The reason for the breakdown of household appliances and electrical household appliances is voltage drops (VL). This is due to the fact that each electrical unit can operate smoothly and efficiently only with certain parameters of electricity, in particular, the voltage in the network and its strength. When these standards are exceeded or lowered, an emergency situation inevitably occurs. In order to minimize or eliminate the risks of large financial losses, you need to take care of the overvoltage protection of the 220V network.
What are voltage drops

In accordance with the definition given in GOST, voltage drops or overvoltage is a sudden short-term decrease or increase in the voltage amplitude, followed by recovery to nominal parameters.
The nature of the origin of this phenomenon is explained by the fact that several decades ago, designers and builders could not even imagine that in modern times such a number of electrical equipment would be concentrated in every apartment. Maximum electricity consumption in the morning and evening negatively affects the operation of the entire electricity grid.
The electricity that flows through the cable is simply unable to withstand such loads, which contributes to their abnormal overheating. Over time, this leads to a weakening of the contacts in the switchboard. Also, neutral wires often burn out, which can cause a voltage surge, for example, from 110 to 360 volts.
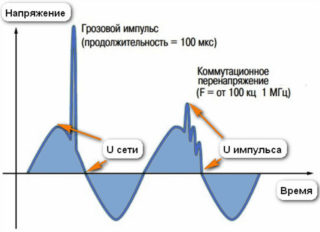
Switching overvoltage
The duration of such an impulse does not exceed a few milliseconds; its formation may be due to one or several reasons:
- When connecting powerful electrical equipment such as electric welding, collector motor, electrostatic induction phenomenon is observed.
- Overvoltage caused by switched processes. They, in turn, are observed at the moment when electrical appliances with high power are turned off or on.
- Lightning discharges. This natural phenomenon can cause voltage surges of up to several kilovolts. No device is able to withstand such changes in the network, and thunderstorms are often the causes of fire and network outages.
The insulating material of most wires is designed for significant PN, therefore, breakdowns rarely occur. If, nevertheless, this happens, an electric arc occurs. As a result, there is a free path for the flow of electrons.
Gases act as conductors, filling all the voids formed. Over time, if the breakdown is not eliminated, the current gradually increases, and the protective automatics will not timely determine the emergency situation. This leads to the destruction of almost all the wiring in the room.
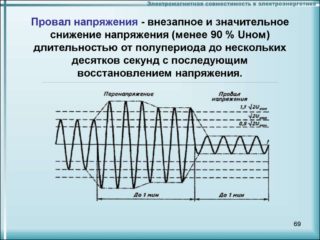
Prolonged overvoltage and dips due to lack of voltage
The uneven three-phase current acts on the neutral ungrounded cable, which contributes to the accumulation of excess voltage in it. The process of increasing its concentration will continue until the malfunction is eliminated or the network finally fails.
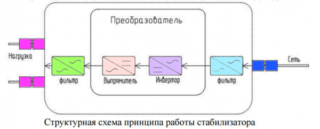
Another dangerous state of the electrical network that can cause significant damage is a lack of voltage or a failure. Such phenomena are quite common in rural areas. The bottom line is that the indicator falls to critical levels, which poses a serious danger to wiring, household appliances and all electrical appliances. Many modern household appliances are equipped with several power supplies, a voltage drop leads to the shutdown of one of them. This stops the technician's workflow. A stabilizer will help to eliminate the problem and prevent it in the future, which fixes critical points and regulates the voltage to nominal values.
Types and principles of protection devices
Overvoltage protection can be implemented in different ways. The following devices are considered the most popular, simple to implement and reliable:
- lightning protection system;
- voltage limiters (stabilizers);
- overvoltage sensors, which are used in conjunction with RCDs, cause current leakage in case of abnormal or emergency situations;
- overvoltage relay.
Uninterruptible power supply units have also been developed that perform similar functions. The specificity of their work is to continue working and turn off the device in accordance with all the rules.
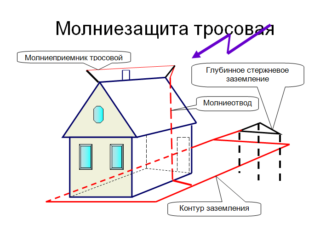
Lightning protection
- A common way is to organize external lightning protection. The force of a lightning strike will fall directly on the elements of the system itself. The approximate current strength is 100 kA. It is possible to protect from a powerful impulse using a combined SPD, which acts as a switch and is mounted in a water electrical distribution board. One such protection system will prevent the failure of all equipment in the house.
- There is no external lightning protection, voltage is supplied to the house through an overhead line. During a thunderstorm, lightning strikes the power transmission line support with a calculated current that passes through the SPD, the value is approximately the same as in the previous version - 100 kA. To protect household appliances from a powerful voltage surge, special protective devices will help, which are installed on the input board, the branch of the line, on the post or wall of the building. During operation of the switchboard, protection occurs according to a scheme similar to the previous method.
If the SPD is mounted on a pole, it is impractical to use differential devices, since voltage surges are still possible at a distance from the house to the pole.
Surge arresters
Protection against voltage surges in the network at overhead transmission lines and substations is carried out using surge arresters - non-linear overvoltage limiters. The structure includes a varistor. Non-linearity consists in the change in the resistance value in accordance with the applied voltage value.
When the power grid is operating normally, and the voltage corresponds to the nominal, the arrester has a high resistance, which does not allow current to flow. If, for example, an impulse is generated during an electric shock, a sharp decrease in resistance is observed, which leads to a voltage surge.
There are compact modular surge suppressors that take up little space in the house's switchboard. These devices are connected to an earth ground or functional earth that carries hazardous impulses.
Surge Protectors
If the voltage in the network begins to jump, the device catches this and turns off the power in automatic mode. The power supply resumes only after the network indicators return to operating mode.
Network filters
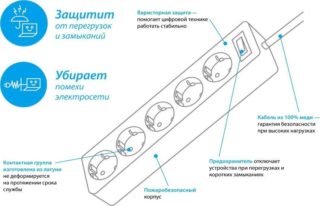
Electrical constructions have significant advantages in comparison with analogs - affordable cost and simple design. Despite the low power, the filter is able to protect household appliances in case of voltage surges up to 450 volts. As practice shows, even if the manufacturer claims high performance, the surge protector does not withstand above 450 volts - it burns out, but at the same time leaves expensive household appliances intact.
The varistor plays a key role in overvoltage protection. When indicators are reached above 450 volts, it is he who burns out. The part reliably protects electrical structures from high-frequency interference that can occur when turning on or off electric motors or welding machines. Another important design detail is the short-circuit fuse.
If you compare between a voltage stabilizer and a surge protector, it is better to give preference to the former, especially when living outside the city or in the countryside.
Before proceeding with the installation of protection against voltage surges of 380 and 220 volts, you need to make sure that the network is completely de-energized. The circuit breaker turns off the electricity supply and checks the output voltage using an indicator screwdriver. The quality of the materials used is also of great importance. Flammable must be abandoned, because sooner or later they will inevitably lead to an accident.