Electrical devices in operation must be grounded. Depending on the purpose, it can be working or protective. The first is for the correct operation of the devices, and the second is for the protection of people. The principle of operation of one and the second is different.
- The main goals and objectives of grounding
- Protective grounding principle
- Lightning protection
- Surge protection
- Protecting people
- The difference between working grounding and protective
- Protective grounding requirements
- Household grounding
- Grounding operation in case of electrical faults
- How the parameters of the main grounding elements are calculated
- Installation of earthing switches
The main goals and objectives of grounding

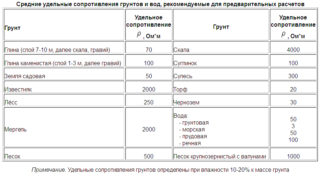
The soil is able to neutralize the electric current, since the degree of its voltage is zero. Resistance is the main indicator of a grounding device, by which one can judge its quality and ability to fulfill its purpose. Resistivity depends on the composition of the soil, the presence of chemicals in it - acidic or alkaline, moisture, looseness. Depending on the composition of the soil, it may be necessary to use a special grounding kit or to completely replace the soil for the correct operation of the grounding devices.
Grounding is the connection of any device, electrical installation or part of the network to a grounding device. It is a ground electrode and grounding conductors through which the current flows into the ground and is neutralized.
There can be several earthing switches. In a distributed scheme, they are located along the perimeter of the object, the electrical network of which must be secured. The conductive part (earthing switches) are usually made of metal. Grounding electrodes are supplied to them, which have direct contact with the soil.
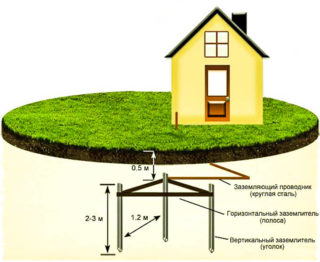
The grounding device is mounted along the loop. A ground loop is a series of electrode conductors that are driven into the ground. Their length is 3 meters, they are located at a short distance from each other. A horizontal metal strip is used as a connection, which is laid in the soil at a shallow depth - up to 1 meter. The connection to the electrodes is carried out using conventional welding. In special grounding kits, parts of the equipment are connected by a thread, which does not in any way affect the working properties.
Working grounding is necessary in the following cases:
- Protecting equipment from static electricity build-up. Natural processes such as lightning can affect the current flowing in a circuit, causing damage to equipment. Electrodes installed in the ground drain off excess current.
- Protection of the network against short circuits.
- Overvoltage protection.
An example of a working ground is a lightning rod that is connected to the electrodes. Especially important in generators, transformers.
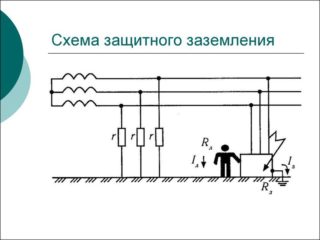
Protective grounding principle
Protective grounding is a set of measures that are aimed at protecting equipment and people who work with it. It is used to eliminate electromagnetic interference arising from a nearby device, as well as to neutralize interference during switching in the power circuit.
Lightning protection
The air environment is a section with high resistance, but the discharge has a power exceeding this resistance, therefore it breaks through it.On its way from the upper atmosphere to the ground, lightning selects areas with the least resistance - wet areas, walls, trees and water droplets. This explains the fact that the discharges often fall into the tree - it has less resistance than the air around it. When it enters the building, the current also passes through the areas with the least resistance - these are metal pipes, electrical appliances or their metal parts, damp walls. If the device is not grounded, touching it while charging can be fatal.
When a lightning rod is installed on the roof, the charge enters it, and then moves into the ground and is neutralized. It is important that currents do not propagate into the object, therefore the materials that are used for arranging grounding have low resistance. According to the rules, it should not exceed 4 ohms. The lightning rod itself must be connected to the electrodes in the ground.
Surge protection

