, the parameters of the elements that are in the drawing are applied. They describe the basic data about the element so as not to make mistakes during installation and select the appropriate device. These symbols are used to draw up drawings of power supply, power equipment and electric lighting. And also in the basic single-line diagram of electrical panels.
Circuit breaker designation in the diagram

The conventional graphic designation of the machine in the diagram is due to GOST 2.755-87 ESKD, alphanumeric - GOST 2.710-81 ESKD. There are no special labeling requirements, so electricians often use their own values and labels. You can find documentation when the definition of a switching device differs in different projects.
Each designer, completing the diagram, can depict an RCD at his discretion. It is enough to indicate the UGO (conventional graphic symbols) and their decoding in the explanations to the diagram.
Depending on the characteristics of the device, the elements have different letter symbols, as well as the following graphic designations on electrical diagrams.
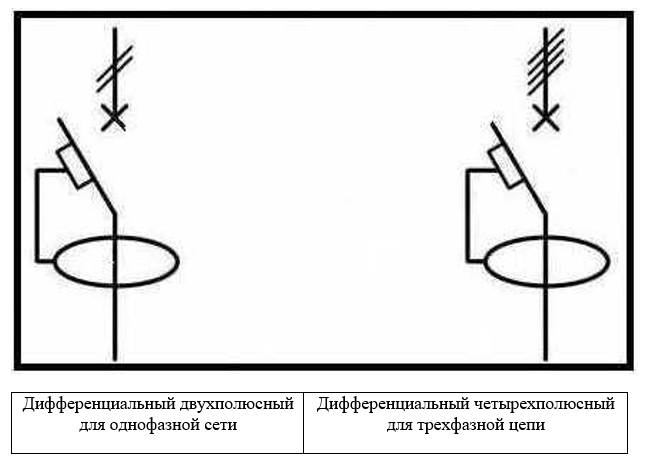
It is recommended to position the circuit breakers as, QF1, QF2, QF3. Switch disconnectors - QS1, QS2, QS3. Fuses in the diagrams are shown as FU with a serial number, where the coding of the letter Q stands for a switch or switch for power circuits, and F is a protective one. This combination is quite applicable not only to ordinary automata, but it can be used to designate a dif automaton in the diagram.
For RCDs, use the QSD combination, the designation of the differential machine on the diagram looks like QFD.
RCD designation in a single-line diagram
This is a type of circuit breaker, the function of which is to disconnect the network or its part when a certain differential current level has been exceeded. The device improves electrical safety, prevents emergencies, both in the industrial sector and at home. The RCD connection diagram is simple, but installation flaws can lead to serious troubles.
So you can designate an RCD on a schematic diagram.
RCDs, together with other elements in project documentation, are most often performed conditionally, which makes it difficult to decipher the principle of operation of both the entire circuit and individual elements. The image of the protective device may look like a conventional switch. But in a non-linear circuit, it represents two switches located in parallel. On a single line - elements, wires and poles are depicted symbolically.
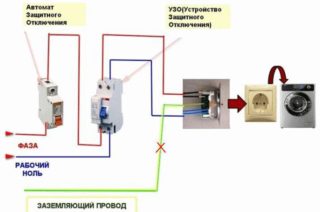
Any schematic image must be correctly drawn up, and then read. The smallest flaw can lead to a malfunction of the RCD or the entire system. It is important to consider the following common mistakes:
- Zero and ground are connected after the protective device. If the diagram is misinterpreted, the neutral can be connected to an open part of the electrical installation or to a neutral protective conductor.
- If the device is connected with an incomplete phase, a false operation of the machine occurs.
- Incorrect connection of the conductors in the sockets will cause the device to operate, even if nothing is plugged into the outlet.
- The connection of neutral conductors of two machines leads to uncontrolled shutdowns.
- A common mistake is the situation when the phases and zeros related to different devices are reversed.
- Non-observance of polarity leads to the movement of currents in one direction. Carefully familiarize yourself with the location of the terminals before installation.
A preliminary scheme is always executed, taking into account possible errors occurring in the network. If the document is drawn up correctly, the operation of the security device is effective.
It is important to remember about safety precautions. It is necessary to periodically inspect the wires, if they are damaged, the RCD is triggered and the power supply stops. Therefore, it is better not to hesitate with the repair.
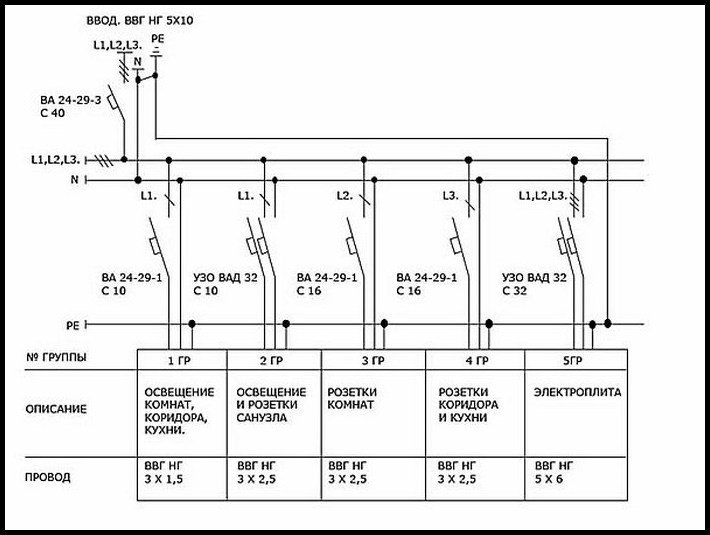
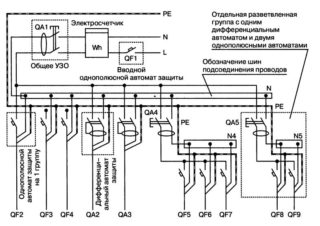
An example of a real project

A single-line schematic diagram (OPS) is nothing more than a drawing of a plan, for example, an apartment. Distribution groups should be indicated on it. To do this, it is necessary to measure all walls and draw a drawing to scale. It will take several copies to depict a separate group on each.
