For the correct choice and organization of the power line, it is necessary to take into account the parameters and load of the conductors. They are a metal thread made of copper, aluminum, steel, zinc, titanium, nickel and provide the transmission of current from its source to the consumer. Conductors have a cross-section - this is a figure formed from their dissection by a plane of the transverse direction. If it is chosen incorrectly, the line will fail or light up during power surges.
- Cross-sectional area as an electrical quantity
- Calculation goals
- The ratio of the cable diameter to its cross-sectional area
- Calculation of the cross-section of a stranded conductor
- Features of self-calculation
- Using a caliper
- Using a ruler and pencil
- Correspondence table of wire diameter and cross-sectional area
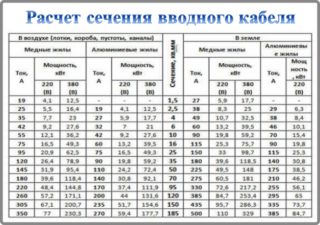
- Determination of the conductor cross-section at the input
- Calculating the wire size for a line of outlets
- Cross-section selection for a three-phase 380 V line with several devices
- Cross-section of wires in old buildings and maximum load
- Which cable to choose for apartment wiring
Cross-sectional area as an electrical quantity
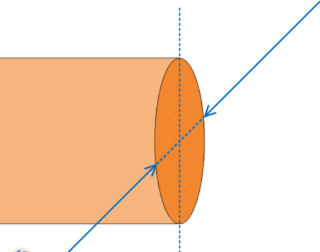
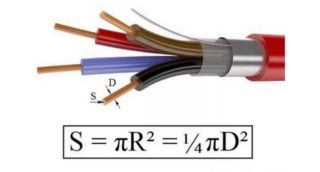
As an example of a section, you can consider sawing a product at an angle of 90 degrees relative to the transverse axis. The outline of the resulting shape is determined by the configuration of the object. The cable looks like a small pipe, so when sawing, a figure will come out in the form of two circles of a certain thickness. If you cross-cut a round metal rod, you get a circle shape.
In electrical engineering, the area of the SS will mean the rectangular cross-section of the conductor in relation to its longitudinal part. The cross section of the veins will always be round. The parameter is measured in mm2.
Novice electricians can confuse the diameter and section of the elements. To determine what is the cross-sectional area of the vein, you need to take into account its round shape and use the formula:
S = πхR2, where:
- S is the area of the circle;
- π - constant 3.14;
- R is the radius of the circle.
If the area index is known, it is easy to find the resistivity of the material of manufacture and the length of the wire. Next, the current resistance is calculated.
For convenience of calculations, the initial formula is transformed:
- The radius is ½ of the diameter.
- To calculate the area, π is multiplied by D (diameter) divided by 4, or 0.8 is multiplied by 2 diameters.
In the calculations, the diameter indicator is used, since its incorrect selection can cause overheating and ignition of the cable.
Calculation goals
It is necessary to calculate the parameters of the cross-sectional area of the conductor for several purposes:
- obtaining the required amount of electricity to power household appliances;
- exclusion of overpayments for unused energy resources;
- wiring safety and fire prevention;
- the ability to connect high-power equipment to the network;
- prevention of melting of the insulating layer and short circuits;
- correct organization of the lighting system.
The optimal wire cross-section for lighting is 1.5 mm2 for the line, 4-6 mm2 at the input.
The ratio of the cable diameter to its cross-sectional area
Determining the cross-sectional area of conductors using the formula takes a long time. In some cases, it is appropriate to use data from a table. Since a copper cable is used to organize modern wiring, the parameters are entered in the table:
- diameter;
- section in accordance with the indicator of the diameter;
- maximum load power of conductors in networks with voltages of 220 and 380 V.
| Core diameter, mm | Section parameters, mm2 | Current strength, A | Copper conductor power, kW | |
| 220 V network | 380 V network | |||
| 1,12 | 1 | 14 | 3 | 5,3 |
| 1,38 | 1,5 | 15 | 3,3 | 5,7 |
| 1,59 | 2 | 19 | 4,1 | 7,2 |
| 1,78 | 2,5 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 |
| 2,26 | 4 | 27 | 5,9 | 10 |
| 2,76 | 6 | 34 | 7,7 | 12 |
| 3,57 | 10 | 50 | 11 | 19 |
By looking at the data in the corresponding columns, you can find out the necessary parameters for the power line of a residential building or production facility.
Calculation of the cross-section of a stranded conductor
- The indicator of the cross-sectional area of one core is found.
- Cable conductors are recalculated.
- The quantity is multiplied by the cross section of one core.
When connecting a stranded conductor, its ends are crimped with a special sleeve using crimping pliers.
Features of self-calculation
Using a caliper
The method is justified if the parameters of a truncated or defective cable are measured. For example, VVG can be designated as 3x2.5, but in fact be 3x21. The calculations are done like this:
- The insulation cover is removed from the conductor.
- The diameter is measured with a caliper. You will need to position the wire between the legs of the instrument and look at the scale markings. The integer is at the top, the decimal is at the bottom.
- Based on the formula for finding the area of a circle S = π (D / 2) 2 or its simplified version S = 0.8 D², the cross section is determined.
- The diameter is 1.78 mm. Substituting the value in the expression and rounding the result to the nearest hundredth, you get 2.79 mm2.
For domestic purposes, you will need conductors with a cross section of 0.75; 1.5; 2.5 and 4 mm2.
