The construction of a residential building includes the laying of electrical wiring, to which many devices of various capacities are connected. Despite their reliability, there is always a risk of current breakdown into the case and injury to a person. In addition, there is a high probability of lightning hitting the structure, which is fraught with fire and destruction. To make life in the house safe, you need to equip grounding in accordance with the PUE, which will ensure the absorption of electricity by the soil in the event of emergencies.
Issues raised in the PUE

The Electrical Installation Rules approved by the Ministry of Energy of the Russian Federation regulate the scope of application of protective equipment, grounding rules and the procedure for its arrangement.
This term refers to a collection of metal parts that, when assembled, provide electrical contact between devices and the ground. This document describes equipment grounding requirements, specifications, and codes.
- Means of production. These include machine tools, lifts of all types for people and goods, refrigeration units, generators, electric motors, heaters, conveyors and other products installed in the factory workshops.
- Electrical appliances for household and industrial use. The grounding of the neutral of the transformer according to the PUE, stabilizers, KTP, rectifier and storage devices is regulated.
- Residential and private houses, summer cottages and cottages. In the buildings of the old building, only the grounding of the cabinets is carried out according to the PUE. Connecting apartments with outlet to sockets is carried out individually at the initiative of residents.
- Pipelines through which explosive and combustible materials are transported - oil, gas, gasoline, diesel fuel, solvents.
- Power transmission line supports. Grounding is required for structures made of metal, which is an excellent conductor of current. It is also necessary to equip concrete pillars with protective structures, the height of which does not exceed 6 m.
- Metal towers for searchlights, antennas and observers. In addition, buildings are equipped with lightning rods.
In accordance with the PUE, the ground loop must ensure guaranteed reception of electricity leakage under any conditions. For this, installation standards have been developed in various types of soil.
Contour design
The components of the grounding system according to the PUE are as follows:
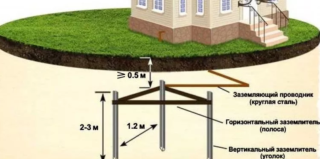
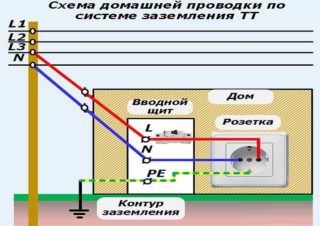
- Circuit board. The part is located in the switchboard, into which cables from grounded objects are led out. The line is attached to the external structures with a nut and a bolt. The flap door must be locked at all times. As a rule, panel boards are installed inside buildings. In the private sector, it is allowed to install the box outside, provided that it is equipped with a canopy.
- Communication. Designed to connect a back box to a structure buried in the ground. The material is a copper cable with armor and iron bars welded together.The line is launched under the floor of the room, outside walls, along the chute drain of the blind area. According to the PUE, the grounding of electrical equipment must be carried out with a cable with a cross section of at least 5 mm.
- Vertical pins. Designed for electrical contact with the ground. Depending on its type, they are driven to a depth of 100-250 cm. The pins are made of black iron or stainless steel. The choice is determined by the financial capabilities of the builder.
- Circuit. Serves as a strap for recessed pins. In accordance with the PUE, the grounding of the metal structures of the building must be carried out using a circuit with a side of at least 200 cm. An individual can ground his property with a frame, the size of which can be 80-100 cm. According to the PUE standards, the ground loop is dug into a depth of 50-100 cm.
- Connecting bolt. Designed for communication of metal connection and circuit. The outer end of the part must be above the ground at a height of 15-30 cm. For safety reasons and to avoid mechanical damage, the contact is covered with a casing.
The installation of the current leakage protection system is carried out at a distance, the value of which is determined by the specifics of the structure. For residential buildings, it is 50-100 cm. For utility structures, it is allowed to remove the contour up to 10 m. In this case, the connection must be carried out with a copper cable.
Influence of soil on resistance
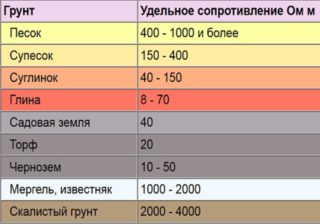
At a voltage of 1000 V, the soil resistance in ohms is:
- asphalt - 200;
- pond water - 40;
- permafrost soil (loam) - 2000;
- wet clay - 20;
- semi-hard clay - 60;
- decomposed gneiss - 275;
- clayey gravel heterogeneous - 300;
- grit - 5500;
- ash and ash - 40;
- silt - 30;
- yellow earth - 250;
- sand is moderately wet - 60;
- sandy loam (sandy loam) - 150;
- garden land - 40;
- salt marsh - 20;
- forest loam - 100;
- peat - 25;
- black soil - 60;
- wet crushed stone - 3000;
- dry crushed stone - 5000;
Conductivity decreases when the soil is wetted. In order not to engage in this event constantly, you should install the circuit on the north side, where the sun does not get. In addition, you need to stretch a cable with a resistance of no more than 0.4 ohm.
Device and types of circuits
According to the definition of the PUE, the circuit is part of the grounding system designed to ensure contact with the ground. Metal has much less resistance than the human body. The product attracts electrons, taking them into the array, directing the excess into the soil through the pins recessed in it.
A mandatory rule is the immersion of the product below the freezing point of the soil. This is due to the fact that frozen ground has a high resistance, which exceeds the conductivity of the human body. Seasonal heaving of the soil leads to deformation of the figure, which is fraught with rupture of welded and bolted joints. In addition, the digging depth depends on the groundwater level. It is recommended to lower the frame 50 cm higher from their top point.
