It is difficult to imagine modern life without the Internet, the connection of which is impossible without a special cable - a twisted pair. This type of wire makes it possible to connect several devices at once, while minimizing the number of wiring. The cable diagram is simple - its cores are connected to a special connector-connector, and it is already connected to a PC or other devices. Many users in this matter resort to the help of specialists, not knowing how the pinout of the wires is performed. However, you can do everything yourself.
- What is twisted pair
- What is twisted pair crimping and how to do it
- Types of color schemes for crimping LAN cables
- Choosing a pinout scheme
- Twisted pair crimping procedure
- Straight 8-conductor cable
- 8-wire crossover
- Straight 4-conductor cable
- 4-wire crossover
- Procedure for crimping with pliers
- Preparing the cable
- Removing insulation
- Preparing veins for loading into connections
- Contact pad crimp
- Crimp quality test
What is twisted pair

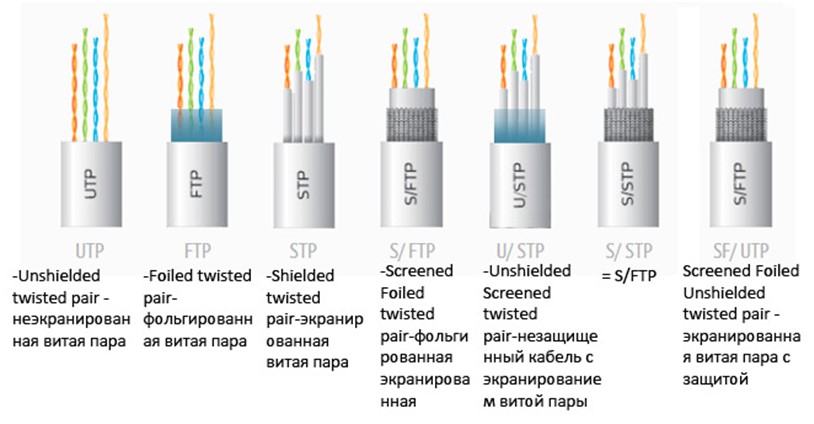
Twisted pair is a 4- or 8-core cable, the cores of which are twisted together in pairs. Each pair of wires has similar colors, for example: yellow and yellow-white, red and red-white, etc. For each cable, special connectors are used - connectors, for 4 or 8 contacts, respectively.
There are several types of twisted pairs:
- UTP - twisted pairs are not shielded, there is no external shield either. The most common type of cables for home Internet networks, when long distances and interference are absent.
- FTP - devoid of shielding, an external shield is present (foil). Such wires are used in office premises, where interference is encountered and data is transmitted over a distance of up to 100 m without loss of speed.
- STP - each pair has a wire-type protective shield, there is also an external shield. Such cables are used in medium-sized offices and in premises with the presence of interference. A high-quality signal is transmitted over a distance of up to 100 m.
- SF / UTP - the pairs themselves are devoid of screens, the external screen is double: a copper braid and a foil film. They are used in industrial plants to protect against interference and preserve a high-quality signal when transmitting over long distances.
- S / FTP - all pairs have a foil shield, external shielding is a copper braid. They are used in buildings with high interference and in places where it is necessary to save the speed of data exchange over long distances.
You should also pay attention to the color of the cable insulation. The most common - gray - standard insulation. Orange and red colors indicate that the cable insulation is made of non-combustible materials.
There are cables for 4 and 8 cores. Four-core cables are capable of transmitting data at a speed of no more than 100 Mbit / s. Eight cores are capable of raising this speed to 1000 Mbps. For long cable runs (over 100 meters), installation of auxiliary amplifying equipment is required.
What is twisted pair crimping and how to do it
The connection of cable cores with a connector is called a crimp - the contact group of the connector, after distributing the wire cores in it, is pressed inward, piercing their insulation and fixing the cable. This creates a reliable and high-quality connection. The most demanded connectors are the rj45 model.
The rj45 socket, through which the pinout is performed, is often referred to by specialists as the 8P8C connector. This marking indicates that both the plug and the socket itself have 8 contacts.All of these contacts can be connected in various schematic variations according to the type of cable connection.

