The standard parameters of the electrical network of private houses are 3 phases, voltage 380 V. Power is allocated 15 kW, and a 4-core cable type is used for wiring. For this reason, switching and protective devices are closed against illegal connection. Self-assembly of an electrical panel for a private house 380 V 15 kW provides for its installation in an area accessible for inspection and basic application.
- Characteristics and specificity of a three-phase network
- The structure and elements of the electrical panel
- Choosing a three-phase electrical panel assembly scheme
- Using a cross-module for a three-phase switchboard
- Assembling a 380 V switchboard only on differential circuit breakers
- Scheme with two RCDs
- One RCD for each phase
- RCD at the input and single-pole automatic machine
- More than three group RCDs
- Algorithm for load distribution across three phases
- General procedure for grouping the load on machines
- The specifics of the assembly of the shield in a wooden house
- The nuances of the choice of materials
- Switchboard requirements
- Useful tips when assembling the switchboard
Characteristics and specificity of a three-phase network
The 380 V electrical network is designed to connect three-phase and single-phase equipment. In the case of a three-phase connection, it is connected to 3 phases and neutral to evenly distribute the load of powerful household appliances.
The presence of three phases allows the use of 4-5-core wires with a smaller cross-section and difavtomats for 3-4 poles. The allocated power for the 380 V network is divided equally in phases. That is, if 18 kW is allocated, each phase will be 6 kW.
With the help of a three-pole or four-pole type circuit breaker, the line is de-energized in the event of an increased load of one phase. Taking into account the time delay of the difavtomat, it is required to correctly distribute this load.
Without load sharing, "phase imbalance" occurs, which leads to a permanent shutdown of electricity.
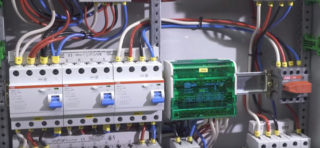
The structure and elements of the electrical panel
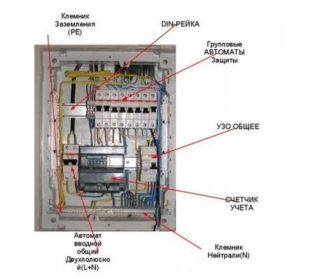
For a three-phase switchboard with a power of 15 kilowatts and a consumption power of 15 kW / h, you will need the following components:
- Electricity metering device. The counter is installed in the dashboard immediately. Electronic models with high accuracy and reliability are suitable for a home network. They work at several tariffs, display data on a digital display.
- Electrical panel. It is a box of various sizes. The outdoor version should have a DIN rail, a lock, an inspection hole for taking readings. The optimum level of dust and moisture protection is IP 54, the wall thickness is 1 mm.
- Difautomat at the input. A three-pole model is suitable, connected to three phases.
- RCD. A protective element against the emergence of a dangerous potential on the device body.
- Automatic switch. In a private house, a 25 A device is required for input, for a lighting system - for 6.3 or 10 A, for a power circuit - 16 A. The power of such a switch is from 7 kilowatts.
- Voltage relay. Prevents damage to household equipment due to voltage fluctuations.
- Measuring devices. A voltmeter and an ammeter in one housing is an optional device.
To prevent impulse fluctuations and protect against lightning, you can replace the relay with an SPD.
Choosing a three-phase electrical panel assembly scheme
The assembly of a 380 shield for a house is carried out according to several schemes. Unlike an apartment, in addition to protective automatics, an RCD is installed in houses, through which lighting is started. The purchase of an element affects the budget of the work, but the power supply system turns out to be reliable and safe.
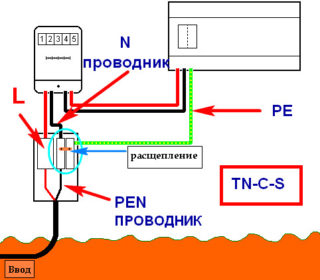
The installation of a distribution box provides for the organization of the grounding line. A private house is grounded according to the schemes:
- TN-C-S. Recommended by PUE, but only suitable for new highways with regular maintenance.
- TT. It is mounted on the basis of protective devices and a ground loop.
The operability of the constituent grounding schemes is supported by the user.
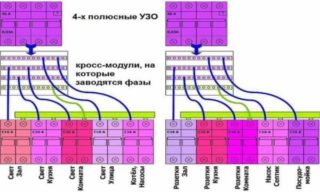
Using a cross-module for a three-phase switchboard

For ease of assembly of a 380 V switchboard and the possibility of reconnecting machines to other phases, a cross-module is used. It is placed after the counter. A feature of the device is the presence of three outputs for three phases and several outputs with similar phases.
Through the cross-module, the load is divided into difavtomats. The connection is done like this:
- The termination cable is inserted into the socket.
- The core is fixed with a clamping screw.
- To reconnect the phases, the screw is unscrewed, the wire is removed and connected to the free output of the desired phase.
It is only necessary to swap the wires when one of the phases is overloaded.
Assembling a 380 V switchboard only on differential circuit breakers

