Many systems are responsible for the comfort in the home. Water supply, energy supply, heating, lighting make people's lives more comfortable, safer and easier. Light affects the psychological and emotional health of a person, eye fatigue, the value of rest, so it is important to choose the right backlight correctly. To create a high-quality lighting system, you need to calculate the number of bulbs, determine the required illumination level and carry out other calculations.
- What is taken into account in calculating the illumination of a room
- Illumination standards
- Calculations
- Light source characteristics
- Incandescent lamps
- Halogen sources
- Fluorescent devices
- LEDs
- LED lighting calculation
- Calculation of the number of LED lamps in a room with a white ceiling, gray wallpaper and light laminate
What is taken into account in calculating the illumination of a room

The creation of high-quality lighting in each room depends on a number of factors. These include the area of the room, its purpose, the arrangement of furniture, the need for zoning, decoration and other criteria.
Previously, calculations for each specific room were made taking into account the capacity. We used tables in which, depending on the type of room, the total power of the lamps was calculated. This method is incorrect, as power is a unit for calculating energy, not luminous flux. There is a connection between these two quantities, but it does not obey a strict ratio that is suitable for all lighting fixtures. This method was only suitable for incandescent bulbs. Fluorescent, LED and other appliances consume different amounts of electricity and give a different level of brightness.
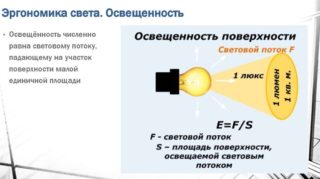
The choice of light sources is based on the luminous flux and illumination. These quantities are related to each other. A luminous flux of 1 lm for an area of 1 sq.m. creates an illumination of 1 lux. Each room has its own norm.
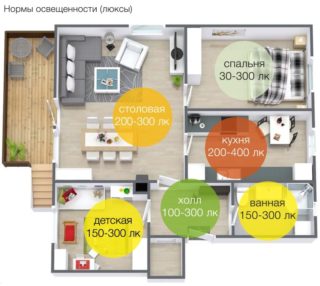
Illumination standards
- living rooms 150 lux;
- children`s 200 lux;
- classrooms, libraries 300 lux;
- room for precise drawing works 500 lux;
- kitchen 150 lux;
- bathroom, toilet 50 lux;
- sauna, bath 100 lux;
- corridor 50 lux;
- staircase 20 lux;
- dressing room 75 lux%
- porch 6 lux;
- platform next to the emergency entrance 4 lux;
- path at the entrance to the house for 4 meters 4 lux.
Illumination levels are considered optimal and proven, so they should be adhered to. More or less illumination can lead to rapid fatigue, the inability to concentrate on the work being done and a negative impact on the human psyche.
Calculations
Calculation example: there is a living room of 15 sq.m. To illuminate it, you need 15x150 = 2250 lux. By this value, bulbs are selected. If we take light sources with an illumination of 500 lux, 5 lamps are required to illuminate the living room.
Such calculations of light by area are not entirely correct, since they do not take into account the individual characteristics of the room. A more accurate way to calculate the luminous flux for a room is using the following formula:
Fl = (En × Sp × k × q) / (Nc × n × η)
This calculation of light includes many parameters, taking into account the type of lamps used, the color of the walls, the presence or absence of a plafond on the lamp.
- Fl (lm) - the required luminous flux that each lamp in the luminaire must have.
- Yong - the norm of illumination, taken in the table for each type of premises.
- Sп - the total area of the room.
- K Is the safety factor. Each type of lamp has its own meaning. For fluorescent lamps 1.2, for conventional incandescent and halogen lamps 1.1, for LEDs 1.
- q - coefficient of uneven glow. Also different for different light sources. Any incandescent lamps 1.15, mercury gas-discharge 1.15, fluorescent 1.1, LED 1.1.
- Nc - the estimated number of luminaires.
- N - the number of bulbs in one chandelier.
- η - the utilization factor of the luminous flux. This parameter takes into account many features of the room, it can be determined from the table. Depends on the area of the room, the height of the light source, the reflectivity of the walls, floor and ceiling, depending on the color of the finish.
This value is only suitable for general lighting. You cannot calculate the illumination level for decorative and accent lighting.
All the above calculations can be done using online calculators.
Light source characteristics
- Base type. Depends on which one is used in the lamp. In large devices, bases E are placed; in spot lighting, G and other types can be used.
- Power consumption. Depends on the specific type of light bulb.
