When installing electrical panels to combine a line of automatic machines or RCDs, prefabricated connecting jumpers of various designs are used. A 3-phase distribution bus is one of such elements used in the arrangement of 380 volt power cabinets. Connectors of this type provide a reliable connection of several 3 or 4-pole circuit breakers in an electrical panel and make it possible to do without the tedious installation of jumpers from copper conductors.
Busbar design

Unlike single-pole devices, where one phase contact is bridged, four insulated combs with fixed pins are provided in the design of the three-phase connecting bus. With their help, the phase contacts are connected on 3 and 4-pole circuit breakers, as well as on residual current devices designed for 380 volts. The fourth row is used to combine zero terminals when connecting several group or linear RCDs.
When carrying out similar operations in 3-pole machines, where only the phases are brought in, the contact taps of the fourth connecting row are simply folded back.
When installed instead of two protective devices, a 4-pole differential circuit breaker that completely replaces them, the comb taps are connected to all contacts involved in the circuit.
Known examples of three-phase bus connectors have designs that differ in pitch between taps in each of the 4 rows (18 mm and 27 mm). The first of them is in demand when combining machines in a single-module design: the total number of seats occupied is 3 or 4. The second, rarer version is chosen with a case width of 1.5 modules: the length occupied is 4.5 or 6 seats. The design of the copper connecting busbars allows the installation of a package of machines with a total number of pins from 12 to 60 pieces.
It makes no sense to purchase combs if you need to install a small number of 3-phase protective devices. Usually they are in demand when installing switchboards with a large number of automatic devices, RCDs and other switching devices.
When getting acquainted with the design of a copper rail, it is also important to take into account its working section, which, according to the standards, should be at least 16 sq. mm. Confirmation of the effectiveness of the use of these electrical products is the approximate calculation of the volume of conductors saved when using buses.
Types of bends
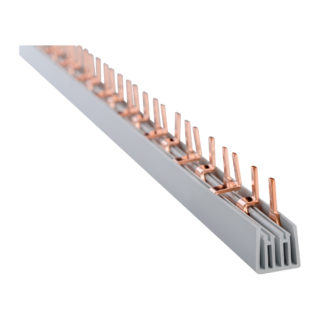
There are two types of connecting contacts of copper busbars, which differ in their design and installation features.
- Connectors made in the form of pins and having the generally accepted designation "Pin". These products are suitable for the vast majority of models of automatic devices.
- Fork elbows, labeled as “Fork”.
The second variety is rarely used in domestic conditions, which is explained by the special requirements for its installation. For reliable fixation of such taps, a special clamp is required, which is not provided for by the complete set of most of the connected AB. Regardless of the type of diverting pins, their cross-section is selected so that the copper material does not overheat at operating currents up to 63-100 Amperes inclusive.
When choosing three-phase buses, differing in the type of connecting taps, the design features of the machine itself are taken into account. For each set of devices connected to a DIN rail, very specific brands of dies are suitable.If you try to make a connection with a ridge, the taps of which do not correspond to these devices, they will not go all the way into the fixing slots. In this case, a small part of the plane of the shank will remain open for touch.
According to the PUE, the presence of parts of the comb that are not protected by insulation is a violation of safety requirements.
As an example of the use of busbars of various classes, we consider automatic switches of the "ABB" brand, which are traditionally produced in two different versions. The first of these are referred to as "S200". They are designed for the installation of a PSH busbar. For Class II instruments marked as "S200L", dies with the designation PS are required.
Experts note that Chinese tire products with standard taps in size and pitch sometimes do not fit with machines from other foreign and domestic manufacturers. Therefore, professional electricians are advised to purchase them only after consultation with an electrical engineer.
Advantages and disadvantages
- simplicity of design, significantly reducing the installation time of the entire switch cabinet;
- reliable electrical contact between the terminals of individual modules;
- double reduction in the number of connections, significantly increasing the operational reliability of the entire structure.
The latter is explained by the fact that when installing standard wire jumpers, one phase terminal has two contact ends cleaned of insulation. When using a three-phase comb, only one branch is connected to each of the phases.
The disadvantages of using such connectors include:
- the inconvenience of updating three-phase machines or RCDs, since in this case you will have to remove the entire comb;
- the impossibility of increasing the total number of devices in the line. This will require a larger tire.
- during installation, you will need to select the same type of machines, since the same comb may simply not fit different devices.
Professionals offer a simple solution to the problem of adding new devices to the samples already available on the din-rail. To do this, install a pair of backup devices with the most "popular" ratings of 16 and 25 Amperes on the mounting plate in advance and connect only their upper contacts (the lower terminals will remain in reserve). All this time, the switching mechanisms of the machines remain in the off state.
If you urgently need to use another device, it is enough to connect a new load to its three lower contacts.
Tire installation procedure and maintenance
During installation, it happens that the uninsulated part of the comb does not completely enter the contact crimps. To avoid this violation, the plastic insulator in its design, slightly protruding outward, will need to be positioned with a protrusion towards the screw fastening. If this is not done, you will get a not very neat connection with a partially bare plane, devoid of the smoothness of the bending lines.
When installing 3-phase combs, special attention is paid to the location of insulators, since violation of this rule is fraught with dangerous phase-to-phase short circuit.
When installing connecting busbars that combine the terminals of the RCD and three-phase circuit breakers, it is imperative to observe the marking specified in the standards. It is located on the instrument housings and indicates the order of the phases.

The combs are available for sale in the form of rulers already measured according to a standard size with a different number of mounting pins. Immediately before connecting the three-phase machines, their total number is calculated and, taking into account the thickness of the module, the excess is cut off from the bus.Situations are possible when devices of different classes (three-phase 3-pole AB and 4-pole RCDs) are combined in one line in the control cabinet. In this case, the installation of copper jumpers is somewhat complicated, since in the area of the connection to the machines, their spikes will need to be slightly bent to the side.
During the preventive examination of the elements of the switchgear cabinets, special attention is paid to the connecting bars in the place of fixing their taps in the slots of the machines. Over time, from significant current loads in the contact zone, the metal heats up, which manifests itself in the formation of a characteristic darkening. During long-term operation, this place is simply charred and covered with black carbon deposits, which often leads to thinning and a sharp decrease in the conductivity of the bridges.
To avoid the unpleasant consequences of burning, it will be necessary to replace the copper bus, for which you will have to completely dismantle it. Due to the design features of the crossing combs, it is not possible to replace one of the 3 or 4 rails. In this case, you have to change the entire product assembly.
A three-phase connecting comb used to combine the input of circuit breakers and RCDs is a very reliable way to obtain a single structural unit. Rows of several different types of modules with a reliable connecting bus are installed not only in closed distribution cabinets. Such a structure can be mounted in any other place inside the house, well protected from the weather and specially designated for this purpose.










