The electrical industry offers customers a wide selection of conductors for creating electrical wiring, connecting devices to the mains. All products (wires, cords, cables) have their own technical characteristics, operating conditions and purpose. To be able to understand the variety of goods and choose the best option for work, you need to understand what wires are and correctly decipher the marking.
Basic concepts
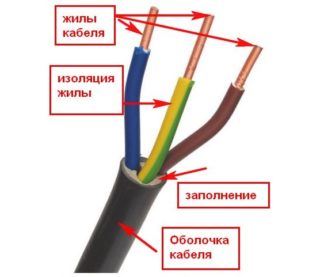
A wire is a product that consists of several parts that conduct an electric current. Conductors are used to connect instruments to a power point. The main parts are the lead conductors and the insulating layer.
A core is a metal wire that conducts an electric current. Its most important characteristics are the material of manufacture, the number of thin wires and the cross-sectional area. Wires can be divided into single-wire (monolithic) and multi-wire. The flexibility of the conductor depends on the number of cores - it increases with the number of wires. How much current the wire can carry depends on the cross-sectional area. Each material can pass a different current at the same cross section. To select a wire, you need to use special tables, which indicate the maximum load at a certain cross-sectional area.
Insulation is a dielectric protective layer that helps protect people from direct contact with the current conductor. In addition, insulation allows you to place several cores side by side without the risk of a short circuit between zero and phase, and also protects the wire from negative environmental influences. Usually the insulating layer is made of PVC, rubber, polyethylene and other materials.
It is not uncommon to make several layers of insulation. Additional protective layers are necessary when laying the wire in difficult conditions, unstable soils, under roads. Also included are armor, outer and outer protective layers.
Information about the material of the wire and insulation, the cross-sectional area can be found in the alphanumeric marking. It is regulated by the rules and is the same for wires and cables for different purposes. Letters indicate the type of conductor, material of execution, flexibility and other characteristics. The numbers show the cross section and the number of cores.
Difference of conductors by material
The main materials from which different types of wires are made are copper and aluminum. Less commonly, the conductors are made of steel wire. The types of cables and wires and their purpose depend on the properties, characteristics and positive qualities of a particular material.
Aluminum

The conductors made of aluminum have become a real discovery in electrical engineering. Aluminum is the fourth most conductive material after silver, copper and gold. This made it possible to reduce the cost of cable production and make electrification easier.
The benefits include:
- cheapness;
- chemical resistance;
- light weight.
Disadvantages:
- fragility;
- destruction of the protective oxide film under the influence of temperature;
- the complexity of soldering;
- deterioration of electrical conductivity due to the presence of impurities;
- short service life.
Aluminum requires regular maintenance, so this wiring will cost more than copper over time.In addition, the short service life and fragility make the long-term use of aluminum unprofitable. For this reason and for safety reasons, it is forbidden to use aluminum wires in the laying of new power lines.
Copper

Copper conductors are highly conductive. Other benefits:
- high flexibility;
- elasticity;
- Reliability;
- firmness;
- ease of soldering and welding;
- long service life.
Disadvantages:
- cost;
- high weight due to high density;
- oxidation of contact in air - it is necessary to lubricate the damaged area with special agents.
Copper is more beneficial to use. This is due to its characteristics, duration of operation and ease of installation. It is copper conductors that are used in all types of electrical wiring.
The main types of wires
The most important factor when choosing an electrical wire is the power of the connected household appliance. In everyday life, the types of electrical wires PUNP, PPV, PVS, ShVVP and others are most often used.
Flat wires

All cables from this group have similar characteristics and purpose.
- PUNP - a flat conductor with protection and single-wire copper conductors of the PBPP brand (also called PUNP) has a cross section from 1.5 sq. Mm to 6 sq. Mm. PVC is used as external and internal insulation. Working temperatures - from -15 ° to + 50 ° С. The minimum bend radius is 10 diameters. Operates at voltages up to 250 V and a frequency of 50 Hz. The main use is lighting group, sockets.
- PBPPg - Already by the name one can understand the distinctive feature of this conductor - it is its flexibility. The multi-core structure allows the bending radius to be reduced to 6 diameters. Other characteristics are similar to PBPP.
- APUNP - The wire with the APUNP designation is a single-wire aluminum conductor. Section 2.5 - 6 sq. Mm. The rest of the characteristics are similar to the PUNP wire. The cable is rarely used, since it is prohibited by the provisions of the PUE. Low cost.
All of the listed flat wires can only be used in lighting. For other purposes, it is better to purchase other conductors.
With jumpers
The analogue of the described conductor is APPV with aluminum conductors. The section starts from 2.5 sq. Mm. These types of wires are suitable for the lighting and power group.
Single-core