Difavtomat - a device for a separate line, which works as a conventional automatic machine and protection device against current leakage. A separate device can be supplied to each consumer group, distributing the load without phase imbalance.
The advantages of the assembly diagram of a three-phase switchboard on difavtomat for a country or private house:
- protection of each line against leaks, overloads, short circuits using one device;
- quick search for a problem area in case of breakdowns;
- lack of zero tires;
- selection of the number of difavtomats by the number of branch lines;
- independent choice of the principle of grouping elements in the box;
- ease of phase load distribution.
Cons of connection - you will need an overall switchboard, more than 72 modules, which is very expensive.
Models with indication of the cause of operation determine why the differential machine has turned off.
Scheme with two RCDs
The assembly of the panel according to the connection diagram with two 380 Volt RCDs implies the installation of powerful devices at the input. Neutral and grounding buses are located near each consumer group. Zeros are fed through a separate mounting rail:
- the element is painted blue with nail polish or acrylic paint;
- teeth are removed from the tire after 1;
- the neutral wire is connected from the bus;
- the teeth are inserted into the grooves and tightened with the clamping screws.
After the RCD, a cross-module is installed, where the phase is started. Line breakers are thrown at the exit.
The advantages of the scheme include:
- affordable cost of consumables;
- small dimensions of the box;
- ease of switching one or two consumers from the group.
There are many more disadvantages of the assembly:
- high costs for three-phase RCD models;
- difficulties with reconnecting group consumers;
- long search for the cause of the problem;
- disconnection of 50% of consumers from the network at the time of operation of one machine;
- problem with load balancing and separate placement of wet and dry zones.
The scheme is suitable if you have a suburban wooden house that is used periodically, and not all year round.
Sign or apply labels to avoid confusing tires.
One RCD for each phase
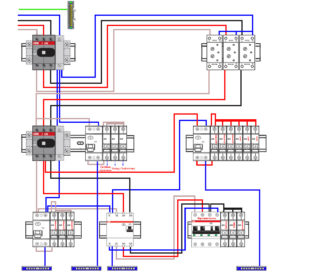
The circuit can be assembled from two-pole RCDs and cross-modules after each. The load, distributed over the phases, is fed to the outputs of the residual current devices. There will be three neutral and grounding buses - according to the number of RCDs.
The benefits of being connected include:
- logical distribution of consumer groups;
- shutdown of 20-25% of consumers when one RCD is activated.
The disadvantages are the problematic allocation of "wet" rooms into a separate group without phase imbalance, the time spent searching for breakdowns.To eliminate the disadvantages, you can assemble each group on a separate din rail, install an RCD, and then place the machines in series.
Install individual RCDs on dangerous lines.
RCD at the input and single-pole automatic machine
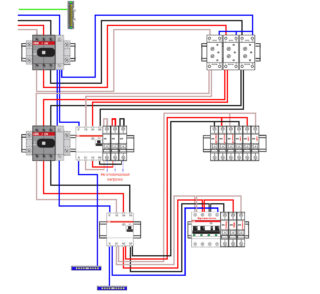
The simplest and most popular assembly of a three-phase switchboard, which does not allow changing the order of the elements in the future. The phases are loaded only once. The scheme differs in budgetary cost and is implemented in a small panel for 54-72 modules.
At the input, an RCD is installed, and single-pole models are used to distribute the load. PUE limits the user in the number of connection lines. The basis is clause 7.1.83, where it is said that the total leakage current should not exceed 1/3 of the nominal value. Under the current leakage of the PUE network, they mean 10 μA per 1 m of wire.
The circuit is advantageous in terms of the cost of elements, a small box size, which contains about 32 modules. Its disadvantages include problems with grouping, the inability to change the phase load, the presence of zero buses. To equalize the voltage, you will have to almost completely sort out the shield. Otherwise, a strong voltage imbalance, heating of the bus with zero burnout and overloading of machines is possible.
The RCD often trips in a false mode.
More than three group RCDs
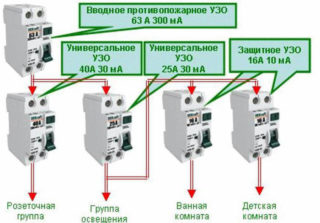
Electricity in a country house and a cottage flows through a large number of lines. In the case of installing 3 protective devices, problems arise with the search for damages, separate group wiring of wet rooms and the street.
A multilevel protection system with individual RCDs after group RCDs will allow organizing separate power supply for "wet" and "dry" zones. The number of groups per phase is determined by the number of consumers, the characteristics of the breakdown of the load and the size of the switchboard.
Before work, you need to calculate the costs for each node, taking into account the cost of a din-rail, bus, cable. The implementation of an introductory board with more than 3 RCDs, designed for 380 Volts, has several nuances:
- in order not to get confused, you need to sign or mark each wire, machine and RCD;
- indicate to which phase the conductor is brought out. For example, three RCDs are connected to the first phase. The first one indicates L1-1, the second - L1-2, the third - L1-3.
Despite the complexity of the scheme, the system is personalized. If one RCD has tripped, the fault can be detected on a specific line. When the device is activated, a small amount of equipment is turned off.
Algorithm for load distribution across three phases
The main difficulties in assembling the structure are grouping and even division of the load so that powerful equipment does not become the reason for shutdown due to overload. This will come out with a total power not exceeding the nominal and not simultaneous operation of all devices.
General procedure for grouping the load on machines
Simple and reliable is the scheme with the installation for a separate consumer group or powerful equipment of an individual machine and RCD. The disadvantages of connecting are a large three-phase shield and the cost of its arrangement. An alternative is to supply several lines to one machine and the correct sequence of their combination:
- To connect sockets and lighting devices, you need to use different machines. This will exclude the de-energization of the entire network in the event of a breakdown of one group.
- A bathroom, kitchen or sauna ("wet zones") cannot be placed in the same group with the "dry" ones. Automatic machines for humid environments are selected with different characteristics.
- Street group - lights and sockets are connected to separate automatic devices. It is allowed to combine this group with outbuildings.
- Separate machines are used to power automatic gates, security lighting and ACS.
- To power powerful household appliances, personal RCDs and automatic machines are installed.You can group an electric oven with an electric stove, a washing machine and a dishwasher, a flow-through and storage boiler. To avoid overloading, it is not recommended to connect the devices at the same time.
For the correct formation of groups, make a list of lines with an indication of the load of each.
The specifics of the assembly of the shield in a wooden house
The increased degree of flammability and the risks of fire situations provide for a special procedure for installing the shield in wooden houses. Initially, the lumber is impregnated with anti-fire agents that can hold fire for up to 20 minutes. To exclude the possibility of fire, you will need to adhere to a strict sequence of work.
The nuances of the choice of materials

