Due to the use in everyday life of a large number of electrical appliances (microwave ovens, electric kettles, computers, etc.), it is often necessary to adjust their capacities. For this, a thyristor voltage regulator is used. It has a simple design, so it's easy to assemble it yourself.
Nuances in design

A thyristor is a controlled semiconductor. If necessary, it can conduct current very quickly in the desired direction. The device differs from the usual diodes in that it has the ability to control the moment of voltage supply.
The regulator consists of three components:
- cathode - a conductor connected to the negative pole of the power supply;
- anode - an element connected to the positive pole;
- controlled electrode (modulator), which completely covers the cathode.
The regulator operates under several conditions:
- the thyristor must fall into the circuit under the general voltage;
- the modulator must receive a short-term pulse, allowing the device to control the power of the electrical appliance. Unlike a transistor, the regulator does not need to hold this signal.
The thyristor is not used in DC circuits, as it closes if there is no voltage in the circuit. At the same time, in AC devices, a register is necessary. This is due to the fact that in such circuits it is possible to completely close the semiconductor element. Any half-wave can cope with this, if such a need arises.
The thyristor has two stable positions ("open" or "closed"), which are switched by voltage. When a load appears, it turns on, when there is a loss of electric current, it turns off. Beginning radio amateurs are taught to collect such regulators. Factory-made soldering irons with tip temperature control are expensive. It is much cheaper to buy a simple soldering iron and assemble a voltage register for it yourself.
There are several schemes for mounting the device. The most uncomplicated is the hinged type. No printed circuit board is used for its assembly. Also, no special skills are required during installation. The process itself takes little time. Having understood the principle of operation of the register, it will be easy to understand the circuits and calculate the optimal power for the ideal operation of the equipment where the thyristor is installed.
Scope and purpose of use
They use a thyristor in many power tools: construction, carpentry, household and others. It plays the role of a key in the circuits when switching currents, while working from small pulses. It turns off only at zero voltage level in the circuit. For example, the thyristor controls the speed of the knives in the blender, regulates the speed of air injection in the hair dryer, coordinates the power of the heating elements in the devices, and also performs other equally important functions.
In circuits with highly inductive loads, where the current lags behind the voltage, the thyristors may not close completely, leading to equipment damage. In construction devices (drills, grinders, grinders, etc.), the thyristor switches when a button is pressed, which is in a common block with it. At the same time, changes occur in the operation of the engine.
The thyristor regulator works perfectly in a brushed motor, where there is a brush assembly. In asynchronous engines, the device will not be able to change the speed.
Operating principle
The specificity of the operation of the device lies in the fact that the voltage in it is regulated by power, as well as by electrical interruptions in the network. At the same time, the current regulator on the thyristor passes it only in one specific direction. If the device is not turned off, it will continue to work until it is turned off after certain actions.
When making a thyristor voltage regulator with your own hands, the design should provide enough free space to install a control button or lever. When assembling according to the classical scheme, it makes sense to use a special switch in the design, which shines in different colors when the voltage level changes. This will protect a person from unpleasant situations, electric shock.
Methods for closing the thyristor
The supply of a pulse to the control electrode is unable to stop its operation or close it. The modulator only includes a thyristor. The termination of the action of the latter occurs only after the current supply is interrupted at the cathode-anode stage.
The voltage regulator on the thyristor ku202n is closed in the following ways:
- Disconnect the circuit from the power supply (battery). In this case, the device will not work until a special button is pressed.
- Open the anode-cathode connection with a wire or tweezers. All voltage goes through these elements, entering the thyristor. If the jumper is opened, the current level will be zero and the device will turn off.
- Reduce voltage to minimum.
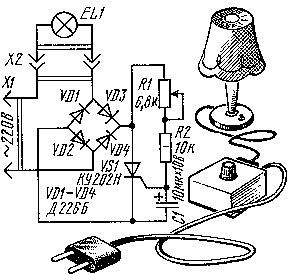
Simple voltage regulator
Even the simplest radio component consists of a generator, a rectifier, a battery, and a voltage switch. Such devices usually do not contain stabilizers. The thyristor current regulator itself consists of the following elements:
- diode - 4 pcs.;
- transistor - 1 pc;
- capacitor - 2 pcs.;
- resistor - 2 pcs.
To avoid overheating of the transistor, a cooling system is installed to it. It is desirable that the latter has a large power reserve, which will allow charging in the future batteries with a low capacity.
Methods for regulating the phase voltage in the network
Alternating electrical voltage is changed using electrical devices such as thyratron, thyristor and others. When the angle of these structures is changed, the load is supplied with incomplete half-waves, and as a result, the effective voltage is regulated. Distortion causes current to rise and voltage to drop. The latter changes its shape from sinusoidal to non-sinusoidal.
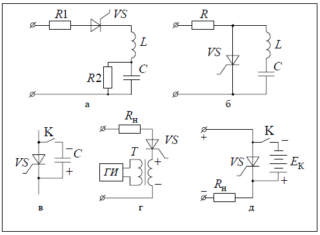
Thyristor circuits
The system will turn on after enough voltage is collected on the capacitor. In this case, the opening moment is controlled by a resistor. In the diagram, it is designated as R2. The slower the capacitor charges, the more resistance this element has. The electric current is regulated through the control electrode.
This circuit makes it possible to control the full power in the device, since two half periods are regulated. This is possible due to the installation of a thyristor in the diode bridge, which acts on one of the half-waves.
The voltage regulator, the diagram of which is presented above, has a simplified design. One half-wave is controlled here, while the other passes through VD1 unchanged. Works in a similar scenario.
When working with a thyristor, a pulse should be applied to the gate electrode at a certain moment in order for the phase cut to reach the required value. It is necessary to determine the transition of the half-wave to the zero level, otherwise the adjustment will not be effective.

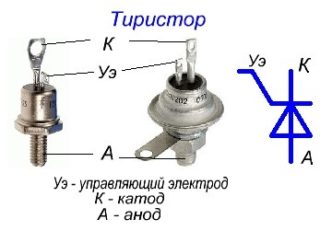
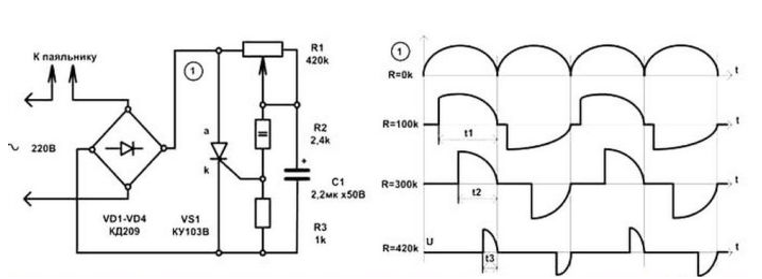
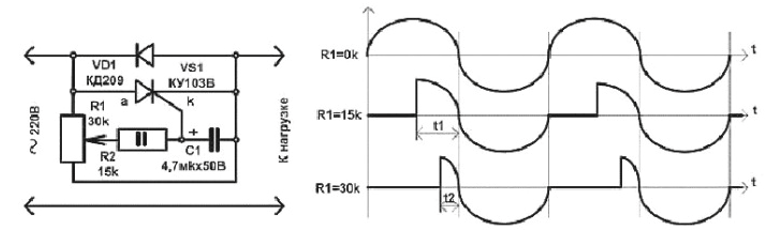








The thyristor closes when the current through it is zero, and not the voltage across it is zero.KU-201 and KU-202 are thyristors controlled by the anode, they are depicted in the diagrams differently.