Almost everyone has heard of such a method of protection against electric shock as grounding electrical equipment. The installation of a three-wire electrical line in modern building structures is a must. Older buildings did not use such a protection system. In this case, electricians resort to zeroing the wiring.
What is grounding for?

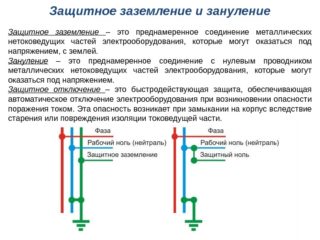
From the normative documentation of GOST No. 12.01.009-76 it follows that protective grounding is the creation of a single circuit with the ground and metal live parts that can be energized during the operation of electrical appliances, for example, the case of a microwave oven or washing machine.
Grounding is required so that when voltage is generated in places where it should not be, electricity goes into the ground. This allows you to prevent electric shock to residents of an apartment or house. As a rule, such phenomena are observed when the integrity of the insulating layer is violated and the current-carrying conductor of the case is touched.
Types of grounding in a domestic environment

At that time, the operation of the TN-C system was widespread, in which the PE ground wire was switched with a working zero into a single conductive PEN conductor, and a two-wire wire was connected to the apartment. This system is outdated, a new one has come to replace it - TN-C-S. Its peculiarity lies in the disconnection in the switchboard of the PEN wires to PE and N.
All modern buildings or structures subject to modernization are serviced in a three- or five-wire circuit. Three lines are fed into the room:
- land;
- working zero;
- phase.
All modern computing and household appliances are adapted for a three-wire system. Plugs and sockets are equipped with dedicated grounding terminals.
If the building is outdated and not equipped with a grounding system, and the wiring is two-wire, all modern three-wire electrical devices lose their qualities. For example, a surge protector becomes a normal carrier. In this case, the installation of grounding in the apartment according to the normative document PUE 1.7.132 is prohibited.
What is the grounding of electrical appliances
There is a concept - a deafly grounded neutral. 3 phases come to transformer substations via power lines. A deaf-earthed neutral is its own earthing that is installed around. It goes from the substation to residential buildings and buildings with phase conductors.
Zeroing is implemented as follows: in the switchboard, wiring is made, which comes from a dead-grounded neutral and breaks to zero in front of the machine, which goes to the apartment. In essence, this will remain a deafly grounded neutral, which is used for neutralization.
It is forbidden to empty the equipment from the working machine, it is life-threatening.
If the zeroing process is successfully completed, when the case of the switched on device with a current-carrying bare core is touched, a short circuit will occur and the machine will immediately work at the entrance to the apartment.
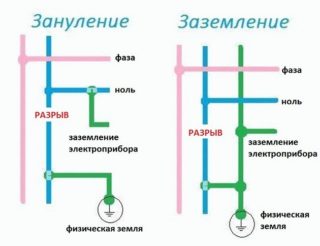
Zeroing and grounding - what is the difference
Both protection systems perform the same function - they protect households from electric shock when touching a bare wire or faulty electrical installations. The difference is that grounding instantly de-energizes the room in case of a dangerous contact, and grounding leads all the "danger" into the ground.
Difference in scope
- In multi-apartment buildings, grounding is installed on both sides of the building or around. Old buildings are for the most part an exception; they may have no outline at all. In country houses, the implementation of the ground loop is the concern of the homeowner. Typically, the ground loop is triangular in shape.
- Protective grounding in apartments is used only in the absence of grounding. As a rule, we are talking about old-style apartment buildings. Implementing this method of protection, it is additionally required to purchase and install automatic machines and RCDs.
In industrial sectors, grounding is one of the components of the common grounding of large rooms and all equipment located in them. Zeroing in a domestic environment is not a completely safe way of switching the grounding circuit of electrical devices to a working zero.
What's better

Grounding in comparison with grounding has a large number of advantageous features.
- The ground loop can be implemented independently at home. This requires a small amount of metal and a welding machine. If we talk about grounding, then for the implementation of protection, knowledge is required, which is associated not only with the calculation, but also with the choice of the most suitable point for connecting the wire to the neutral.
- If there is a break in the neutral wire in the switchboard, the grounding system will immediately fail and be inoperative. In this case, grounding is superior, since the PE wire used is not welded or burned out. It is recommended to check its condition once a year and tighten the terminals if necessary.
Thus, it is better to give preference to grounding as it is more efficient and easier to implement. You can do it yourself without having any special skills.
Grounding and grounding requirements
The main requirement is correct implementation, which will ensure complete safety and protection of a person from electric shock in case of emergency or abnormal situations.
The main requirements for grounding are voltage withdrawal to soil layers. The earth absorbs electrical current, preventing damage to human health.
Requirements for grounding - shutdown of protective automatics if current-carrying elements or bare wires come into contact with the surfaces of metal cases of electrical parts and household appliances, where there should be no voltage.
Practical advice

