Surge arrester or surge suppressor nonlinear - the main device (switching device) to protect the branch of the power line from sudden surge overvoltage. Replaced valve resistors. Production and installation standards were introduced by GOST R 52725-2007. In different sources, to designate a limiter, there is the concept of a spark gap without spark gaps or the abbreviation UZPN.
The need for surge protection

Impulse overvoltage - a sharp increase in the potential difference in the network, exceeding the maximum limit of the operating voltage. The jump is short - up to 1 nanosecond (1 x 10-9 sec.), so conventional ultrasonic detectors may not have time to work and pass a pulse into the internal power grid. The amplitude can be 10 times the nominal.
Origin:
- atmospheric (thunderstorm) - caused by a lightning strike with an average current of 200 kA into a lightning rod of a house or objects next to it (the current goes into the ground, but EMF appears in the house wiring);
- switching - malfunctions or replacement of switching equipment / circuit sections, starting powerful electrical equipment, failure of a transformer.
Regardless of the nature of the occurrence, such malfunctions carry a risk for all connected devices: ignition of the wiring insulation (designed for 1-1.5 kV), damage to the electrical circuits of the devices and their complete unsuitability for repair.
Device and principle of operation of the nonlinear limiter
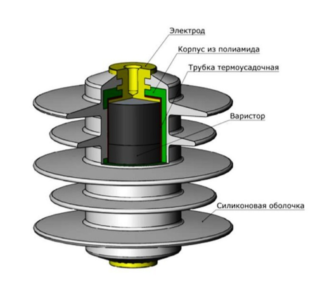
The operation of a surge arrester is based on a specific property of a varistor - a semiconductor with a nonlinear current-voltage characteristic. With a regular potential difference, the electrical permeability of the element tends to zero and amounts to several mlA. A sharp voltage jump opens the tunneling conductivity (> 1000 Am), the resistance practically disappears, and the pulse is promptly removed from the system. The conductor material is zinc oxide, sometimes with the addition of oxides of other metals (cobalt, bismuth, etc.).
The arrester consists of circular cross-section resistor plates (the number is based on the design overvoltage), which are stacked in a column, placed in a fiberglass tube and sewn into a ribbed insulating jacket. Tightness provides filling of voids with a viscous silicon-organic compound. The structure is tightly clamped by flanges on both sides. A feature of the device in the implementation of a quick and safe output of thermal energy into the environment - during the reception of the pulse, the temperature of the varistor reaches 100-150 ° C.
The design of modern modular restraints is different. This is a plastic case 17.5 mm wide (OIN-1), which contains a thermal fuse, a removable varistor block and terminals with notches. There are models with indicator lights. DIN rail mountable.
On one side of the arrester, the power cable is fixed, and on the other - the ground.
Types and main characteristics of surge arresters
Impulse voltage limiters are distinguished by insulating material (porcelain and polymer), design (single-column and double-column), voltage classes and protection.From the transcripts it is clear what an arrester is in an electrician. Reading designations in accordance with GOST:
SPN - X - 1/2/3/4 XX
The first abbreviation stands for non-linear surge suppressor. On the market, there are options for OPS (C - networks) or SPE (I - impulse) products.
- X - tire material: P - polymer, no letter - porcelain;
- 1 - network voltage class in kV: 1.5, 4, 6, 10, 36;
- 2 - the highest effective operating voltage, kV: 3 - 475;
- 3 - rated discharge current, kA: 5, 10, 20;
- 4 - current throughput, A (up to 200 - 1 class of throughput, 750 - 2, 1100 - 3, 1600 - 4, over 1601 - 5);
- XX - letters denote a climatic region or their combination (common: U - moderate, Chl - cold, UHL), the number indicates the conditions of placement (1 - outdoors, 2 - under a canopy, 3 - indoors, 4 - in spaces with artificial microclimate regulation, 5 - in conditions of high humidity).
In the description of modular arresters, the number of poles P1-4 is indicated.
Protection classes and circuit for connecting arresters to the network
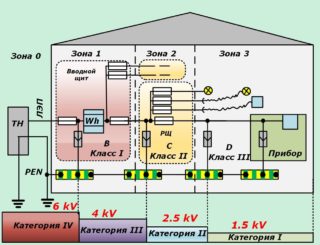
For comprehensive protection of internal power supply systems from the penetration of a powerful destructive impulse, the arresters are distributed in stages depending on the protection class.
- Class B accepts the consequences of a direct lightning strike on power lines or home electrical protection equipment. Installed on an external switchboard at the input of the power line to the structure.
- Class C handles switching surges and lightning storms that have passed the first stage of protection. The device is placed in the main switchboard inside the cottage or in an annex-garage, an entrance of a multi-storey building, on the administrative building floor.
- Class D is designed to extinguish residual effects. Useful directly in front of electrical appliances. The limiter can be integrated into the socket.
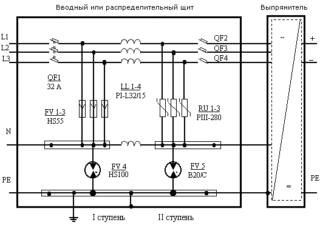
The arrester connection diagram has its own characteristics for single-phase and three-phase networks, TNC and TNS grounding principles (combined or not, main and protective conductor).
The devices are installed parallel to the main network in front of the auxiliary generator, meter and other equipment. To avoid the consequences of a possible short circuit to earth, a circuit breaker is used in front of the arrester.
In the scheme for connecting OIP-1 to a single-phase network, a power line fits to one terminal, and an earthing cable is fixed to the other. When separating zeros, the main one is connected to the ground separately. A three-phase network assumes protection of each phase separately (and zero for TNS).
Safety and efficiency of electrical protective equipment

The safety of electrical systems in office buildings and apartment buildings is the responsibility of public utilities. In a private house, the owner takes care of the security himself.
Installation of surge arresters should be entrusted to a professional, although the difficulties are initially invisible. It is important to avoid cheap, low-quality equipment, which itself can become a hotbed of danger. Electrical equipment must be used strictly in accordance with the technical specifications.
It is rational to check the serviceability of the equipment in March – April before the start of the thunderstorm season. There are 2 main methods of diagnostics of protective devices: non-contact measurement of the heating temperature with a thermal imager is carried out first of all, according to the results, the passing current is additionally monitored with a micro- or milliammeter.
The modular voltage limiter is equipped with an operability indicator window: green indicates readiness to perform functions, red indicates a fault. In the latter case, prompt replacement of the varistor part is prescribed. Thus, this type of electrical equipment is easier to use at home.
Surge arrester - electrical equipment that protects against short-term high-amplitude voltage surges.It is not able to cope with sustained overvoltage or a drop in potential difference, therefore it is used in conjunction with an ultrasonic probe and an RCD.