When selecting materials, the following nuances are taken into account:
- A wooden house can only be electrified with a copper cable. The wire must be marked "ng" and LS - two-layer non-combustible insulation.
- Selection of conductor cross-section. You can calculate using the formulas or use the PUE table.
- All points of the wiring, including the outlet and lighting, are grounded.
- It is allowed to use a three-, four-core wire.
- Mandatory installation of an RCD to protect the breakdown along the hull and fire the logs.
- Installation for each line or group of a separate machine with a capacity in accordance with the total load on the network.
- Separate shutdown device for each group. For a two-story building, a 25 A model is sufficient at the input and separately for a group - a 16 A device.
- The choice of sockets depending on the method of wiring - hidden or open.
The meter should be located in front of the input machine for the convenience of sealing.
Switchboard requirements
The correct electrical panel for a house made of wood is metal, which does not come into contact with lumber. The wall thickness of the product is from 1 to 2 mm, but in case of a short circuit, the electric arc burns through the metal. In this case, you can finish the wall with bricks and put the box on the finished surface. The second option of the interlayer is an asbestos-cement slab or laying a cut of asbestos fabric under the box, folded several times.
Useful tips when assembling the switchboard

To assemble an electrical panel with electricity meters and protective equipment designed for 380 V 15 kW, you will need to purchase a high-quality moisture-resistant box. The wires are thrown onto the machines with special crimping tips, crimped with pliers.
Insulation tape will not provide a reliable coating. It is more convenient to work with heat-shrinkable tubes, which, when heated with a hairdryer or a lighter, tightly crimp the product.
The cores are selected with the same cross-section. Different cable cross-sections in one terminal of the switch will lead to melting of the insulation and fires.
The finished box must have marked elements. This will make it easier to turn off the power supply to a separate room. You can sign the knots with a marker or stick paper labels on the tape.
The input distribution device is installed on a pole, from which electricity is supplied. From the power line, a cable is pulled through the shield to the house, and only then the electrical groups are wired. The legislation provides for the division of the panel into devices for input and distribution of power supply.









And nothing that according to the PUE - 7 (7th edition), only one phase and 0 can be brought to a private house?
I won't say anything about the shield assembly, probably everything is correct.
Here is the use of a 3-phase network in private households - complete nonsense! Most electrical appliances are single phase! This must be understood first of all! So it is necessary to use a single-phase network! Cable section ?! well, three veins are always more expensive than one. Perform proper placement of panel boards and the cost of wires is minimized. Moreover, using a 3ph-1ph balun, you will get a stable single-phase voltage.Well, in fact, where devices with a 3-phase power supply are needed, stretch a separate cable .... So gentlemen, consider the assembly of the shield, and do not theoterize about the organization of the power supply of the facility, otherwise you will have to be sent to the USA practice (well, we like to compare "how is it"?)
GZSh is not done after the counter .. only BEFORE ... The earth will return from the counter and it will be fun for devices. And do not tighten the screw, there is a seal.