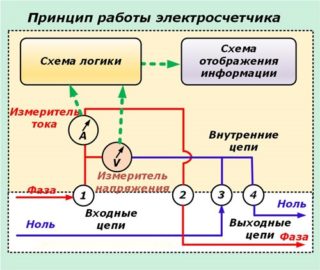
The first electricity metering devices appeared in the 19th century. This can be explained by the massive studies of electromagnetism carried out by scientists. Today, electricity meters are divided into several types and are installed in all rooms where people consume electricity. Its main task is to stabilize and, if used correctly, minimize utility bills.
Classification of electricity metering devices

All meters for electricity are classified by type depending on the type of connection, design features and measured values. Devices are divided into directly connected to the power line and devices that are connected to the electrical circuit using measuring transformers.
Depending on the design features, electric meters are divided into the following types:
- Electromechanical or induction. The principle of operation of the electric meter is as follows: a moving part made of a conductive material is directly affected by a magnetic field, which is formed by stationary conductive coils. The moving part is a disc, and the coils produce currents, driving this disc. The amount of resource consumed is directly proportional to the number of revolutions of this disk.
- Static or electronic metering device. The principle of operation of an electronic electricity meter is as follows: electronic, they are solid-state, the parts are susceptible to the effects of voltage and alternating current, which creates pulses at the output, the number of which is equal to the volume of the measured energy resource. Such an electric meter device makes it possible to measure active energy by converting voltage and analog current signals into counting pulses.
- Hybrid types of metering devices are quite rare. The peculiarity of the electric meter device lies in the similarity of the design of mechanical and electronic devices.
Electric meters are classified into several types according to the measured values and the number of tariffs. In the first case, metering devices are single-phase and three-phase, in the second - one- and two-tariff.
The device and principle of operation of the electricity meter
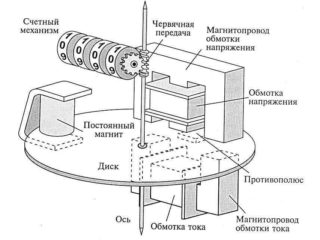
In order to record the active power consumption of alternating current in real time and continuously, it is required to install single-phase or three-phase induction metering devices. If direct current metering is important, which is widespread on the railway and all types of electric transport, electrodynamic metering devices are installed.
Induction electric meters are equipped with a disc made of aluminum, when the resource is consumed, this moving element rotates due to the vortex flows created by the induction coils. In this case, two different forces are encountered - the magnetic field of the induction coils and the magnetic field of the eddy currents. The resulting currents flow in the parallel load circuit. Each coil is equipped with a core that is magnetized by alternating current. Exposure to continuous alternating current leads to the fact that the poles of the electromagnets are constantly changing. This leads to the passage of a magnetic field between them. It is this that pulls the aluminum disc along with it, forming a rotation.
The speed of rotation of the disk is directly proportional to the magnitude of the currents in both coils. In the production of electricity meters, simple connecting techniques from mechanics are used, due to which the rotating disc is associated with the digital readings on the panel.
Consumption accounting is based on forward voltage and current. All data is fed to the indicator, in advanced models the data is stored in the device memory.
- The devices read information more accurately, which helps reduce utility bills.
- In comparison with mechanical electricity meters, they are compact in size and more attractive in appearance.
- They automatically switch to day and night rates, no human participation is required. Even at the production stage, the device is programmed for two time intervals - from 07:00 to 23:00 and from 23:00 to 07:00.
- Improved models need to be checked once every 5-16 years. Such a check is required for the correctness of accounting and accrual of funds. The verification should be done by the energy supply company.
The first check of the device operability is carried out in the factory, the date must be indicated in the accompanying documentation.
Among the disadvantages of two-tariff metering devices, they highlight the high cost and their unreliability in comparison with mechanical counterparts. As practice shows, electronic models fail more often.
Schematic diagram of an electric meter
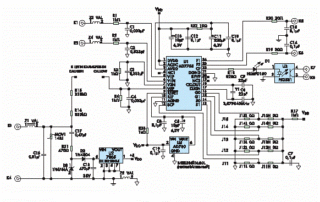
The scheme of operation of all types of electrical devices has no fundamental differences, they are all similar.
Several simple sensors are used to measure power:
- Voltage sensors whose operation is based on a known divider circuit.
- Current sensors based on an ordinary shunt through which the phase of the electrical main passes.
The signal recorded by these sensors is small, so it needs to be amplified using electronic amplifiers. Then analog-digital processing is carried out to transform the signals and multiply them.
The next steps are filtering the digitized signal and displaying the data on the instrument display:
- integration;
- indication;
- transfer of calculations;
- transformation.
In this scheme, the input sensors used are not capable of providing measurements of a high class of vector accuracy, and hence the calculation of power.
If high measurement accuracy is required, the circuit is additionally equipped with special instrument transformers.
If, in comparison, we consider the principle diagram of the operation of a single-phase electronic metering device, in it, the VT is additionally connected to zero and phase, and the CT is an integral component of the phase wire rupture. Since the signals come from two transformers, no additional signal amplification is required. All further transformations are performed by the microcontroller, it controls the display, random access memory and electronic relay. The output signal can be further transmitted through the RAM to the data channel.