Equipotential bonding or equipotentialization refers to the reduction of the difference in electrical voltages between human-accessible open parts of electrical equipment. It is applicable to such elements of protective systems as grounding N and PE - conductors, as well as buses of the PEN type, which for this purpose are also connected by means of metal jumpers. The main purpose of this electrical procedure is to get rid of dangerous potential differences and prevent the possibility of electric shock to a person. In practice, this means that all conductive parts of the equipment on the consumer side, as well as elements of building structures used as grounding, are electrically connected to each other.
Types of leveling systems

Leveling systems used in electrical networks are divided into basic and additional devices. To understand their differences, you will need to consider each of these approaches separately.
Main system
This type of leveling structure is abbreviated as BPCS. At its core, it is a contour assembled from metal plates and combining the following elements into a single whole:
- the main grounding bus (GZSh), intended for the assembly of all elements to be grounded;
- metal fittings of a residential building or other structure;
- elements of protection of buildings from lightning discharges and lightning;
- heating pipes and radiators;
- metal boxes for ventilation systems;
- water supply and sewerage pipes.
Usually, for the installation of the GZSh, a separate seat is selected in the input distribution cabinet (ASU). In its absence, any metal assembly is used for this, from which a branch is made by means of a steel or copper strip to the ground loop.
Additional alignment
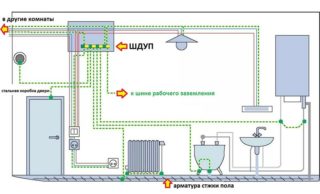
The additional equipotential bonding bus ShDUP is a special steel structure mounted for the purpose of electrical connection of the following elements located in a wet room:
- the body of the shower stall and the bath itself;
- conductive parts of the ventilation system, if the entrance to the bathroom is decorated with a metal box;
- sewer pipes;
- the body of the unit for drying towels;
- water pipes and radiators, as well as all other parts that need to be grounded.
For the additional equipotential bonding bus, you will need to equip a special cabinet or metal box, from which copper conductors are pulled to each of the listed objects. Such a system is considered as an auxiliary, that is, complementary to the BPCS. This explains the impossibility of their separate use and functioning.
Purpose and device of the ShDUP
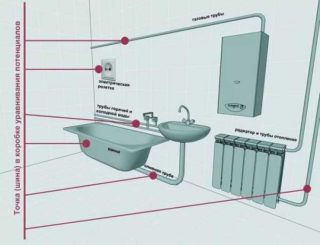
An additional potential equalization system covers the following mandatory elements:
- Without exception, all appliances located in rooms with high humidity - in bathrooms, kitchens, in basements and attics of private buildings - and subject to grounding.
- Elements of metal structures directly adjacent to these premises and going beyond their planning boundaries.
- Neutral conductors of the grounding system.All other equalizing bends are connected to them.
In the absence of zero N conductors on this branch, the entire system is connected to the PE bus installed in the switch cabinet at the entrance to the building.
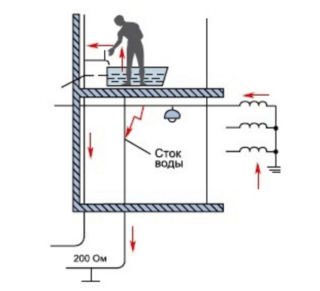
This procedure also applies to heating rails of the "warm floor" system, tightly embedded in concrete pavements. Before installing them, it will be necessary to close the set of steel pipes with a metal mesh, which is subsequently connected to the system in which the ShDUP bus is provided. To provide additional protection in the power supply circuits of heating devices, it is recommended to install an RCD for a current of up to 30 mA (see clause 7.1.88 of the PUE).
Ways of connecting elements connected to U4 type ShDUP buses are very different. The following typical schemes are widely practiced:
- radial connection to potential equalization elements;
- daisy-chain connection, ensuring the continuity of the equalization circuit.
In any case, such commutations are performed using a special prefabricated equipotential bonding unit - for these purposes, the ShDUP box is used. This design is a kind of assembly of several conductors into a single conductive system connected to the zero bus of the switch cabinet.
Parameters of DSPP conductors

For the additional equipotential bonding system, only conductors specially designed for this purpose are suitable. According to the provisions of the PUE (see clause 1.7.138), their characteristic dimensions must meet the following requirements:
- when connecting two own conductive parts of the equipment, the cross-section of the smaller of the protective conductors connected to the grounded parts is selected as the main one;
- when connecting own and third-party conductive elements of equipment or devices, half of the cross-section of the protective conductor connected to the open part of the grounding loop is taken as the basis.
In accordance with clause 1.7.126. PUE protective conductors are made of the same material as phase conductors, and their cross-sections are strictly regulated.
The minimum values of the cross-section of copper conductors used in DSPP systems and not included in the power cable must comply with the requirements of paragraph 1.7.127 of the PUE. The value of this parameter is selected based on the following considerations:
- it should be equal to 2.5 mm2, subject to reliable mechanical protection against deformations and other extraneous influences;
- its value reaches 4 mm2 in the absence of the necessary protection.
In addition to all of the above, the general scheme of the DSPC includes elements of protection against lightning and lightning discharges.
Lightning protection function

Potential equalization in special structures designed to protect structures from lightning strikes is a serious measure that reduces the threat of a fire at these facilities. In such systems, the dangerous potential difference formed due to the accumulation of charges of atmospheric electricity can reach enormous values - up to 15 kV.
Their arrangement is similar to the cases already considered, except that an additional branch is made here, going to the grounding bus or the descent of the lightning rod. The cross-sections of the connecting conductors are selected according to the same calculation as for the general case of the BPCS device. According to the requirements of the PUE, not a single new electrical network, necessarily equipped with lightning protection, will not be accepted into operation if it does not provide for artificial potential equalization.
Fitting the leveling rail
ShDUP buses are usually placed in boxes that differ in the way they are installed on structural elements. They can be placed in the following locations:
- in the cavities of adjacent wall walls;
- directly within the walls themselves.
In addition, they are often wall-mounted. Their installation and fastening in the elements of wall structures is envisaged even at the construction stage. The specific location of the box with the bus is selected according to a previously drawn up scheme and taking into account that there is free access to them. This is necessary to monitor their condition and service.
In an already built and operated building, open boxes are installed, available for the necessary electrical installation operations. The place of their installation is chosen so that the length of the collecting conductors and the grounding bus is minimal. This will save on consumables.
The arrangement of a reliable potential equalization system at any operating facility is a guarantee of protection of people working or living in it from electric shock.