Using a ruler and pencil
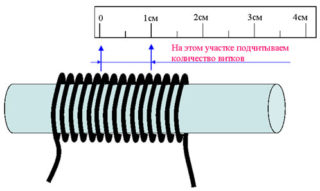
In the absence of a special measuring device, you can use a pencil and a ruler. Operations are performed on a test image:
- An area equal to 5-10 cm is stripped from the insulating layer.
- The resulting wire is wound around a pencil. Full turns fit tightly, there should be no space between them, the "tails" are directed up or down.
- Ultimately, a certain number of turns should turn out, they need to be counted.
- The winding is applied to the ruler so that the zero division coincides with the first winding.
- The length of the segment is measured and divided by the number of turns. The resulting value is diameter.
- For example, there are 11 turns, which take 7.5 mm. When dividing 7.5 by 11, 0.68 mm comes out - the diameter of the cable. The section can be found using the formula.
The accuracy of the calculations is determined by the density and length of the winding.
Correspondence table of wire diameter and cross-sectional area
If it is not possible to pass diameter testing or make a calculation upon purchase, it is allowed to use a table. The data can be photographed, printed or rewritten, and then used to find a standard or popular core size.
| Cable diameter, mm | Conductor section, mm2 |
| 0,8 | 0,5 |
| 0,98 | 0,75 |
| 1,13 | 1 |
| 1,38 | 1,5 |
| 1,6 | 2 |
| 1,78 | 2,5 |
| 2,26 | 4 |
| 2,76 | 6 |
| 3,57 | 10 |
When buying an electric cable, you will need to look at the parameters on the label. For example, VVNG 2x4 is used. The number of veins is the value after "x". That is, the product consists of two elements with a cross section of 4 mm2. Based on the table, you can check the accuracy of the information.
Most often, the cable diameter is smaller than stated on the package. The user has two options - to use a different one or choose a cable with a larger cross-sectional area in diameter. Choosing the second, you need to check the insulation. If it is not solid, thin, different in thickness, stop at the products of another manufacturer.
Determination of the conductor cross-section at the input
The selection of the cross-section is carried out so that the permissible current of the conductors for a long period is greater than the rating of the machine. For example, in the house, a three-core VVGng copper conductor, laid in an open way, was launched at the input. The optimal section is 4 mm2, so you need VVGng 3x4 material.
After that, the indicator of the conventional shutdown current for the machine with a rating of 25 A is calculated: 1.45x25 = 36.25 A. copper conductor with a cross section of 6 mm2 and a permissible limiting current of 42 A.
Calculating the wire size for a line of outlets
Each electrical appliance has its own power indicators. They are measured in watts and are indicated in the passport or on a sticker on the case. An example of finding a cross section will be a power line for a 2.4 kW washing machine. The calculations take into account:
- wire material and installation method - three-core VVGng copper cable hidden in the wall;
- cross-sectional features - the optimal value is 1.5 mm2, i.e. you will need a 3x1.5 cable;
- use of an outlet. If only an automatic machine is connected, the characteristics will be enough;
- the protection system is an automatic machine with a rated current of 10 A.
For double sockets, a copper cable with a cross section of 2.5 mm2 and an automatic machine with a rating of 16 A are used.
Cross-section selection for a three-phase 380 V line with several devices
Connecting several types of household appliances to a three-phase line provides for the flow of the consumed current through three cores. Each of them will have a smaller value than a two-wire one. Based on this phenomenon, it is allowed to use a cable with a smaller cross-section in a three-phase network.
For example, a generator with a power of 20 kW and a total power in three phases of 52 A is installed in a house. Based on the values in the table, it turns out that the optimal cable section is 8.4 mm2. Based on the formula, the actual cross section is calculated: 8.4 / 1.75 = 4.8 mm2. To connect a 20 kW generator to a 380 V three-phase network, a copper conductor is required, the cross-section of each core of which is 4.8 mm2.
Cross-section of wires in old buildings and maximum load
In the high-rise buildings of the Soviet period, aluminum wiring is used. Taking into account the correct connection of the nodes in the switch box, the quality of the insulation and the reliability of the connection contacts, it will last from 10 to 30 years.
If it is necessary to connect equipment with high energy consumption in houses with aluminum wiring, the cross-section and diameter of the conductors are selected based on the power consumption. All data are shown in the table.
| Current, A | Maximum power, VA | Cable diameter, mm | Cable section, mm2 |
| 14 | 3000 | 1,6 | 2 |
| 16 | 3500 | 1,8 | 2,5 |
| 18 | 4000 | 2 | 3 |
| 21 | 4600 | 2,3 | 4 |
| 24 | 5300 | 2,5 | 5 |
| 26 | 5700 | 2,7 | 6 |
| 31 | 6800 | 3,2 | 8 |
| 38 | 8400 | 3,6 | 10 |
Which cable to choose for apartment wiring
In apartments and houses, it is allowed to use a wire marked:
- PUNP is a flat conductor with copper conductors in a PVC sheath. Designed for a voltage of 250 V at a frequency of 50 Hz.
- VVG / VVGng - double PVC-coated flat copper cables. They are used inside and outside structures, they are not subject to fire. They are available with 2, 3 and 4 veins.
- NYM - copper wire for internal single line. It has an insulating PVC sheath and an outer covering, conductors with and without grounding.
When choosing the number of cores, it will be necessary to take into account the ability of current conductivity per unit section. In this case, it is better to make the apartment network from a single-core wire, the thickness of which is greater. Multi-core elements can be bent many times, electrical appliances can be connected to them. Only a cable with thin cores will be of high quality.
The correct cross-section of conductors, taking into account the power of the equipment and the type of network are important factors when organizing a power line. The cable diameter can be calculated independently in several ways. Based on these readings, it is easy to determine the cross-section of the cores by formulas or using a table.