To equalize the voltage across the phases of electrical installations, a neutral wire is used. It is essential to prevent instrument ignitions and fires. The cable is part of the neutral - the common point of the generator or transformer winding, connected like a star. There are two types of conductor - working N and protective PE.
- What is neutral wire
- Principle of operation
- Modes of operation
- What is the danger of damage to the neutral wire
- The response of electrical appliances to zero break
- Tasks and purpose of the neutral wire
- Re-grounding
- TN
- TN-C
- TT
- IT
- What is ground and neutral wire
- Wiring diagram for neutral wire and ground
- Neutral connection rules
What is neutral wire

When working with electricity, it is important to understand what a working and protective neutral conductor is. In the first case, it equalizes the voltage in phase, in the second, it protects the neutralization. Users mistakenly believe that the neutral conductor is exclusively ground. Its main function is to connect the neutrals of installations in a three-phase circuit.
When a different load is applied to each of the phases, the neutral is displaced - the symmetry of the voltages is violated. Some consumers are supplied with increased voltage, others receive reduced voltage. At low voltage, electrical appliances malfunction, at high voltage, they are overloaded and light up. The goal of zero is to equalize the increased and decreased rates, ensuring the balance of the power grid.
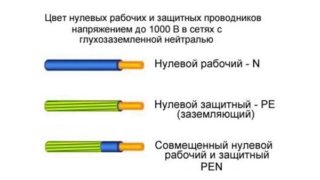
In PUE, the color of the neutral wire is set - blue, which corresponds to European standards.
Principle of operation
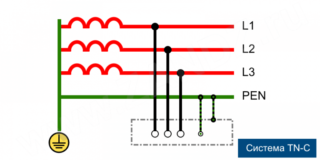
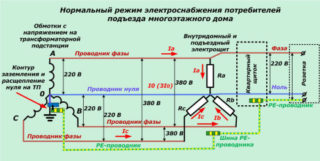
In new buildings and old buildings, the energy transmission scheme is fundamentally different. The power grid of new buildings is designed according to the TN-S principle:
- electricity comes from transformers with a secondary winding connected in a "star" type (wires converging at the zero point);
- the second part of the ends of the cables is diverted to terminals A, B, C, also connected at the zero point, and connected along the grounding loop to the substation;
- The high-voltage wire with zero resistance is divided into protective PE (yellow-green) and working N (blue).
In the general switchboard of the new building, 3 phases, a protective conductor and a neutral wire are supplied.
- the neutral grounded conductor is located in the junction box;
- phase and zero from the transformer are thrown to the building through underground or overhead high-voltage cables;
- the wires are connected in the input panel, forming a three-phase system with an operating voltage of 220 or 380 V;
- from the dashboard, wiring is carried out to apartments and entrances;
- consumers receive electricity from the wires of one of the phases through a network with a voltage of 220 V;
- the difference in load is eliminated by supplying the neutral N-wire.
Electrical connections for older homes are outdated and unsafe.
Modes of operation
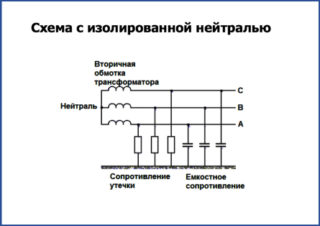
- deafly grounded (380 volt networks - 110 kilovolts) - the potentials of the neutral and ground are the same;
- isolated (networks for 6, 10 and 35 kilovolts) - insignificant current leakage is observed between the neutral and the ground;
- part of a power grid with low impedance and ground impedance.
A neutral wire is used to prevent emergency voltage surges in the phase, for the purpose of relay protection against phase-to-earth faults, and also to ensure the reliability of the operation of electrical appliances.
What is the danger of damage to the neutral wire

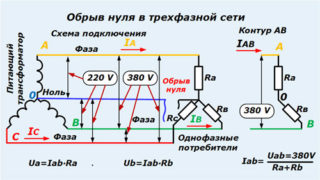
Zero is damaged by mechanical stress, short circuits, poor-quality connections or as a result of old wiring. Neutral break:
- PEN conductor in the power cable - one ground loop remains, which is not visually noticeable;
- combustion of the conductor in the switchboard - the phase conductors are warped, the voltage indicator increases to 380 V;
- a break in the dashboard of the apartment - the second phase remains in the sockets, household appliances are not powered from them.
Damage to the neutral eliminates the potential equalization of networks with different loads, as a result of which household appliances can burn out. Insulation breaks through in such cases. In an old housing stock with a TN-C connection scheme (zero - protective conductor), in case of breakdowns, there are risks of electric shock. In new buildings, zero damage leads to the fact that when touching the equipment, light current discharges are felt.
Electric discharges from touching the equipment case also indicate its malfunction.
The response of electrical appliances to zero break
- malfunction;
- break or burn when connected to the network;
- shock if grounding has not been performed.
The consequence of damage to the neutral is the failure of expensive equipment sensitive to network fluctuations. To eliminate the electrical hazard, it is required to supply an individual shield with a voltage limiter. In case of drops, it will quickly turn off the power.
Tasks and purpose of the neutral wire