The shape of the product is of no fundamental importance. The choice is made based on the availability of free space and the characteristics of the local area.
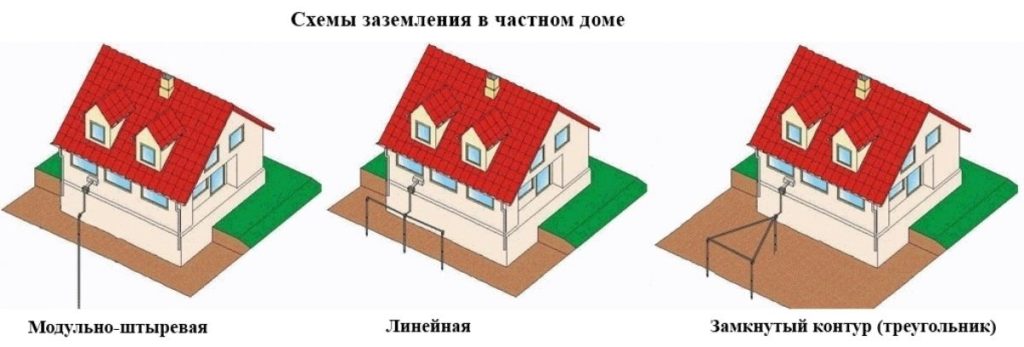
The most common types of configuration of metal frames are:
- rectangle;
- square;
- triangle;
- line.
In some cases, a decision is made to install a frame around the perimeter of the building. Such a project is in demand for the arrangement of high-power electrical installations. The total area allocated for the construction can be up to 20 sq. M. The size is determined by the current and voltage that can theoretically pierce the device's case.
For a small private house, an internal triangular structure with an edge of 100-120 cm is sufficient.To protect against damage to an object with a capacity of 50 kW or more, a circuit with a total length of at least 20 m is required.
Manufacturers offer to purchase ready-made kits consisting of parts with threaded connections and copper plating. The cost of the product is quite high, but not sky-high. The products have excellent electrical performance, are assembled without welding, are efficient and have a long service life.
Types of material

Most often, for the manufacture of metal bonds, ferrous iron is used without any coating. Less commonly, stainless steel is used for furnishing, although its contact properties remain for decades. Copper and brass have excellent characteristics, but these materials are expensive and quickly deteriorate due to electrolytic corrosion. Therefore, iron is the most popular metal in construction.
For the manufacture of submersible electrodes, fittings with a diameter of 16 mm are usually used. These products are characterized by sufficient strength, durability and conductivity.
To assemble the frame, you can use the following types of rolled metal:
- tape 12-30 x 4 mm;
- corner 30-40 x 4 mm;
- round pipe with walls 4-5 mm;
- tee or I-beam with a thickness of 4 mm;
- profile pipe 20 x 40 mm;
- monolithic pin from 10 mm.
There are no strict requirements for the shape of the profiles. The main condition is their integrity and quality connection.
Since the metal is prone to oxidation, the quality of the contacts gradually deteriorates. In addition, there is a possibility of violation of the integrity of the longitudinal parts if they are in alkaline or acidic soil for a long time. The state of metal bonds should be checked at a frequency that corresponds to the chemical composition of the soil. The information received will help to carry out timely repairs, reduce to zero the risk of injury to people and damage to household appliances.
Protective measures for electrical safety
The following electrical safety precautions should be observed:
- protect products from accidental touch;
- put up fences and fences;
- lay plates and exposed cables in a plastic box or corrugated tube;
- close the junction of the core and the circuit with a sealed box;
- install a residual current device in the circuit with a response threshold of 30 mA;
- provide for automatic shutdown of electricity;
- introduce equipotential bonding and equipotential bonding devices.
When installing devices and accessories, you need to ensure that they do not have a mutual influence, which can negatively affect the operation of other options.
Self-production
For work you will need:
- welding machine;
- grinder, puncher;
- level, tape measure;
- pliers;
- shovel, sledgehammer;
- brush, paint;
- corrugated tube;
- aluminum tape.
The work is performed in the following sequence:
- Drafting a project. On its basis, the calculation of materials and equipment is carried out. A small margin should be made, as errors are possible during the work.
- Marking. The sod layer is carefully removed, then a pit of a given shape is torn off. The removed material must be saved as it will be backfilled.
- From the middle of one side or from the corner, a flat trench is dug to the building. It is needed for laying a cable or other current conductor between the frame and the electrical panel.
- The electrodes are cut out. Their ends are sharpened for easier immersion in the soil. After that, the pins are driven into the ground at the corners of the trench.If a corner is used, holes are pre-drilled, and the openings are filled with a mixture of earth and salt.
- The sides of the contour are cut. They are connected to the electrodes and to each other. Welding spots are painted over.
- A bolt is welded to the frame near the ditch. A cable is screwed to it. The joint is closed with a plastic bottle, the neck of which is sealed with aluminum tape.
- Entering the house is done in the basement. To prevent chafing of the cable insulation, a flexible steel tube is inserted into the hole. The cable is pulled into it and connected to the shield.
- The final stage is filling the ditches with soil, leveling it and tamping it.
During operation, it is necessary to regularly water the location of the circuit with salt water. This should be done especially often during dry times.