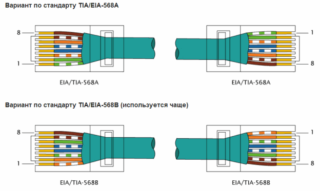
Rg 45 pinout of 8 wires comes in two standards: T568A and T568B. The latter is more in demand and is used much more often, since it is designed to connect a PC with a router or modem. The first standard was created to connect two PCs to each other.
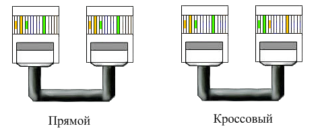
Before considering the crimping process, it is logical to indicate the variations in the connection diagrams of the connectors. There are only two of them: straight and cross.
All twisted pair conductors are marked with a specific color, which allows quick pinout and further crimping of the rj45 socket. The veins of a single pair are similar in color, for example, blue and blue-white.
The differences between straight and cross crimp configuration are obvious. Direct variation is a circuit solution when the colors of the cores coincide on two opposite ends of the cable.
Crossover variation assumes a scheme where the color matching of the cores is slightly changed on opposite ends of the cable. Most often, the conductors numbered 1, 2, 3 and 6 are swapped in places.
Each of these schemes provides for the placement of conductors on opposite edges in such a way that conductor # 1 is opposite conductor # 8 and vice versa - conductor # 8 is located opposite conductor # 1.
In addition to the above 2 configurations, there is also an intermediate one - the console one. It involves placing the conductors upside-down at the ends of the cable. Wire # 1 from the first connector corresponds to wire # 1 from the second connector. Conductors # 8 also match.
Types of color schemes for crimping LAN cables
In accordance with the EIA / TIA-568 specification, there are 3 main color schemes for crimping twisted pair LAN cables (patch cords) using a rj45 model connector.
Patch cords (they are also switching wires) are designed to connect two devices, for example, a PC with a hub, another PC or a switch. Making a patch cord is easy. You need to take a cable of the required length, where the cores are made of stranded wires (to avoid fractures with frequent bends), and squeeze its edges with connectors of the rj45 model.
Choosing a pinout scheme
The specific pinout of the rg45 8-wire is determined by the variation in the connection of computer devices. Direct is mainly used to connect to a switch (hub) of a network card.
Cross-order is used when there is a need to connect two network cards to each other on different PCs. This configuration was used to switch older hubs.
At the current stage of development of digital technologies, the cross scheme has actually become unclaimed. The reason is the development and gradual implementation of automatic detection of network type terminals.
Twisted pair crimping procedure
Twisted pair crimping of 8 wires can be performed according to two standards: 568A and 568B. They are of two types - direct or crossover (crossover) connection. In addition, there is a simplified pinout, crimping 4 conductors, not 8. However, this variation does not support high traffic speeds - no more than 100 Mbit / s. Each option assumes its own crimping scheme.
Straight 8-conductor cable
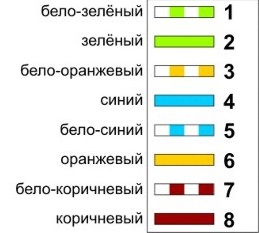
Crimping all 8 conductors in a direct way is necessary to provide high-speed Internet access. Such crimping will allow data transmission at speeds up to 1000 Mbps.
Twisted pair colors:
- orange with white,
- Orange,
- green with white,
- blue,
- blue with white,
- green,
- brown with white,
- brown.
This crimping method is most relevant when connecting the router to a PC. Crossover variation assumes a slightly different distribution of conductors.
8-wire crossover
This type of crimping is used infrequently, as it is designed to connect two switching devices or two PCs to each other.
The color order of the conductors is as follows:
- green with white
- green
- orange with white
- blue
- blue with white
- Orange
- brown with white
- brown.
The crossover is slowly becoming a thing of the past, because modern devices are equipped with MDIX technology and automatically change the signal supply. Nevertheless, such a crimp will still serve for old technology.
Straight 4-conductor cable
This crimp option is used to connect a PC to switching-type devices, for example, to modems.
Rj45 wire crimp, color scheme:
- orange with white,
- Orange,
- green with white,
- green.
This configuration is simpler and assumes data transfer at low speeds - up to 100 Mbps. If the cable breaks, you can simply throw it over 4 free contacts on the connector.
4-wire crossover
Crimping in this way uses four cores of the cable, that is, 2 pairs. In this case, conductors of any color can be used for twisting. Traditionally, green and orange conductors are connected.
A crossover of this type is used extremely rarely, exclusively in home networks, for example, to connect an old PC to another outdated computer. The choice of the color of the conductors does not affect the information transfer rate.
Procedure for crimping with pliers
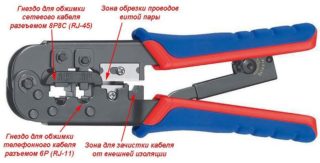
To compress twisted pairs, you need the following tool:
- crimper (pliers for crimping wire ends rj 45);
- stripper (cutter for stripping insulation);
- stationery knife.
If such a tool is not available at home, it is better to seek help from specialists.
Preparing the cable
First, you need to select a cable according to the required number of cores and cut off a piece of the required length from it. For a home network, you need to take a four-core wire with copper conductors. Unused conductors are simply not used. For high speed data transmission, an eight-core cable must be connected.
Removing insulation
It is necessary to remove the insulating layer from the ends of the cable section. It is enough to retreat 3-3.5 cm from the edge and, using a stripper, make an incision on the insulation with a light circular motion. The cut must be done carefully, without pressing hard, otherwise the sheath of the cores will be damaged. This will lead to a decline in the data transfer rate. The braid is not cut to its full depth, but in half. Then it is bent and it bursts along the cut line.
If you don't have a stripper on hand, the insulation can be removed with a knife or utility knife.
Preparing veins for loading into connections

Conductors twisted into pairs that have opened after removing the insulation must be unraveled and straightened. Copper conductors are quite soft, so this operation must be performed carefully so as not to break their sheath.
Further, all conductors are aligned relative to each other, after which they are cut perpendicularly exactly, stepping back from the edge of 3-4 mm. This procedure is best done with scissors. As a result, you should get a straight end row of 4/8 braided cores.
Next, a plastic connector of the 8P format (8 contacts) will be used, with the help of which crimping will be carried out - contact fasteners of copper conductors.
There are no 4-pin connectors, only 8-pin connectors are used for computer networks.
Contact pad crimp

The back of the 8P connector is an entry gateway for copper conductors. This sluice has 8 rectangular cells, into which cores of the correct color are loaded.
The copper conductors of the network cable are loaded into the gateway of the connector without removing the insulating layer. The conductors just need to be inserted into the channels until they stop.
Next, you need to crimp the conductors using a crimper for 8P8C connectors. The block of pincers must be placed on the plastic connector, and then squeeze the handles of the tool until it clicks.
Crimp quality test
After the crimping process, the crimper is removed, and the connection itself is subjected to a strength test by physically pulling the cable out of the connector. A similar test is performed on the other end of the network cable. If everything is done in accordance with the technology, the crimp will not allow the cable to be pulled out of the pressed cells. After that, the crimp can be considered complete.









