A residual current device or RCD is a device used in electrical circuits to protect workers and household consumers from electric shock. Its installation is possible not only in single-phase circuits, but also in three-phase current supply lines, often used in country houses. For a deeper understanding of the features of the operation of the device, you will need to understand its purpose, the principle of operation, as well as all the intricacies of installation within the facility.
Principle of operation
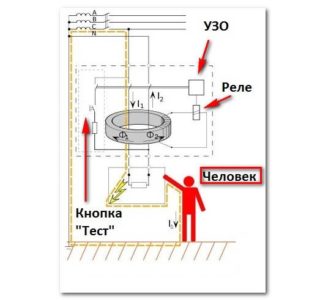
When getting acquainted with an RCD machine, the most important thing is to understand the principle of its protective action. However, it is important to note the following:
- a differential module is provided in the design of the device, which detects the difference in the values of the inflowing and outflowing currents;
- when it is detected, it sends a signal to the executive unit, which opens the power supply contacts;
- since an automatic device is installed immediately after the electric meter (before the switchgear), when it is triggered, the power supply circuit of the object is instantly disconnected.
The principle of operation of an RCD in a single-phase network lies in its ability to respond to the slightest current leakage that occurs in emergency situations (in case of destruction of insulation, for example). This is the manifestation of the protective functions of this device.
In what cases is an RCD necessary

As a reliable protection, RCD machines are useful only in the following cases:
- with obvious damage to the insulation of wires in electrical appliances;
- with careless handling of existing electrical wiring (direct contact with it when drilling walls, for example);
- in case of violation of the rules for handling electrical appliances.
In a situation with damaged insulation, some of the direct current will begin to flow through the body of a person who touches the wiring. In this case, the protective device immediately reacts to the detected input and output mismatch and instantly disconnects the supply line from the load. The disconnection of the machine occurs so quickly that the current during this time does not have time to reach a dangerous value.
When drilling a wall with a de-energized wiring, the current will flow according to the scheme of a person's hand - his leg - a concrete floor - a house grounding armature. Due to this leak, there will be a difference between the input and output currents and the machine will immediately work.
With careless handling of electrical appliances, the situation is even easier. If, for example, a hairdryer, connected to the network, falls into a bathtub filled with water, the leakage current through it will immediately trigger the protection, eliminating injury to a person. The same will happen if any other appliance connected to the mains accidentally gets into the water.
There is no need to install an RCD in the power supply circuit of the object in a situation when the electrical wiring mounted on it is in a dilapidated state. In this case, before updating it, the easiest way is to put the RCD on a particularly critical linear section (in the basement or in the bathroom, for example). If in this place the wiring is kept in good condition, the device will work without false alarms.
How many RCDs are needed for an apartment or house

To determine how many devices need to be installed in an apartment, they usually proceed from the current standards, according to which one RCD is enough for this.To provide a higher level of protection, one more device is placed on especially dangerous branches of household electrical wiring (in the bathroom, for example).
Installation of protection in a separate line with a working neutral of the power supply allows you to protect a person from accidental injury in high humidity conditions.
Often, additional RCDs are installed in such rooms that are dangerous from the point of view of climatic conditions, such as the kitchen, attic and basement of a country mansion or house. Moreover, they can serve a whole group of loads, including lighting bulbs. According to the PUE, linear devices are used in conjunction with a maximum current limiting device (an automatic machine designed for the corresponding setting). Experts advise replacing such a pair with a complex protective device - a difavtomat, combining an RCD and a circuit breaker in one case.
Types of RCDs
- Devices of the "AC" type are designed to work with alternating current of an analog form (sinusoid).
- Class A devices respond to sinusoidal alternating current and pulsating direct current.
- RCDs of type "B" work with all types of currents.
According to their design and the method of switching the executive module, the known protective devices are divided into electromechanical and electronic devices.
In the first models, e / m relays of the usual type are used, in their electronic counterparts - switches on semiconductor elements.
The device can be manufactured in the form of a differential automatic device that combines two functions at once (a conventional circuit breaker and an RCD). This is the difference between the two types of protective devices. As a special type of them, differential current machines (RCBOs), designated as RCD-D, are considered.
Technical characteristics and decoding of designations
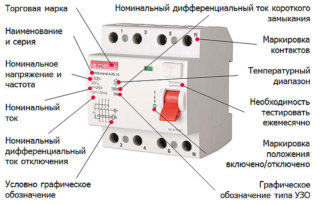
Any RCD circuit breaker included in an operating electrical circuit is described by performance characteristics, the main of which are:
- trademark and serial number;
- the type of current to which the RCD reacts: direct, alternating or pulsating;
- rated working current;
- the amount of leakage at which the RCD disconnects the supply circuit;
- operating voltage.
The first of these indicators is applied by the manufacturer on the front panel of the device case. The trade brand of the protective device can be deciphered immediately and without any particular complications, having familiarized himself with its symbolic designation. As an example illustrating the possibility of such decoding, samples of three different companies are given, each of which the manufacturer designates its own brand and series. These are products from manufacturers Hager, IEK, as well as Schneider Electric.
After the designation of the series, the rated current is indicated on the machine body. This icon means its maximum value maintained by an RCD electrical device for a long time without destruction. The scale of rated currents corresponds to the standard range of similar values for circuit breakers, which makes it possible to replace both of these devices with one differential device.
The residual current of an RCD is the leakage value at which a given device operates with certainty. This indicator is applied to the device case and is designated as I∆n. The icon is deciphered by the numbers after it, meaning more precisely the parameter value for differential currents from the following series: 6 - 10 - 30 - 100 - 300 - 500 mA. The operating voltage of the device takes two values (220 and 380 volts).
Connection procedure
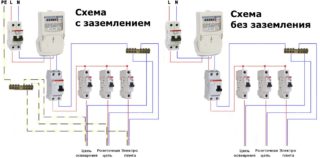
The procedure for connecting an RCD to an electrical circuit is standardized by current standards (PUE, in particular). In accordance with the requirements of the standards, the place of switching on the device is determined taking into account the possibility of general or selective switching of supply lines.If one RCD is used for the whole apartment, it is installed on the DIN rail of the electrical panel immediately after the electricity meter and in front of the linear circuit breakers that protect individual loads.
When using the device as a selective element, it is mounted in a branch from a common power line that needs special protection.
During installation, you must carefully ensure that the phase of the supply wire is connected to the upper terminal marked "1", and diverted from the lower contact marked "2".
The zero of a single-phase network is connected to the upper terminal under the designation "N", and is removed from the lower contact, which has a similar marking. For the case of installing a 4-pole device in a three-phase power line, the number of phase contacts will triple (the N terminals, to which the ground should be connected, will remain unchanged).
Launching and operating rules
When servicing the device, special attention is paid to the following points:
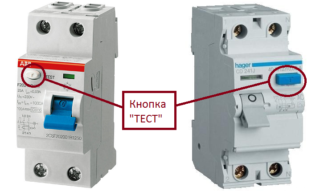
- In modern RCD models, it is possible to test the device using a special "Test" button.
- This procedure is carried out before putting it into operation, which allows you to make sure that the device is connected correctly.
- Testing is carried out in the two most common modes (10 and 30 mA).
During operation, according to the requirements of the PUE, it is necessary to periodically check the test performance of the device, which can be switched on both in the line with and without grounding. In the latter case, the efficiency of the RCD is somewhat reduced.
When considering the purpose of differential-type devices, it should be borne in mind that they are capable of protecting not only power circuits. Such a device is often used to protect the wiring laid before light sources. This is typical for wet rooms such as baths.