Distribution groups are points that will be connected to one automatic unit of the apartment panel. All wiring cannot be connected to the same group. Otherwise, you will need a powerful cable that will be able to withstand the load of all devices.
Distribution groups may look like the following depending on the number of rooms and the availability of energy-consuming devices.
- lighting of the room, hallway and kitchen;
- lights and sockets in the toilet;
- sockets in the living room;
- sockets in the corridor and kitchen;
- electric stove.
Rooms with high humidity are recommended to be connected in a separate group, for which the installation of an RCD is required. If there are small children in the apartment, a protective device is connected to each group.
A schematic or single-line diagram is necessary for the correct connection of the switchboard and distribution groups.
This example shows a 3-phase power connection. The entire apartment is powered by a 5-core lead-in cable with a cross section of 10 mm2. The phases are numbered as L1, L2, L3, grounding is PE, which closes with zero. An introductory machine (VA) switches off all machines of groups that are marked in the same way.
The drawing makes it possible to determine the number and brand of the necessary protective devices. Calculate the number of switches and sockets, as well as how many meters of cable will be required.
All wire connections must be in junction boxes. A separate box is recommended for each room. If, for example, a gas boiler and other electrical appliances are located in the kitchen, two junction boxes are required.
There are no special requirements for the installation of sockets and switches. They are installed so that it is convenient. In the kitchen and workplace, sockets are placed above the table.
Stationary household appliances, boilers, hoods, towel dryers are connected directly through the terminal blocks. Internet and TV sockets can be combined with electrical ones.
The designation of the differential automaton in the diagram
The differential automatic device combines a residual current device and a circuit breaker in one device, which differs from an RCD. In this case, the graphic on the diagram looks like this.
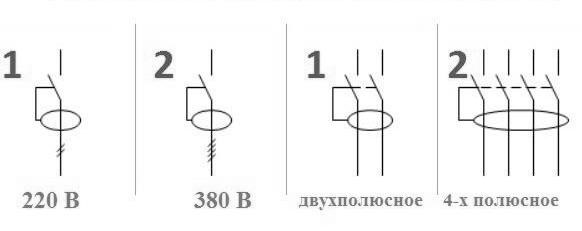
If alphanumeric designations Q1 are accepted for RCDs, then for RCBOs (residual current circuit breaker) - QF1. The letters indicate the functions of the device, and the numbers indicate its serial number in the diagram. Another letter combination is QF1D, where D stands for "differential".
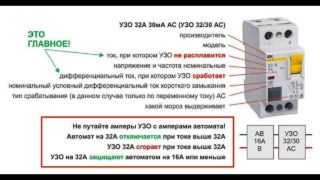
The main characteristic of such devices is the rated operating current at which the machine remains on for a long time. These indicators are strictly standardized, and the current can have values: 6 Amperes; 10; sixteen; 25; 50, etc.
Another important characteristic is speed. The current indicator is indicated by the letters B, C, D before the value of the rated current. For example, the combination C16 says that the automatic speed controller C is rated for a rated current of 16 amperes.
The differential permissible indicator fits into the following row: 10; thirty; 100; 500 milliamps. On the body of the device it is marked with a "delta" sign with a number corresponding to the leakage current.
The operational capabilities of the machine are designed for a rated voltage of 220 Volts for a single-phase circuit and 380 for a three-phase circuit.
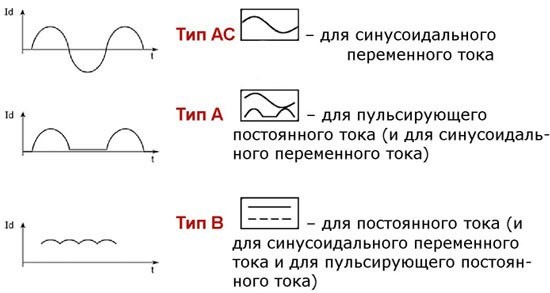
Difautomats are distinguished by types, depending on the leakage current and are marked with the following letter indices:
- A - responsive to AC or DC pulsating current leakage;
- AC - designed for operation with a leakage with a constant component;
- B is a device type that includes both of the previous options.
This characteristic can be marked with a small figure indicating the type of current.
Devices operate on a selective basis, have the ability to delay the response time. This ensures selective disconnection of the device from the network and the stability of the protection system. This characteristic is denoted by the letter S and gives a delay of 200-300 milliseconds. The G mark corresponds to 60-80 milliseconds.
Since the starting currents exceed the operating value, the protection is designed in such a way that the electromagnetic shunt trip trips the device when the current is several times higher than the nominal size.
The regulatory documents contain many special ciphers and signs.Most of them are practically not used in everyday life. To read the electrical diagram correctly, you need to know the basic designations and take into account some of the nuances. One of them is the country of manufacture of equipment, cables or wiring, since there is a difference in marking and symbols, which makes it difficult to correctly interpret the drawing.