The installation role of the conductor neutral wire is the connection of the neutralized elements of electrical installations with the neutral of a solid ground. In fact, it equalizes the potential difference between the phases, diverts currents from areas with short circuits, prevents injuries and evenly distributes the load across all apartments.
The star-type piping system has vector characteristics that are identical to the transformer substation. The connection is reliable, but only if the quality of the wires and the rules for their connection are observed.
Re-grounding
Re-grounding of the neutral conductor is a protection installed at intervals determined by the rules of the PUE along the entire length of the neutral. The tasks of re-grounding include reducing the voltage force in the neutral wire and electrical appliances that were neutralized relative to the ground. This property is advisable as protection against a break in the neutral wire and in case of a breakdown of electrical voltage to the body of electrical devices.
To make a reconnection, it is necessary to conduct a continuous neutral from the shield to the neutral conductors. In the conditions of high-rise buildings, various systems are used for re-grounding.
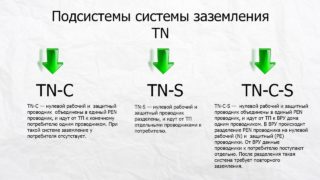
TN
- TN-S - protective and neutral conductors are separated along the length of the entire line;
- TN-C-S - the functions of the PE and N wires are combined in one part of the conductor taken out from the transformer.
If communications are connected in a private house, natural grounding conductors are used - metal pins in the ground. Regulatory documents do not recommend the use of natural conductors, since it is impossible to calculate the resistance that the soil gives when the current spreads.
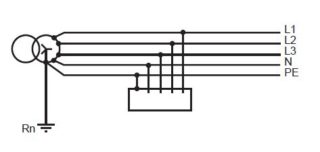
TN-C
Grounding in houses built before the mid-90s, for which a four-wire method was used - 3 phases and 1 zero. The protective and operating functions of the neutral are performed by a common conductor throughout the entire line. The consumers are powered from the PEN cable.It is also used for grounding.
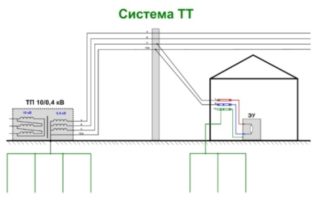
TT
It is used to supply electricity in suburban and rural conditions. The current flows through the power lines on the poles. Installations are allowed in cases where TN is impossible or very expensive to make. When an increased current is applied to the devices, the power circuit is turned off completely through the RCD.
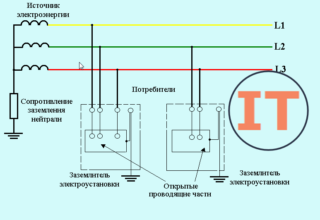
IT
Network with insulated neutral of the transformer. Discharged from the ground or grounded through a high impedance receiver. The ground line is drawn along a separate bus, and the socket contacts are already connected on it. The organization of the system is appropriate for educational, medical institutions.
What is ground and neutral wire
The grounding conductor ensures the safety of the power line in the event of a breakdown. Its normal mode of operation is wired; in case of critical failures, the current potential is diverted to the soil. The PE cable is marked with a blue-yellow color.
Neutral and protection in one wire are designated PEN, marked in blue with yellow and green stripes at the ends.
Wiring diagram for neutral wire and ground
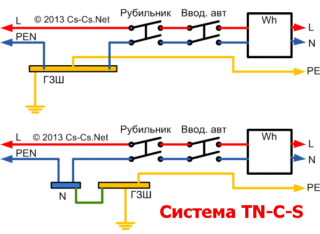
Separate TN-CS grounding line.The neutral shields and protective conductors of the home switch are connected to each other. If there are two wires, the PEN cable is divided at a certain point into neutral and protection. The PE wires are thrown up to the N conductors. The protection of the circuit depends on the break point:
- To the place of separation. The phase conductor and the protection device drain the voltage to the neutral, and from it to the protection wire.
- After the place of separation. Hazardous electricity is not transmitted to the body of household appliances, but is immediately transmitted to the protection wire.
In high-rise buildings, it is not always possible to make such a grounding line.
Separate ground loop TN-S.The grounding of the network is carried out at the place of the neutral transformer point, from where the wiring is led out to the devices. A three-phase apartment network with a fully insulated neutral wire is maximally protected against failures. A zero conductor damaged in any area does not interact with the protective one, therefore it has no risks to human health. The only problem is the temporary shutdown of equipment.
Neutral connection rules
- for electrical installations with a voltage of more than 1 kV, a dead-grounded neutral is required, which diverts large fault currents into the ground;
- for equipment up to 1 V, isolated or dead neutral can be used;
- a deafly grounded neutral must be zeroed and connected to the ground line through a transformer;
- grounding and neutral are made using copper (cross-section 4 mm2), aluminum (cross-section 6 mm2), insulated (1.5 mm2 and 2.5 mm2) cables;
- copper cables connected in one twist must have a cross section of 1 mm2, of aluminum - 2.5 mm2;
- if 3 wires are pulled from the flap of an apartment or floor, a protective neutral is used;
- if the group network is carried out using two cables, the neutral of the protection is extended from the near board;
- all household appliances join to zero - kettle, air conditioner, computer, washing machine, boiler, refrigerator.
Provided the correct wiring diagram is used, the protective neutral conductor will be able to prevent the destruction of the electrical network and injury in case of a short circuit. The neutral evenly distributes the load across all lines, floors and apartments of a high-rise building.During its initial and repeated connection, it is worth being guided by the PUE.