A device called an "electric current generator" is known to most consumers from popular sources. They mainly relate to powerful electric machines that generate energy in hydroelectric power plants. However, in addition to large-sized station units, the industry produces compact electromechanical generators that are used as stand-alone devices in all spheres of human activity.
Operating principle

The first samples of electric generators were intended for operation in the field and at facilities remote from industrial centers. With their help, it was possible to power up electric welding machines or the required number of lighting devices. Over time, these autonomous devices began to be used in houses and other suburban buildings, which was explained by such a common phenomenon as an unstable power supply. Electric generators are especially widespread in areas remote from the city, where power outages are considered common.
An electric generator is a device capable of converting thermal energy into electricity. Another name is electromechanical induction generators. As a source, energy carriers are used that have a significant heat capacity, sufficient to release the required amount of heat. It can be:
- diesel fuel;
- traditional gasoline;
- natural gas or just firewood.
Generators operating on alternative sources (without fuel) have become widespread. These include air (wind), water, solar and thermal energy converters.
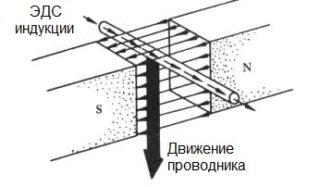
The principle of operation of electricity generators is based on the transformation of heat generated as a result of fuel combustion into mechanical rotation of the drive. Due to this, an electromagnetic field is formed in them, leading to the appearance of an EMF in the stator coils. The electrical circuit of the unit is selected in such a way that an alternating voltage of the required type, value and quality is obtained at the output.
Generator types

According to the class of the energy carrier (fuel) used during operation, all known generator devices are divided into the following types:
- gasoline;
- diesel;
- gas;
- wood-burning units or hydrogen-powered ones, for example.
The first two types of electric generators attract the user by the fact that they use a ready-made engine that runs on the appropriate fuel and only needs to be completed with the drive part. Wood, hydrogen and gas samples are more complex devices and are characterized by low efficiency.
According to the degree of autonomy, all devices manufactured by the industry are divided into stationary and mobile models, and according to the type of alternating current received at their output, into single-phase and three-phase. According to the intended purpose of the units, the known types of power generating devices are divided into main and reserve ones, and according to the field of application - into household and industrial products.
Applications and selection rules

The field of application of electric generators extends to many areas of human activity, forced to use them as main or auxiliary sources.A typical power generator is used in the following areas:
- during the construction of bridges, dams, crossings and other construction projects remote from the main power line;
- when carrying out field work related to the use of electricity and at summer cottages (in the absence of centralized power supply);
- at winter quarters, polar stations, in hunting grounds, as well as in remote military units.
Generators are in demand in private houses and public buildings located in rural areas, where power outages occur with enviable regularity.

When choosing branded generators, it is important to consider the following characteristics:
- type of energy carrier (combustible material);
- output power;
- cooling methods;
- availability of additional functions.

The first of these indicators is selected based on the operating conditions - ease of use and storage of fuel supplies in a residential building. For city apartments, the most suitable option is a gas generator, for the connection of which it is enough to issue the appropriate connection. The output power is selected taking into account specific needs: which units are supposed to be connected to the source. In the same way, the method of cooling the equipment is selected, which is optimal for the unit with the declared capacity. Among the additional functions of the devices, the following features stand out:
- adjustment of the output voltage;
- obtaining a constant (rectified) current;
- availability of redundant output terminals and relay-regulator.
Before going to the store, it is also important to decide on the presence of individual indication devices in the model you like, by which it is possible to control the voltage level. You should also take into account the cost of the purchased product, which should be justified by the benefits obtained during its operation.
DIY fuel-free generators

Generators operating on the principle of using free energy have attracted the attention of many naturalists for a long time. Tesla and other famous scientists were also involved in the development of fuel-free devices. To date, many schemes have been invented that work on various energy principles. List of these devices:
- Hendershot apparatus;
- generators of Romanov, Tariel Kanapadze and Adams;
- devices of Smith and Bedini.
Self-assembly of such a generator is most conveniently considered using the example of the Adams model.
Preparatory operations
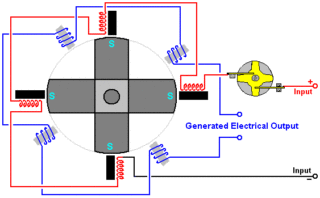
To assemble the device with your own hands, you will need to prepare many initial parts:
- magnets;
- copper conductors;
- two coils;
- sheet steel (as a means for making the body of the device);
- bolts, washers and screws.
The magnets are chosen equal in size and as large as possible. In this case, the induction field turns out to be more powerful, and much more energy will be generated.
When assembling the generator, the plus pole of one magnet is installed strictly opposite the other, also plus one.
Copper conductors are selected so that their cross-section is about 1.25 mm. On their basis, two coils are wound, which are sometimes taken from old motors of a suitable size. When self-winding, they carefully ensure that the turns lie exactly in a row, very close to one another. Auxiliary parts will be required to fasten individual elements of the assembly device.
Assembly

The procedure for assembling a homemade generator:
- Holes are drilled in the magnets for mounting on the coils.
- They are alternately fixed to the frames with bolts.
- The coils with magnets are mounted on a pre-welded metal frame in such a way that a small gap remains between their planes.
The gap will allow the magnets to rotate freely.
At this stage of assembly, the unit is already ready for testing. To carry it out, it is enough to manually turn the magnets around their axis several times. Provided that the structure is correctly assembled, voltage will appear at the ends of the windings fixed to the frame.
The considered self-made device is the simplest sample of a free energy generator, intended for demonstration purposes. On its basis, after appropriate refinement, a full-fledged device is assembled that can generate electricity for lighting a country house or summer cottage. For those who do not want to engage in the assembly of a homemade structure, it is better to purchase a finished product from trusted manufacturers.








