PV 3 is a copper power conductor that is insulated with PVC (polyvinyl chloride). It is used in many devices and electrical circuits - various devices, household appliances, light networks, etc. The main difference from previous models is increased flexibility, which is especially important when laying complex electrical wiring. It has certain characteristics and parameters, which can be clarified using the markings on the outside.
- What does marking mean
- GOST and design differences
- Elements of construction of wires PV3
- Technical characteristics of wire PV-3 (PuGV)
- Wire laying conditions
- Conditions in which the use of wire PV-3 is allowed
- Load currents of wire PGV
- Application area
- Checking upon purchase
- Cable selection instructions
- Errors when using the PV-3 cable
What does marking mean

The cable is used in different situations - wiring, devices, devices. There are different types and types of wires, the characteristics of which are indicated from the outside (on the "rubber" part). Symbols - letters, numbers, signs - allow you to define:
- the number of lived inside and their material;
- insulating type;
- section - the cross-sectional area of the element - from 3.5 to 24 cm squared;
- allowable voltage - nominal values of electrical indicators;
- attitude to environmental influences - humidity, heating;
- features of the internal design;
- flexibility - usually marked with numbers from 1 to 6, PV3 wire has an average value.
Design features are also reflected in the labeling. For example, the solidity or multi-wire of the internal element, the presence of insulation. Additionally, the type is indicated - wire, cable or cord.
GOST and design differences

The last part of the marking indicates the recommended temperature level for operation and the number of technical documentation - GOST or TU. The latter contain information on methods and techniques for making a wire. Manufacturers are obliged to indicate the number of GOST, TU, but in recent years they "forget" to do this because they rarely adhere to the recommended parameters.
Installation wire PV 3 is single-core, multi-wire. The material is copper. Due to these characteristics, the cable conducts electricity well, bends easily in different directions, and does not deform. The marking is deciphered as follows:
- P - means the type "wire";
- B - insulation option, in this case polyvinyl chloride;
- 3 - flexibility class.
Technical characteristics allow using the PV-3 cable in different conditions and devices, including those with high humidity.
Elements of construction of wires PV3
Each cord or cable has specific design features. The type and number of elements is influenced by the purpose, operating conditions, and the maximum voltage level. The structural details of the PV 3 installation wire are:
- copper conductor (according to GOST No. 22483 it can be solid or multi-wire);
- external protection (insulating layer).

Despite the minimum number of elements, the wire has high technical characteristics, thanks to which it is used in various fields. For example, the PV 3 grounding cable is used in residential buildings and electrical devices.
Technical characteristics of wire PV-3 (PuGV)

If the cable needs to be laid in a limited area (electrical panel, wiring inside the devices), it is important to use soft multi-wire cables of the PUGV class, which include PV-3. The characteristics of such wires are typical:
- permissible voltage of alternating voltage is 450 to 750 V, for direct voltage - up to 1000 V; frequency up to 400 Hz;
- possible humidity level - up to 98%;
- temperature limit for installation work - minus 15 ° Celsius;
- flexibility - up to 5 solid section diameters;
- the insulation of the wire remains operational at temperatures up to 160 ° Celsius;
- possible cross-sections of PV-3 wires - from 0.05 to 40 square cm.
The service life of standard cables depends on operating conditions, environmental conditions and installation method. Usually the maximum limit is indicated - 15 years. In "aggressive" conditions, the term can be reduced to two years. For example, if the PV-3 wire is laid in an open way, it is exposed to constant exposure to ultraviolet radiation, precipitation, and temperature changes. Average warranty period is 1 year.
Wire laying conditions
The PV-3 cable is installed in different conditions, subject to certain recommendations. If the ambient temperature is below 15 ° Celsius, the wire must be warmed up. Otherwise, damage and cracking when bent can not be avoided.
It is important to observe the permissible bending limits - no more than five outer diameters. PV-3 has average flexibility, therefore it is not recommended to create excessive pressure.
An additional point is that condensation or moisture must not be allowed to enter the inner rod.
Conditions in which the use of wire PV-3 is allowed

