The electric cable is an invisible thing, but necessary in the house. Provides lighting, electrical appliances, heating and water heating and much more. Varieties, types and species number in the hundreds. It is enough for a beginner to know the most popular models.
- Varieties and features of electrical cables
- Lived in the wiring
- Insulation of electrical wiring
- The main types of electrical wires
- PBPP wire (flat)
- Modification of PBPPg
- Aluminum conductor APUNP
- Two- or three-conductor PPV
- Wire under the APPV brand
- Aluminum APV with PVC insulation
- Modification PV1 - PV5
- Connecting cord PVA with PVC insulation
- PVC-sheathed flat cord ШВВП
- Varieties of electrical cables
- VVG brand
- Power KG flexible
- Armored VBbShv
Varieties and features of electrical cables

The concepts of an electric cable and a wire should be separated, if only because they have different power indicators.
A cable is a product that combines three or more insulated conductors. They have additional protection from special materials: parchment, lead or rubber.
El wire is a product that consists of conductors united by a common casing. Their number can be from one to five.
Lived in the wiring
The core is often made of copper, since the current conductivity of this metal is high. It can be monolithic or consists of thin wires. The copper type of stranded conductor is stronger and preferable for wiring, as there will be high current conductivity with minimal heating.
There is one big drawback: inconvenience in use. The twisting of the veins does not give a complete connection, in contrast to the monolithic construction. Twisting friction leads to fracture, the section is reduced. In such cases, connecting parts (connectors) with threaded clamps are used.
Connections and fasteners are indispensable. However, stranded wires look sloppy and crooked when stapled. An unclosed box is also not an option, since the conductive parts fall out.
Insulation of electrical wiring

Insulating cable sheaths are made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). This material protects the consumer from unwanted contact with electrically conductive parts. In this case, the products are subject to:
- internal mechanical damage;
- superficial fractures, bends, twisting;
- excessive overheating,
- chemical oxidation.
This leads to malfunction of the cable and is a danger to humans.
To avoid deplorable situations, security measures are taken in the premises: the modern installation method involves laying wires in cable channels with different cross sections. They provide protection and visual control of the condition of the products.
The main types of electrical wires
Wires vary in power level, purpose and application conditions. It is enough to understand 9 types to find the right one for everyday use.
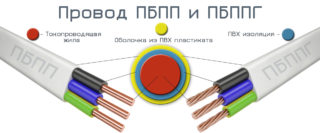
PBPP wire (flat)
The most common wire for household and power lines. Copper live parts allow a powerful load to be connected. It cannot work with high voltage (no more than 250 V).
PVC insulation hides a solid copper core. The cross section of this design ranges from 1.5 to 6 mm2.
The wire is heat-resistant (up to 50 ° C), while it does not withstand low temperatures (up to -15 ° C). Used when installing a socket line in residential premises.
Modification of PBPPg
The characteristics are similar to the previous type:
- immunity to heat;
- intolerance of low temperatures;
- withstands slight stress;
- section (up to 6 mm2).
Differs in a number of points:
- beam structure of the vein;
- high elasticity;
- prone to breaking or abrasion;
- the design includes 2 wires
PBPPg wire is popular in the domestic environment due to its flexibility and ease of installation.
Aluminum conductor APUNP

The cheapest electrical aluminum wire option on the market. Straight core with a cross-section from 2.5 to 6 mm2 is recommended for use in temporary buildings and in circuits with a low load.
Electricians note the only advantage - cost. But with constant use, this type can be dangerous.
Two- or three-conductor PPV
Current conductors or cores in this modification are held together with an insulating PVC strap. The product itself is also wrapped in PVC. The wire is capable of withstanding 450 V, at a frequency of 400 Hz. Resistant to low and high temperatures in the range from -50 to + 70 ° C.
Wire under the APPV brand

Similar in structure to PPV:
- resistance to temperature changes;
- multiple conductors;
- the presence of clips;
- work with high voltage and frequency.
An aluminum conductor with a cross section of 2.5 mm2 reduces the quality of the wire and the price. Used when laying open and closed wiring.
Aluminum APV with PVC insulation
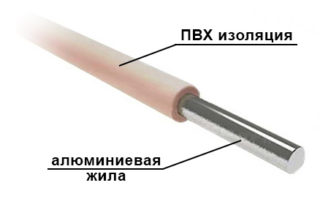
Available in two designs: monolithic and multi-core (bundle).
The cross-section range for a monolithic core starts from 2.5 and ends with 16 mm2, for a bunch one - from 25 to 95 mm2.
Popular for building electrical lines, as it is resistant to high humidity. Withstands from -50 to + 70 ° C.
Modification PV1 - PV5
Characteristics and technical indicators coincide with AR, only copper is used instead of aluminum.
Differs in color insulation and use of wire when assembling controlled cabinets.
Connecting cord PVA with PVC insulation

The electrical cord can contain up to five strands per bundle. The power is an order of magnitude higher than that of other species. Section from 0.75 to 16 mm.
Convenient to connect home appliances thanks to color separation. Supports operation in a network with a voltage of 380 V and a frequency of 50 Hz.
PVA is flexible, moreover, it is protected from pinching and fractures. The temperature regime is limited (from -25 to + 40 ° C).
PVC-sheathed flat cord ШВВП
Two or three wires are placed in the PVC sheath. The modification is flat, looks like a flattened cord with two connected parts. There are varieties with three conductors and a stranded structure of the current-carrying part.
Convenient, safe for outdoor wiring. Withstands voltages up to 380 V with a cross-section up to 0.75 mm2.
Varieties of electrical cables
VVG brand

Standard cable. Available in two variations: beam or solid structures. It can transmit current with voltages up to 1000 volts. Some models are up to 3000 V.
Suitable for drawing lines of force. The range of cores ranges from 1.5 to 5 mm. Temperature fluctuations are kept from -40 to + 50 ° С.
Some modifications differ in the insulating structure, the type of metal cores (instead of copper - aluminum) and the shape of the cable.
Power KG flexible
The virtue is flexibility. The GK power cable consists of four conductors (in individual series up to six) with insulation. Withstands a wide range of temperatures (from - 60 to + 50 ° С). Designed to connect power equipment.
Armored VBbShv
The robust cable can withstand high voltages. The current conductors are bundled and solid cores with ranges of 50-240 mm2 and 16-50 mm2, respectively.
The structure of the cable insulation is complex: belt insulation with tape screen, steel armor, bitumen and PVC. There are varieties with aluminum conductors. Do not burn or emit harmful substances when heated.