When completely or partially replacing, modernizing or repairing wiring in an apartment or a country house, it is important not to neglect the rules of personal safety. A few practical tips:
- If a two-wire electrical network is installed, when installing a three-wire outlet, the ground loop and operating zero must not be connected. This is a violation of one of the basic safety rules.If you neglect it, the housing of a household appliance connected to the network will always be energized, which negatively affects performance and operational life, and also poses a danger to the life and health of humans and pets.
- During the construction of a summer house or a country house, the installation of grounding is a prerequisite for the operation of electricity. An inexpensive grounding system with a simple design will save human health and the integrity of all expensive household appliances and electrical appliances.
- To provide electricity to powerful household appliances, for example, a washing machine, dishwasher, boiler, it is recommended to run a separate wiring line in the room. This is due to the fact that when these devices are started simultaneously, RCD sensors (residual current devices) and safety sensors will often work, completely shutting off the supply of the resource to an apartment or house.
A safety device and an RCD are two completely different electrical devices. Each of them has its own design features and performs certain functions.
The residual current device is a protection for humans and pets, a fast response device. An automatic machine is an electrical device that detects changes in the parameters of an electrical network, in particular, its overload. Its main drawback is that it may not work immediately, but after a certain time. In order to combine the capabilities of two protective devices and level their shortcomings, a hybrid device, a difavtomat, was developed.

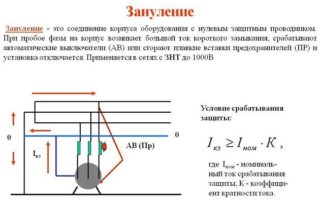








... It is forbidden to empty the equipment from the working machine, it is life-threatening.
1. Where did you find this "zero" on the machine?
2. What does it mean from "working machine"?
Difference in scope
... In multi-apartment buildings, grounding is installed on both sides of the building or around. ...
1. On both sides of the building, grounding is part of the lightning protection of the building; slopes go from the roof, from the lightning protection mesh.
2. Grounding of electrical installations of the building is performed at the entrance to the electrical installation, called "re-grounding".
He has a ground-zero jumper drawn when grounding. With a short circuit, when kiloamperes flow through the short circuit, the voltage at zero is not zero at all, there can be up to 50-100 volts. he wants the voltage on the case at this moment to equal the voltage at zero. and taking into account that all the equipment is stuffed with DC circuits, where the ground, at the same time, is a minus, all boards, in the presence of a jumper, work on white smoke, smoke comes out - the board stops working, and the electrician who plugged the jumper buys a new board.
The entire article is written according to "GOST". The two-wire system used to be considered a gost system too. GOSTs have changed, but people are not changing. New GOSTs are drawn by the same "specialists" who drew old GOSTs. "Modern" grounding "According to Russian" in any case is connected to zero in the switchboard, ground-to-zero jumper and does not have a circuit separate from zero. As a result, when it is short to zero, a current flows, which is limited only by the resistance of the very same neutralizer-grounding conductor. At the peak of a short, dressing at zero jumps under a hundred. The same thing happens on the ground, but atk is the same on the case of any grounded equipment, because into the panel electrician, instead of a separate grounding device, he "soldered" another ground-zero jumper. And most importantly - everything is in accordance with GOST. And if the operators of the equipment with a short circuit, from the case, only slightly "invigorates", then from the boards, which are more expensive than the life of an electrician who connected zero to the ground, there is smoke, because ground is not only a case, but also a minus for all DC circuits. So that somewhere in the high-frequency 2.5 volt controller one of the outputs fails, a minimal jump on the minus is enough.
Commentary "specialist" which is a complete zero in electrical engineering. If you do not put a jumper between zero and ground, short-circuit. from faulty equipment, more than one such "specialist" will beat and expensive boards will burn out quite a bit. And so that nothing in the DC circuits burns out, you need to install a separate protection in front of them!
If you do not want a fire, do not ground.
Here is an extract from GOST 30331.1-2013: 20.75 Type of system grounding: A comprehensive characteristic of the power distribution system, which establishes the presence or absence of grounding of live parts of the power source, the presence of grounding of exposed conductive parts of an electrical installation or electrical equipment, the presence and method of making an electrical connection between grounded parts energized and indicated exposed conductive parts. This means that it is essentially a power distribution system. And there are only three systems: TN (with TN-C, TN-C-S, TN-S subsystems), TT and IT. The second letter in the designations of these systems just speaks of whether the open conductive parts (HFC) of electrical installations are grounded or grounded. TN (with these systems, you basically have to deal), the second letter N indicates that the HRE of electrical installations are connected to the solidly grounded neutral of the transformer, i.e. are zeroed (see PUE, p. 1.7.3). But in TT and IT systems, the HRS of electrical installations are grounded. But these are rarely used systems (especially IT). The TT system is used when the TN system cannot provide electrical safety. Try to name at least one reason when the TN system does not provide electrical safety? This means that we found out that protective grounding is used in the TN system (see PUE, p. 1.7.31), and not grounding. True, in TN systems there is also re-grounding, used mainly on overhead power lines and grounding of the potential equalization system in apartment buildings, but they have a slightly different purpose.
Try to name at least one reason when the TN system does not provide electrical safety? when you have zero burned out and you have a potential of 350 volts.