The PGV soft cable can be used in different conditions. Technical characteristics allow laying the wire in rooms with high humidity (bathrooms, baths). Much depends on the type of wiring - open or closed. The insulating layer retains its performance characteristics at sharp temperature fluctuations (from -60 ° to + 70 ° Celsius).
Load currents of wire PGV
None of the current GOST establishes the permissible limits of the load currents of the PGV cable. Therefore, the Rules for the Installation of Electrical Installations are applied - several regulatory documents developed by the Ministry of Energy of the USSR and Russia (the requirements are common for all countries). The maximum current level depends on the cable size. For example, for a wire with a diameter of 0.75 square mm, the limit is 15A of the load, and for a cross section of 5 square cm - 215A.
Application area

On the one hand, the PV-3 cable has a wide area of operation and application, on the other hand, it cannot always be used. The wire is single-core, which significantly reduces the scope of application. For example, for electrical wiring, it is generally recommended to run multicore cords. According to GOST PV-3 it is suitable for:
- electrical wiring, lighting;
- connection of electrical appliances and installations in residential and non-residential premises.
The cable is not a power cable, therefore it is not suitable for the same types of installation, two and three-phase connections. Here you need a cable with two and three cores, respectively.
The main purpose of the PGV cable is grounding, where a single-core wire is enough. If the main cable requires additional flexibility, you can use several PV-3 wires twisted together. In rare cases, soft cords are connected to power cabinets and machines in production.
Checking upon purchase

Manufacturers rarely adhere to the established standards of GOST and TU. Therefore, the electrical goods market is filled with counterfeit products. In most cases, such wires lead to short circuits, power surges, and fires.Therefore, before buying, you must carefully check the packaging, manufacturer, store (supplier).
Key recommendations:
- choose goods marked with GOST - the designation is at the end of a row of symbols on the cable;
- there must be a special sticker on the packaging material;
- marking symbols should be located along the length of the cable - average pitch - 0.5m;
- check the compliance of the section parameters - you can use a caliper;
- check the documentation - the seller is obliged to provide certificates confirming the quality of the products.
Professionals recommend that you periodically check the operation of the cable using power tests.
Cable selection instructions
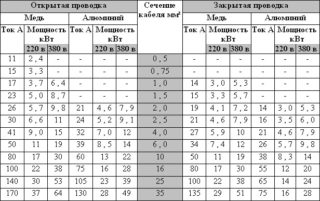
To choose a wire for the network, you need to decide on several parameters - section, material, brand. The most common materials are copper and aluminum. Copper has better conductivity and does not corrode. Aluminum is a soft material; strong bends in cables tend to break quickly. When in contact with air, aluminum is rapidly oxidized, and an oxide film forms on the surface. Such a film does not transmit the current signal well, and provides an unreliable contact.
The defining parameter of the section is diameter (d). At low current values, a copper conductor is used with a diameter of more than 1 mm2, an aluminum one - 2 mm2. When working with large currents, the diameter is selected based on the power of the network. The selection of the diameter is made according to table. 3, taking into account the laying of the cable through the pipe or open.
Errors when using the PV-3 cable
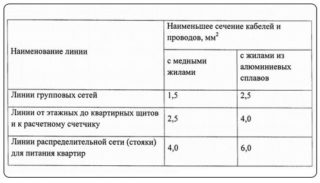
If the PV-3 wire is laid independently, some peculiarities and common mistakes should be taken into account. First of all, it is necessary to check the correspondence of the cross-sections of the inner core and the solid cable. If the diameter is smaller, overload and burnout cannot be avoided.
The inner cores of the wires must not be allowed to touch. This happens most often when connecting two-key and three-key switches. In this case, there will be a simultaneous closure of two networks, and therefore an interruption in work, lack of voltage, fire.
Soft single-core cable PV-3 is used in various conditions. The range of cross-sections and voltage levels allows for external and internal installation. For complex systems, stranded wires are used.