- Supply voltage. The mains voltage is 220 V, the frequency is 50 Hz. Not all lamps operate at this frequency; 12V and 24V devices require a step-down transformer.
- Colorful temperature. The optimal range for a room is from 2600 K to 5000 K. Warm light is given by lamps at 2600-3500 K, daylight white 3500-4000 K, cold 4000-5000 K.
- Light flow. Indicates how brightly the light will illuminate the area.
In houses, for general illumination, 4 types of lamps are used - incandescent, halogen, fluorescent, LED. They all have their own characteristics, pros and cons.
Incandescent lamps
This is the cheapest type of light bulb. They give a pleasant yellow light. Incandescent lamps have already been almost completely replaced by other light sources, as they are ineffective. The disadvantages include low efficiency, high energy consumption, short service life, fragility and insecurity.
Halogen sources
Advantages - wide variety, higher efficiency, color temperature range from 2800 to 3000 K.
Disadvantages - high temperature during operation, fragility, non-environmental friendliness, difficulty in disposal, high energy consumption.
Fluorescent devices
Advantages: high luminous efficiency, low energy consumption, long service life, wide operating temperature range.
Disadvantages: the presence of mercury inside the flask, the complexity of disposal, the presence of UV radiation, flickering, long start-up, a limited number of on and off cycles.
LEDs
LED light sources are considered the most successful option for the home. They do not contain harmful substances, they work only on the glow from a semiconductor crystal. They have a wide range of colors, sizes, shapes.
The advantages include low energy consumption, high efficiency, durability, flicker-free, safety, wide operating temperature range, and a variety of color temperatures. Due to low heating, LEDs can be installed in stretch ceilings without fear that the canvas may be deformed. When purchased from a reputable manufacturer in a professional store, a guarantee is given, according to which the lamp can be changed in the event of a manufacturing defect.
LED lamps have one significant drawback - high cost. Cheap models will not be made of quality materials, so the lamps will quickly burn out due to the lack of sufficient heat dissipation. Also, a device of unknown production may lack a driver - then the lamp will react to any voltage surges and will quickly fail.
LED lighting calculation
Luminous flux of one light bulb = lighting area * light level of a given room / number of lamps.
Lighting per square meter equals:
Illumination level = number of lamps * luminous flux / area of the room.
The number of bulbs depends on the installation method of lamps and chandeliers. If the lamps are to be installed in a classic chandelier, the luminous flux should be selected according to the required intensity level. If point light sources are mounted around the perimeter, the intensity level must be divided by the luminous flux of the lamps. It should also be borne in mind that the luminaires on a stretch ceiling should not be located closer than 25 cm from each other.
The effective lighting angle of the LEDs is 120 degrees. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the light spreads evenly and that there are no unlit areas of the room. This can be achieved by proportionally reducing the wattage of each light bulb.
The installation height is also taken into account. Spot devices are placed 20-30 cm higher than the bulbs in the chandelier, so the intensity should be about 20% higher.
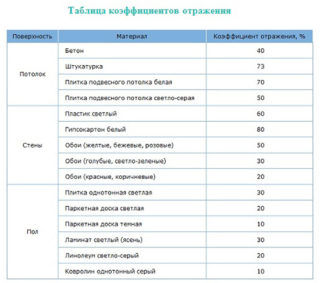
Often, the replacement of classic light sources with LED ones is carried out during a major overhaul or other construction work. As a result, it may turn out that there is not enough light in the room. The main reason is that in the calculation of the luminaires for the area of the room, the reflection coefficients from the surfaces were not taken into account.
- white surface - 70%;
- light - 50%;
- gray - 30%;
- dark - 10%;
- black - 0%.
The reflection coefficient will be equal to the sum of the floor, ceiling and wall coefficients, divided by 3. The resulting average value can be used in the final calculation.
Calculation of the number of LED lamps in a room with a white ceiling, gray wallpaper and light laminate
Average reflectance = (0.7 + 0.3 + 0.5) / 3 * 1.2 = 0.6
If LED devices with a luminous flux of 1200 lm are installed in the room, the required luminous flux will be 1200 * 0.6 = 720.
To calculate how many LED lamps are needed to illuminate a room of 20 square meters, you can use the formula: illumination level * room area / luminous flux. Then for the living room (illumination 150 lux) the number of 20 W lamps (gives a luminous flux of 250 lumens) will be 150 * 20/250 = 12 pieces.
The calculation of the power of LED lamps for a room is as follows: the area is multiplied by the number of lamps and by the power of each product.