To control various electronic equipment, a device is required that is characterized by miniature dimensions and a high degree of reliability. These devices include AC and DC solid state relays. They have found their application in domestic and industrial environments. The relay can be independently assembled and installed with your own hands without much difficulty. The only criterion preventing widespread adoption of the device is its cost. Before using a solid-state relay, you need to understand its parameters, operating principle, design.
Principle of operation
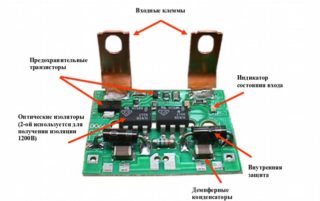
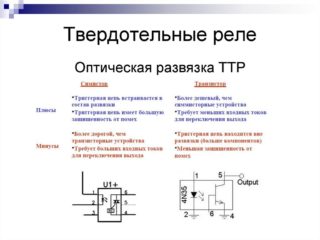
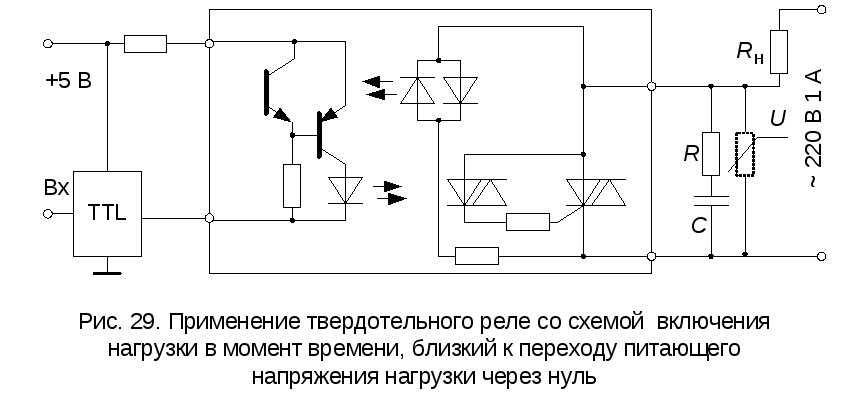
A solid state relay is a modular semiconductor device used to open and close electrical networks. It is presented in the form of transistors, triacs, thyristors. Solid state relays are also called SSR (solid state relay).
The main components that make up the relay:
- input node;
- circuit breakers;
- trigger circuit;
- denouement;
- switching unit;
- protective circuit;
- output node.
Most solid state relays are used for automation connected to a 20-480 volt power grid.
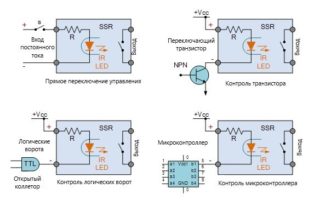
The principle of operation of the device is simple. The relay housing contains two contacts and two control wires. Their number may vary depending on the phases that have been connected. Under the influence of voltage, the main load is switched.
When working with a relay, it must be borne in mind that under high voltages there is a risk of small leakage currents that can harm equipment. This is because little resistance remains in the relay.
Notable models
The main characteristics depend on many factors. Popular domestic models produced by KIPprbor, Proton, Cosmo include:
- TM-O. Devices with a built-in "zero" circuit through which a phase transition passes.
- TS. Models that turn off at any given time.
- The most popular and used ones are TMV, TSB, TSM, TMB, TSA. They have an RC output circuit.
- TC / TM - power. Currents reach values of 25 mA.
- TCA, TMA - used in sensitive devices.
- TSB, TMB - low-voltage models. The voltage does not exceed 30 V.
- TSV, TMV - high voltage. The voltage reaches 280 V.
Foreign counterparts include products manufactured by Carlo Gavazzi, Gefran, CPC.
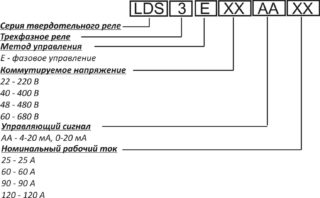
Decoding
Models SSR, TSR (single-phase and three-phase respectively) are the most popular. Their resistance is 50 Mohm or more at a voltage of 500 V.
The designation is written as SSR -40 D A H. SSR or TSR indicates the number of phases. 40 - load in Amperes. The letter denotes the signal at the input (L 4-20 mA, D - 3-32 V at direct current, V - variable resistance, A - 80-250 V at alternating current). The next letter is the input voltage (A - AC, D - DC). The last letter is the range of output voltages (N - 90-480 V, no letter - 24-380 V).
Features of working with the device