The automatic reclosure is made of aluminum and is a single-core conductor with a cross-section of 2.5 mm2. up to 16 sq. mm. single-wire and 25-95 sq. mm. for a multi-wire structure. PVC is used as insulation, which allows it to work at 100% humidity and temperatures from -50 ° C to + 70 ° C. There are no restrictions on use.
Also, representatives of single-core wiring products are PV1 and PV3. The numbers in the marking indicate the flexibility class. A single-wire copper core with a cross section of 0.75-16 sq.mm is used as a wire. or stranded with a cross section of 16-95 sq. mm. Soft wire PV3 is actively used in places where frequent bends and transitions are required.
Conductors for electrical cords

PVA is a copper wire with a stranded structure with a cross section of 0.75-16 sq. Mm. The insulation is multi-colored for the convenience of the master, the shell is white. It operates at a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 380 V. It has a high level of flexibility. Designed for approximately 3000 flexions or more. Operating temperature range from -25 ° С to + 40 ° С. PVSU modification is applied from -40 ° С to + 40 ° С.
ShVVP is a copper stranded conductor for connection, consisting of two to three stranded conductors. The section is 0.5-0.75 mm2. Not used for wiring inside walls. The main application is the lighting group and low-power household appliances.
Power cables

For indoor and outdoor wiring, crimp power cables are used. The most common is the domestic VVG. It is used to transmit current with voltage up to 1000 V. There are various modifications of wires with single-wire and stranded conductors with a cross-section of up to 240 sq. Mm. External and internal insulation is made of PVC. Maximum operating temperature + 40 ° С, humidity 98%. The most popular modifications include AVVG (made of aluminum with single-wire conductors), VVGng (non-combustible), VVGz (with filling between the insulations of rubber chips or PVC threads). The minimum bend radius for all versions is 10 diameters.
The European analogue of VVG is NYM. It is more reliable because it is made of high quality materials and has passed more stringent testing. As intended, it is a household cable for sockets or lighting. The maximum voltage is 660 V. The bending radius is 4 diameters. Operating temperature range from -40 ° С to + 70 ° С. Do not use NYM in direct sunlight or direct into concrete.
Flexible cable KG consists of 1-6 stranded copper conductors. It is designed to operate at voltages up to 660 V and a frequency of no more than 400 Hz. For internal and external insulation, rubber is used, which gives the wire additional flexibility. Operates at temperatures from -60 ° C to + 50 ° C. Scope - connection of powerful installations (welding machine, heater, generator). It is expensive, therefore, VVG cables are more often used in everyday life.
VBBShv - copper conductor with single or stranded conductors. Has a cross-section up to 240 sq. Mm. The insulation is made of PVC material. Under the lower shell, there is an armor made of two metal belts. It can withstand loads up to 1000 V and temperatures from -50 ° C to + 50 ° C. The following modifications are usually used - AVBBShv (made of aluminum), VBBShvng (non-combustible), VBBShvng-ls (no smoke and corrosive gas emission during smoldering).
Conductors for the transmission of information

Telephones, computers, television antennas are connected using special cables for transmitting information.
Antenna cable RK75 consists of a single or stranded copper conductor. The cross section is 1 sq. Mm. The insulating layer is made of polyethylene and braided shielding. The outer insulation is made of cambric. It is used to transmit low-current high-frequency signals.
Computer twisted pair is used to connect a PC to a local network. It consists of 4 or 8 wires that are intertwined with each other in pairs. A breaking thread is installed for additional protection. There are different types of cables with and without shielding, which are used for different purposes.
Telephone wires are low current. They allow you to install telephone lines in the house or lay them between substations.
Specialized cables

For work in non-standard conditions, conductors with special characteristics are used. These include the PNSV heating wire. Made of steel and galvanized. For insulation, heat-resistant PVC or polyethylene is selected, which retain their properties in the temperature range from -50 ° C to + 80 ° C. They work at a load of 220-380 V. The main field of application is the creation of warm floors.
WFP - copper cable with a cross-section of up to 25 sq. Mm. double insulated with polyethylene or PVC. It works up to 660 V. It is able to work with sudden pressure surges and temperatures from -40 ° С to + 80 ° С. It is usually used to power pumps that are lowered into wells.
RKGM - copper single-core power heat-resistant installation cable. The section reaches 120 sq. Mm. Works at voltages up to 600 V.Silicone rubber is used as the insulation material. The outer shell is made of fiberglass. Properties are maintained at temperatures from -60 ° C to + 180 ° C. Scope of application - places with high temperatures (baths, saunas, electric ovens).









