Historically, it was more profitable and cheaper to obtain electricity in the form of alternating current generated by generators of power stations. Such a representation made it possible to effectively transmit it over great distances. At the receiving end, it was converted into a single-phase voltage, convenient for consumers, and in this form entered the power line. However, the internal circuits of most modern electrical consumers require a constant power supply, the value of which is selected from the standard range of 5, 9, 12, 24, 36 or 48 Volts. To obtain them, a special voltage rectifier (for 24 Volts, for example) had to be introduced into the circuit of electronic devices.
Rectifier working principle

For a clear understanding of the principle of operation of a DC rectifier, you first have to take into account that semiconductor elements (diodes) are used to rectify AC voltage. Their distinctive feature is the ability to conduct current only in one direction. Due to this property, the alternating voltage applied to them at the output will have the form of positive ripples with cut off the lower halves of the half-period of the oscillations. With positive half-waves, a current will flow through the diode, which is the basis for the formation of a constant power supply. To obtain it, additional electrical elements are required.
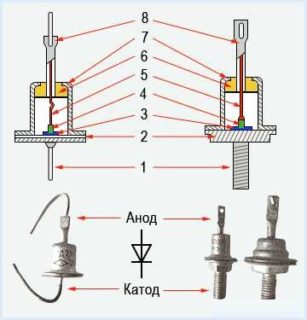
Any current rectifier includes the following main units:
- A step-down transformer that converts 220 volts to the desired value;
- a set of diodes (bridge);
- smoothing (filtering) capacitor;
- stabilizer made on the basis of transistor elements.
Many variants of electronic rectifiers are known, differing in the number and method of connecting diodes, as well as in their operating parameters. Of particular interest are various approaches to the inclusion of diode elements in the circuit. The stabilizing stage of the rectifier is assembled on transistor switches called electronic relays.
Rectifier types
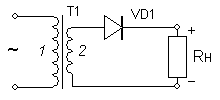
Depending on the method of switching on semiconductor diodes, all AC rectifiers are divided into the following types:
- half-wave (half-wave);
- full-wave (full-wave with a midpoint or Mitkevich schemes);
- bridge or Gretz rectifiers;
- rectifiers with a doubling of the operating voltage and other less common circuits.
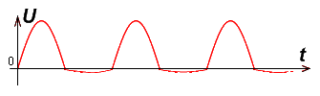
Half-wave is the simplest method used for AC rectification. Another name is zero rectifier circuit.
With the help of devices of this class, it is possible to obtain only a pulsating (used only half) output current. Circuits based on the half-wave principle are characterized by low conversion efficiency and are rarely used. Their full-wave counterparts have two diodes in their composition and provide rectification of half-waves of both polarities. They are more efficient and are used in the simplest power supplies.
Single-phase bridge rectifiers, the so-called 4-diode Gretz circuits, are characterized by high efficiency, which is understood as the efficiency of using the power received from the transformer.
The voltage at the output of semiconductor rectifier bridges is a good basis for subsequent smoothing and stabilization - obtaining direct current.
They are widely used in devices with increased energy intensity such as generators with output voltages from tens to hundreds of volts. Their advantages include:
- low reverse voltage (fraction of a Volt);
- small dimensions;
- high efficiency of using the transformer (in comparison with the Mitkevich scheme).
A significant drawback of bridge circuits is twice the voltage drop across the diodes, which makes it necessary to choose the output parameters of the transformer with a margin during their development. This part of the usable power is then lost at the junctions of the four diodes.
Rectifier types by functionality
According to their purpose and functionality, well-known samples of rectifiers are divided into single-phase and three-phase devices. The former are used in the electrical networks of apartment buildings and private houses and are designed to power household appliances. The second is an electronic module of 3 of the same type of units, manufactured according to one of the following schemes:
- single-ended rectifiers;
- push-pull systems;
- combined modules: with two three-phase windings with parallel and series connection of diodes.
The use of single-ended transformation circuits is limited due to the low efficiency of the rectified voltage. Their two-stroke analogs are widely used in DC motors and other electric machines containing brush assemblies in their design. In addition to classic rectifiers designed for installation in collector motors, there are circuits that can increase the output voltage several times. A special case of such solutions is a voltage doubling rectifier.
The rectifier circuit with voltage doubling differs only in details from the options already considered. Such devices are usually called multipliers, which are easily assembled by hand.
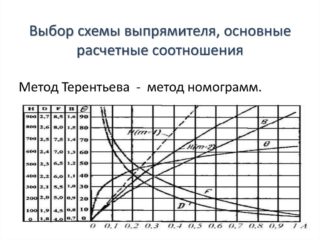
Basic relationships when calculating a rectifier
- input voltage acting in the secondary winding of the transformer;
- the current in the diodes, flowing in the circuit, taking into account the load;
- the capacity of the electrolytic capacitor, selected based on the specified ripple smoothing factor;
- maximum voltage on it.
It is important to consider the voltage drop across solid state diodes when open.
The calculated ratios for this case are presented in the following form.
- The current in the transformer winding is equal in magnitude to its maximum value in the load (Iwind = Iload).
- The voltage in the secondary winding in no-load mode is U2 ≈ 0.75Uload.
- It is recommended to take rectifier diodes with the following parameters: Urev> 3.14Uload, and Imax> 1.57Iload.
Rectifiers are widely used in various fields of electrical engineering and electronics, including modern control systems. Therefore, it is so important to understand what rectifiers are and what types of them are used to build the most efficient circuits.