When working with a 220v solid-state relay (220v control), you must adhere to the following rules:
- The connection must be screwed. It is quite reliable. Soldering of parts is not necessary, twisting is prohibited.
- Do not allow dust, water and metal objects to enter the relay. They lead to component failure.
- Do not apply unacceptable external influences on the housing.These include liquid flooding, shock, vibration, falls.
- Do not touch the device during operation. The cabinet heats up and can burn a person.
- Do not install the relay near flammable objects.
- Before connecting the circuit, make sure that the assembled connections are correct.
- When the case is heated above 60 degrees, additional cooling is required using radiators.
- A short circuit must not be allowed at the output.
Subject to the requirements for operation, the relay will perform its work reliably and efficiently for the entire declared period.
Advantages and disadvantages
- Durability. A semiconductor device can withstand tens of thousands of on and off cycles.
- A high-quality connection is being created.
- Competent load control.
- High performance.
- Lack of electromagnetic interference in a closed network.
- Fast response.
- Quiet operation.
- Miniature dimensions.
- No contact bounce.
- High performance.
- Possibility of smooth transition between AC and DC networks. Depends on the power and type of device.
- Wide range of applications.
- Withstands overloads in 2000.
- Protection against sudden and large surges of voltage and current.
There are also a number of disadvantages due to which an electromechanical relay can be more profitable in application. First of all, this is the high cost of the product and the complexity of its purchase. Solid state relays are only available from a professional electronics store. Difficulties also arise during primary switching - high current surges may appear. Microcurrents arising during operation also negatively affect the relay.
Operational requirements are also imposed on the operation of the device - the room should have a normal level of dust and humidity. The optimum values can be found in the documentation for the relay.
Solid state relays cannot work with devices whose voltage exceeds 0.5 kV. Increasing the recommended values can lead to melting of the contacts.
Areas of use
Despite the high price, solid state relays are actively used in various fields. They successfully cope with the following tasks:
- Temperature control with heating element.
- Maintaining the right temperature in technological processes.
- Switching control circuits.
- Replacement of non-contact type starters.
- Electric motor control.
- Heating control of transformers.
- Backlight level control.
In each case, a certain type of relay is used.
Classification of solid state relays

Solid state relays can be classified according to various criteria. According to the characteristics of the controlling and switching voltage, there are:
- DC solid state relays. They are used in constant electricity circuits with a power of 3 to 32 watts. They are distinguished by high specific characteristics, the presence of LED indication, and reliability. The operating temperature range is wide enough and ranges from -30 to +70 degrees.
- AC relay. They are distinguished by a low level of electromagnetic interference, no noise, and low power consumption. The operating power range is from 90 to 250 W.
- Manual relay. With the help of such devices, you can independently adjust the operating mode.
According to the type of voltage, single-phase and three-phase relays are distinguished. Single-phase devices are used in networks with a current of 100 to 120 A or from 100 to 500 A. They are controlled by receiving an analog signal and a variable resistor. Three-phase relays are used for switching on three phases simultaneously. Amperage 10-120 A. Three-phase models last longer than single-phase ones.
Reversible devices are distinguished into a separate group of three-phase solid-state relays. They are distinguished by marking and contactless connection. The main function is reliable switching of each circuit separately. They protect the circuit from false positives. The main application is found in asynchronous motors. To work with the relay, a fuse or varistor must be installed.
Relays are classified according to the switching method:
- capacitive or reductive devices, as well as low induction devices;
- with random or instant triggering;
- with phase control.
By design, we can distinguish models that are installed on a din rail and on a special transition-type bar.
Selection Tips

Solid state relays can only be purchased from a specialized electronics store. Experienced specialists will help you choose the best device for a specific purpose. The following factors affect the cost of the product:
- relay type;
- the presence of fixing mechanisms;
- body material;
- turn-on time;
- manufacturer and country of origin;
- power;
- required energy;
- dimensions.
When buying, it is important to consider that there must be a power reserve several times higher than the working one. This will save the relay from damage. Special fuses are also used additionally. The most reliable are:
- G R - used in a wide range of loads, characterized by high speed.
- G S - operate over the entire range of currents. Reliably protect the device from overloading the mains.
- A R - protect the components of the semiconductor device from short circuits.
Such devices provide high protection against breakage. Their cost is comparable to the price of the relay itself. Fuses of classes B, C, D have lower protective properties and, accordingly, lower cost.
For reliable and stable operation of the relay, you need to choose a cooling radiator. This is especially true when the temperature rises above 60 degrees. The current reserve for a conventional relay should exceed the operating currents by 3-4 times. When working with induction motors, this figure should increase up to 8-9 times.
Connection diagrams
The most commonly used schemes are:
- Normally open. The load is energized when the control signal is present.
- Normally closed. The load is energized when there is no control signal.
- The control and load voltages are equal. It is used to work in AC and DC networks.
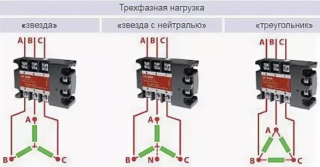
- Three-phase. It can be connected in different ways - "star", "delta", star with neutral ".
- Reversible. A kind of three-phase relay. Includes 2 control loops.
Before assembling the diagram, you need to draw it on paper.
Connection to the network is made through starters or contacts. When using a three-phase relay, all 3 phases must be connected to the appropriate terminals on the top of the instrument. The upper phase contacts are marked with the letters A, B C, zero - N.
The device also has lower terminals marked with numbers 1, 2, 3. They are connected according to the following algorithm:
- 1 - to the output of the coil in the contactor.
- 3 - for any phase that bypasses the relay.
- 2 - to network zero.
Power elements are connected as follows: live phases must be connected to the corresponding terminals on the contactor; load conductors - to the output of the contactor; the zeros are combined on a common bus in the junction box.
Setting up the relay will be considered using the example of VP 380 A:
- Connect the device to the network.
- Look at the display. In the absence of voltage, the numbers will flash. The appearance of dashes signals a change in the phase sequence or the absence of one of them.
In the normal state of the mains, after about 15 seconds, contacts 1 and 3 should close, supplying power to the coil and to the network.
If the connection is not correct, the screen will blink. Then you need to check its correctness. You can set the necessary settings using the buttons on the case. Buttons with triangles are responsible for setting the desired limits.