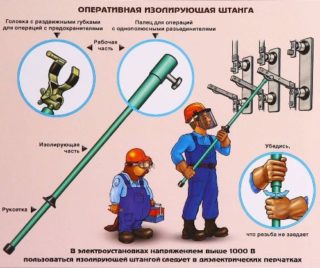
When working in electrical networks and on existing electrical installations, in accordance with the requirements of the PUE, electrical protection means are necessarily used. They are designed to ensure the safety of operating personnel when working at electrical substations and other facilities. To understand the structure and features of their use, it is important to familiarize yourself with the existing classification of protective equipment.
Classification of electrical protective equipment

Electrical protective equipment is classified according to features such as functionality and voltage value in networks, where, according to the PUE, their use is considered mandatory. In accordance with the first of these factors, they are all divided into main and additional equipment. According to the type of networks where these tools are applied selectively, the following options are distinguished:
- Basic and additional equipment for networks with an effective voltage below 1000 Volts.
- Exactly the same classification is adopted according to the PUE for power lines above 1000 Volts.
In all these cases, the joint use of basic electrical protective equipment and complementary inventory and equipment is practiced.
According to the method of application, they are all divided into individual and collective protective items, the purpose of which is clear from their name. Means for protection against e / m fields, as well as for individual purposes, are considered as a separate category. The latter are necessary to create safe working conditions for each individual member of the team of electricians servicing a high-voltage line or electrical installation.
Equipment check

To maintain protective equipment in working order, in accordance with the PUE, their systematic accounting and periodic testing are organized. To do this, at any operating facility, representatives of the safety service establish a special journal, which indicates the following mandatory information:
- name;
- inventory number;
- date of last and subsequent test.
To identify damaged and in need of testing inventory, its systematic examinations are organized.
The frequency of inspections of all categories of protective equipment is established by the administration of each specific facility, the exact dates are approved by its head. Upon their completion, the results of the inspection carried out are also recorded in the register. In addition, all regularly used electrical protective equipment is checked immediately before starting work. With this approach, any employee, as necessary (during the elimination of an accident or during operational switching), is always confident in their availability and readiness to perform their functions.
At the end of the next test, a special tag must be hung or glued to each sample of protective equipment for an electrician.
The tag indicates:
- voltage and current values used during testing;
- exact date of the next product inspection;
- the name of the unit to which it is assigned;
- inventory or serial number.
All these data duplicate the information, in accordance with which the records of protection means are kept in the journal.
General terms of use
The procedure for using electrical protective equipment and equipment is described in detail in the regulatory documentation regarding the observance of safe working practices in installations and switchboards. The requirements of the PUE provide for the following rules for their use:
If it is necessary to work with a specific inventory, first of all, its serviceability (suitability for use) is carefully checked.
- The appearance of the protective equipment should be carefully examined. It is not allowed the presence of any dirt, as well as damage to the case.
- A prerequisite is the inadmissibility of using insufficiently dry rubber products (with traces of leaking liquids, for example). They are not recommended for use in winter frost and during rainfall.
- Any protective equipment must have a check mark indicating the date of the next test.
If at least one of these points is violated, the existing equipment is unsuitable for use, since when working with it, accidental injury to a person is possible. According to the current rules, it is removed from the kit in order to eliminate malfunctions or conduct unscheduled tests.
When planning work operations and operational switching in rooms with a high level of humidity, rubber protective products designed specifically for these purposes are allowed for use.
Requirements for individual species

The general set of protective equipment according to the PUE includes not only special equipment, but also a special current tool. Its main purpose is to protect a person working in power grids from direct contact with high potential. A number of special requirements are imposed on specific types of protective equipment of any type, which are listed below:
- The individual items included in the set (rubber gloves, for example, as well as rubberized shoes and other things) are kept in a perfectly clean condition. Only in this case they are able to perform their functions, consisting in reliable isolation of the human body from open conductive parts of electrical equipment.
- Protective devices with gripping handles (they are used when working in electrical installations with any voltage) must have restraining rings on their holders.
- With the tool, he takes the handles only in areas located before the limit ring.
The latter requirement is due to the fact that the standards determine the maximum permissible clearance to live parts, which is considered safe. In this case, special attention is paid to the insulated part of the holder, the length of which is made sufficient in order to provide guaranteed protection against electric shock.
All means used in the maintenance of power supply systems are designed to operate in a given voltage range. As a rule, this parameter is applied to the tool body or in a special place in protective equipment. In the PUE it is separately stipulated that its real value often differs from the declared value, therefore, one should focus on the value taken with a small margin.
Main types
- rubber gloves with good dielectric protection;
- a special tool with reliably insulated handles;
- special pliers and rods;
- Potential indicators protected against high voltages.
The first two positions are the easiest way to protect a person from exposure to hazardous voltages. More complex tools related to the professional activities of workers in high-voltage laboratories are the last three positions. They are used when performing operational switching associated with the following actions:
- disconnector control;
- replacement of blown fuses;
- installation of arrester elements and other operations.
Insulating clamps are used when it is necessary to replace fuses in existing electrical installations up to and above 1000 Volts. When working with them, it is imperative to use additional protective equipment (gloves and glasses). Voltage indicators are in demand when you need to make sure of its presence or absence at the point being tested. They are available in two versions:
- two-pole devices that fix the potential when the active current component flows;
- single-pole pointers that operate only with a capacitive component.
In the same category, but only for circuits above 1000 Volts, it is customary to include rods and pliers of all types, as well as other special devices.
Additional inventory

Additional electrical protective equipment used when servicing electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 Volts traditionally include:
- special dielectric galoshes and rugs;
- special insulating supports and auxiliary pads;
- insulating caps.
They got their name from the direct appointment, which consists in additional protection of the operational personnel involved in the work. The specified inventory, as such, is not able to provide full protection against all damaging factors, but together with fixed assets, it is quite effective. Under certain operating conditions, it protects operating personnel even from touch and step potentials.
Personal protective equipment
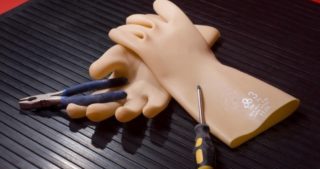
Personal protective equipment for workers:
- protective helmets to protect the head of working personnel;
- glasses and shields to protect the eyes and face;
- gas masks of various types and classic respirators for respiratory protection;
- cotton gloves and mittens for hand protection.
This list also includes protective equipment to prevent an accidental fall of a worker from a height. These include safety belts and safety ropes.
Protective equipment is a mandatory attribute of special units involved in the maintenance of existing electrical installations. Protective tools and special equipment are also in demand during operational switching and urgent repair work.