The PUNP wire, widespread at one time, is an electrical product known in the past, belonging to a special class and intended mainly for domestic needs. Its direct purpose is to serve as the basis for the manufacture of power cords in lighting fixtures and in other household consumers. Today it is classified as an outdated cable product and is not recommended for practical use. Despite this, the PUNP brand is appreciated by most specialists and attracts them with its ease of installation and comparative low cost.
Decoding and marking

The decoding and application of the PUNP wire are inextricably linked, since it can be used only after its purpose is understood. To decipher the designation of this product, just read the following information:
"P" - "conductor";
"UN" - a universal sample;
she is also the letter "P" for flat type.
"Universality" of PUNP is considered a relative concept, since it is suitable only for solving a narrow range of everyday tasks.
Digital and color coding are classic, corresponding to the generally accepted standard. The protective conductor is placed in a yellow-green coating, and the neutral conductor is in blue insulation. In this case, the phase bus is usually white or brown. The outer layer of the PUNP wire sheath with the designation applied on it has a non-standard white color.
Design features and selection rules
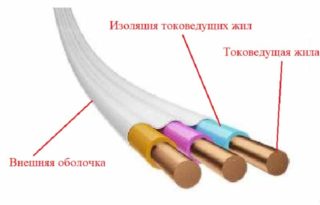
In terms of its internal structure, this cable belongs to products that are traditionally called flat, since the conductors inside the sheath are laid in one line. The veins themselves at PUNP are copper and consist of several thin wires.
Violations of the standard, often observed in the last century, were manifested in the fact that some manufacturers had only one wire inside the core. The consequence of this is its high resistance, leading to the release of a large amount of heat. Before buying a cable, you need to carefully examine its cut and make sure that the inside is made up of several wires.
Each of the two or 3 working cores is protected by a separate PVC sheath, while the overall outer sheath is made of the same material. They are not distinguished by high strength indicators and sometimes are damaged already at the stage of sale. When purchasing PUNP, attention is also drawn to this.
In order to prevent irreparable mistakes when buying a PUNP, the date of its release, which is often overdue, must be checked. It is best to immediately abandon such a sample, since the shelf life declared by the manufacturer of 30 years is most often not true. There is also its analogue, designated as APUNP, made of aluminum. In practice, it is found only in very old houses with dilapidated electrical wiring.
This modification is not found on the open market, since its characteristics do not meet the requirements of modern standards.
The features of the PUNP device also include a limited choice in the number and cross-section of conductors. The number of individual cores is no more than 3, and their cross-sections correspond to the range of values from 1.5 to 6 mm square.
Characteristics and scope
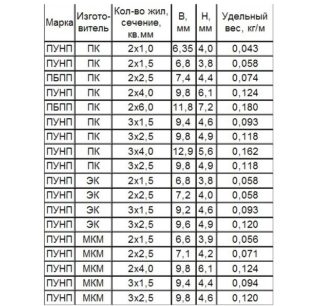
Before using the product, it is important to familiarize yourself with its technical characteristics:
- The maximum withstand voltage is 250 volts.
- The current frequency is 50 Hz.
- The range of permissible temperatures is from -15 to +50 degrees.
- The maximum temperature of surface heating of the coating is up to 70 degrees.
- The guaranteed service life is up to 30 years.
From the above list it follows that this type of product cannot be attributed to universal products even with a strong desire. The PUNP wire is allowed to be used in a limited range of temperatures and voltages, which is suitable only for single-phase household networks. In the 90s of the last century, the scope of its use was limited to the installation of sockets and lighting devices, no more. It was only allowed to be laid in cable ducts or corrugated pipes. This is due to the fact that PUNP completely lacks any protection, and its flexibility and softness only increase the likelihood of mechanical damage. That is why the areas in which this product can be applied are very limited.
Reasons for refusing PUNP

At one time it turned out that this wire was manufactured according to the very "dubious" TU 16.K13-020-93 and at the moment does not meet modern requirements. In addition, the sheath plastic compound did not contain any additives to protect the wire from hazardous factors. Today this GOST has been canceled as not meeting modern standards.
The inadmissibility of application is clearly demonstrated by the example of the section regulation, the deviation of which from the norm according to the old TU was allowed within 30%. In reality, this meant that the 2.5 mm wire used for laying in the wall actually had a cross section of 1.7 mm. When plugged into any power-hungry consumer connected to it, such a cord could not withstand the load, overheated, and the shell melted.
In addition, manufacturers often underestimated the thickness of the protective shell, the nominal value of which was already not large enough (only 0.4 mm). This disadvantage sharply reduced the electrical safety and reliability of the wire.
Despite the presence of many disadvantages, PUNP is still in demand among users. This is explained by the fact that it is cheaper, lighter and much more flexible when compared with VVG.
When is it allowed to use

When carrying out installation operations, if possible, other types of cable are selected, which are the closest analogues of PUNP (VVG or PVS, for example). But if they were not found, you will have to be content with what you have, taking pre-determined precautions. To do this, first of all, the diameter of the cores is measured using a vernier caliper. Then a formula is used to calculate the cross-section of the PUNP, according to which the square of the value obtained after the measurement is multiplied by a factor of 0.785.
Depending on the result, a decision is made about specific places where it is allowed to be applied. It is usually assumed that the calculated cross-section of 2.5 mm corresponds to the real 1.5 mm square. Such a cable can be used in the following situations:
- as a power cord for floor lamps or table lamps (its standard length is 1.5 meters);
- to connect TVs or not very power-consuming computers to the network;
- for the manufacture of garlands based on LEDs.
In no case should any heating devices be connected using PUNP. Powerful electrical appliances such as energy-intensive stoves and panels, as well as microwaves, toasters and kettles are excluded. In addition, when using this cable, it is not allowed to simultaneously connect several devices to the network at once. If you translate these options of loads to the current equivalent through the cable veins, a maximum current of up to 2 Amperes is allowed.
Verification methods
- Measure the cross-section of its cores and the thickness of the insulation.
- Determine the resistance of copper conductors.
- Check it for mechanical strength.
To check the first of these parameters, you need a vernier caliper, and to measure resistance, you will need an electrical measuring device - a multimeter turned on in the "Ohm" mode. For testing, take a piece of cable one meter long, and then the tester measures its resistance in Ohms. It should not be more than the standard specified in the tables for samples of cable products. To test it for strength at home, you need to pull the test piece by the ends and then check how much its insulation will stretch and whether one of the cores is broken.
The PUNP wire should be used only in exceptional cases when its substitute is not at hand. But even with this approach, you first need to take special measures to allow you to use it with minimal risk.