Electronic equipment is sensitive to power surges or powerful electrical installations operating in their radius. A sudden lightning strike in the vicinity can damage the electronics.
As an example: during a thunderstorm, an excess charge may occur in the copper cable that connects the houses and through which the current flows. The charge, as its size increases, can destroy the cable. In this case, an SPD is installed on the power line - an impulse overvoltage protection device so that the excess charge is released into the ground.
Protecting people
Instrument cases, all metal elements are capable of conducting current. If you touch an ungrounded appliance that has accumulated static electricity, you may receive severe shock. This will affect primarily the cardiovascular and nervous system. Rubber shoes, rubberized gloves, and an absolutely dry room help to reduce the impact, but people rarely walk around an apartment or office in rubber boots. Connecting the third wire to the device body, and then connecting it to the electrodes, allows excess current to be disposed of into the ground.
In old private and apartment buildings, grounding measures were not carried out, therefore all electrical appliances pose a potential danger to people.
Self-made devices can look like this: a wire is connected to the body of the device, which is brought out to the street and connected to a metal product driven into the ground (pipe, corner, bucket, fittings). These products are good conductors of current, unlike the human body, so the current selects the metal and goes into the ground.
The difference between working grounding and protective
In the functional (working) grounding scheme, all current-carrying structures are connected to electrodes installed in the ground. For the correct operation of the working grounding, fuses are also used, which take the voltage on themselves and fail.
A functional earthing is provided if the manufacturer's instructions and requirements are attached to the devices that protect the device.
More requirements are imposed on a protective grounding device, since it has more important tasks: saving people's lives.
| Purpose of the working grounding device | Purpose of protective grounding |
| Large instrument power | Three-phase appliances less than 1 kW |
| Electronic sensitive equipment | One- and two-phase devices not in contact with the ground |
| Medical devices | Equipment with a power of more than 1 kW |
| Electronic technology, which is the carrier of important information | In circuits with fuses and a neutral protective conductor |
The most reliable grounding is provided in the electrical circuit of the house. The cables that fit into each outlet must be three-wire. The third conductor is connected to the ground and conducts static electricity, and also prevents short circuits and lightning from entering the building.
Protective grounding requirements
Nuances that affect the functionality:
- Soil resistance due to its physical and chemical characteristics. Wet clay, graphite chips, peat, salt marshes or seawater conduct current best. Worse - dry sand or hard rocks - granite, crushed stone, quartz, asphalt, concrete.
- The area of contact of the ground electrode with the soil. The larger the area, the more favorable conditions are created for the flow of current, the faster it happens. You can increase the area by installing more electrodes along the contour of the building. In this case, they are joined together with a steel plate into a single unit. If you increase the size of one electrode, the total area will also increase. The installation of a vertical metal contour helps to increase the area if the lower layers of the soil have more resistance than the surface ones.
Since it is difficult to achieve ideal soil resistance, devices are designed based on its characteristics. Each electrical installation has its own standards for the resistance of grounding devices. For example, for an electrical substation with a voltage of more than 100 kW, the resistance should not be more than 0.5 Ohm, and for a home network with a TT system, as well as the use of automatic shutdown, up to 500 Ohm.

Metal earthing switches should not be covered with paints and varnishes. Sometimes an underground part of a building with metal structures is used as a grounding device - electrically conductive concrete with reinforcement inside. Gas metal pipes cannot be used to solve the grounding problem.
According to the Rules for the Installation of Electrical Installations, grounding is subject to:
- Networks with voltages above 380 V.
- Extremely hazardous and outdoor installations.
Parts of the equipment to be grounded and grounded:
- Enclosures for electrical equipment.
- Secondary transformer winding.
- Electric device drives.
- Distribution boards, cabinet frames.
- Equipment metal structures.
- Iron cable sheath.
If the voltage does not exceed 42 VAC or 110 VDC, grounding is not required.
Household grounding

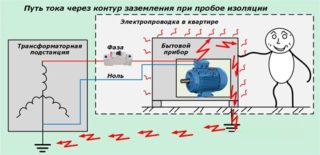
Most of the accidents in the domestic environment are associated with touching the device, which has damage to the insulation. The human body in this case is a current conductor. Electric hobs, washing machines and dishwashers, heating radiators, microwave ovens, boilers, PCs, dishwashers - all these are metal structures that conduct electricity well and can be harmful to health without grounding.
A short circuit is a contact between the phase and neutral wires in the network, which leads to the operation of the emergency protection and disconnection of the device from the power supply. Most often, it is not a short circuit that occurs, but a leakage of current that accumulates in the housing of household equipment. Doing so can lead to electric shock.
For human safety, it is necessary to install sockets with earthing contacts. A three-wire cable must be connected to the outlet. With a two-wire and three-wire system, grounding is equipped in different ways - from a junction box or an electrical panel.
Gas, water or district heating pipes cannot be used as a ground electrode.
Grounding operation in case of electrical faults
In the second option, the current leakage may not be significant, the equipment protection device will not react to voltage and will not turn off the device. The person may receive a minor blow.
If the body is not grounded, but the RCD is installed, it will work in 0.02 seconds after a person touches the body of the device. This time is not enough to harm health.
The most effective circuit from the point of view of safety is the presence of grounding and an RCD. In the event of a current leakage and its transition to the ground, the RCD reacts and turns off the device.
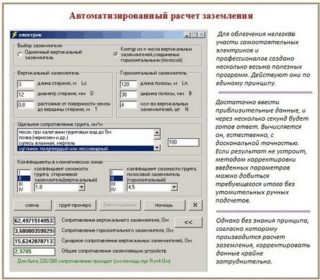
How the parameters of the main grounding elements are calculated
- soil resistance in this area;
- length, thickness, diameter of electrodes, as well as their number.
In practice, in all cases there are discrepancies with the planned work plan, since the soil indicator must be analyzed more accurately. It is almost impossible to do this: on 100 square meters, it is necessary to drill about 100 mini mines up to 10 m deep in order to assess the soil layers, its composition and the inclusion of elements - clay, limestone, sand and other components.
Installation of grounding devices is carried out according to the main principle of grounding: the presence of a margin of safety, having averaged values of the parameters. The lower the resistance obtained, the better for all electrical appliances and people.
Installation of earthing switches
Vertical electrodes perform their functions more efficiently, since they can be installed at greater depths. When laying horizontally at a shallow depth, the resistance increases, especially in winter, when the upper layers of the soil freeze through.
For electrodes, pins are used, the length of which is more than 1 meter (usually 1.5 m). It is easy to hammer such structures into the ground using a conventional hammer; the connection is made in a horizontal plane at least 0.5 m in depth.