The base absorbs the load from the ground part of the structure. The foundation for the house is made stable, strong, durable, its dimensions, material and shape are determined by calculations. The design takes into account the characteristics of the soil, climatic indicators in the region, the magnitude of the load. The wrong choice of design leads to financial and labor losses during rework.
- Features and foundation for the house
- Important factors when choosing a foundation
- Assessment of soil and groundwater
- Soil types
- Foundation depth
- Types of foundations for the house
- Columnar
- Tape
- Pile
- Platen
- Fully and shallow foundations
- Technology for building a foundation for a house
- Insulation and waterproofing of the foundation
Features and foundation for the house

The foundation is the load-bearing part of the structure, to which the forces are transferred from the weight of the building, people, operation of equipment, precipitation and wind. Materials with high load-bearing capacity are used, such as concrete, stone, metal.
To select a foundation, the following characteristics are applied:
- height - the distance between the upper cut and the sole;
- laying depth - the gap from the soil surface in the plan to the bottom of the structure;
- shape is a visual concept that defines the general arrangement of contours.
The foundations are arranged so that the sole is located below the soil freezing mark, where the soil does not swell. Shallow structures are used on lands with stable characteristics. Foundations are monolithic, prefabricated (glass or solid), combined.
Important factors when choosing a foundation
The design work begins with a geotechnical survey at the construction site to determine the thickness of the overlying layers and their characteristics.
The calculation takes into account many other factors, on which the choice of the base and its dimensions depends:
- the level of soil freezing;
- elevation of ground moisture;
- the estimated operational life of the building;
- building structure and load value;
- material for the construction of the foundation;
- the presence of underground utilities on the site.
The load is determined by summing all the forces from the building. The area of the base depends on this, since an increase in quadrature means a decrease in the transmitted force. The designer finds the best option to ensure strength and minimize material costs for construction.
Assessment of soil and groundwater
The swelling of the soil depends on the moisture saturation. The soil water level is determined by the first aquifer from the surface of the earth, which constantly exists in the thickness. Ground moisture destroys building materials and differs in different aggressiveness: general acid, leaching, sulfate and other types.
The depth of soil freezing ranges from 0.5 to 2.0 meters, which is explained by the density of the soil layer, humidity and climate. The characteristics of the soil affect the choice of the depth of the foundation for a one-story house made of foam blocks, bricks, frame structures and determine the features of the construction of the basement.
Soil types
Clastic and rocky rocks are represented by stone, which does not suffer from frost and moisture. Such soil belongs to stable species, is ideal conditions for construction and is more often found in mountainous areas. The sandy soil does not swell and serves as a good foundation platform. Such earth is permeable to liquid, easily rammed, compacted. The concrete in the sand does not get wet, because moisture leaves quickly due to the porous structure.
Dusty and fine-grained sands belong to the category of heaving formations, show the properties of quicksand, which must be taken into account when carrying out construction work. Clays, sandy loams, loams do not swell in a relatively dry state and interact well with the surface of the foundation. A high level of ground fluid leads to deterioration of properties, and uneven shifts in the depth of the rock begin.
Foundation depth

The level of the sole is taken regardless of the freezing mark, if the foundation is erected in non-porous soil, and the structure is heated in winter. The depth of freezing is not taken into account if the calculation shows that the deformations are insignificant, and the strength of the structure will not be violated during the freezing and thawing cycles.
The concrete foundation for low-rise construction is usually laid to a depth of:
- heaving soils - no less than the freezing depth adopted in the region;
- conditionally heaving with a freezing mark at 1 m - not less than 0.5 m; at the level of 1.5 m - not less than 0.75 m; more than 1.5 m - from 1 m;
- stable coarse-grained sands - not less than 0.5 m.
If the sole is located above the freezing mark, drainage of atmospheric and ground water is made to reduce the degree of moisture.
Types of foundations for the house
Depending on the height, there are deep and shallow foundations. Foundations serve as a supporting structure or additionally protect the structure from seismic activity in the region. There are experimental anti-seismic designs, such as floating or swinging types of foundations for a private house, which equalize the pressure of unstable soil.
Supports for the house are of the design:
- columnar;
- tape (monolithic concrete or prefabricated from blocks);
- pile (monolithic or prefabricated);
- on screw piles;
- slab.
The material is concrete, ceramic clay bricks; reinforced volumetric frames or flat meshes are inserted for reinforcement. A shallow foundation for a house with your own hands can be made of concrete, where expanded clay and slag are poured instead of crushed stone. This material has the best heat-shielding properties.
Columnar

These types of foundations for a private house are used in the case of a low weight of the structure and a low effort on the foundation. Columnar views are made in the form of free-standing supports supporting walls and columns. The material is brick, concrete, rubble, rubble concrete, reinforced concrete blocks
The device of columnar options is allowed in the construction of a two-story or multi-story building, but a strapping is made from a metal profile, reinforced concrete or wooden beam on which the walls are built. A crushed stone-sand cushion is made under the sole to reduce the influence of soft ground.
The minimum dimensions of the columnar support are 0.5 x 0.5 m, the height depends on the calculation. The sole can be round, square, rectangular. The pillars expand downward, thus increasing the bearing capacity of the structure.
Tape

The foundation runs along the perimeter of the house, the walls rest on it. The concrete and reinforced concrete option requires the installation of timber formwork, chipboard, OSB. The reinforcement frame is placed inside so that the bars after pouring are inside the tape. The transverse size of the strip depends on the width of the wall, the basement floor can protrude beyond, be flush or narrower.
Prefabricated foundation structures for a brick house are made from factory blocks, which are placed on a cement-sand mortar. Metal embedded parts are welded together to create a solid belt.
Strip-type masonry made of rubble stone or red brick is allowed. Elements are placed with bandaging of horizontal and vertical seams. Longitudinal metal reinforcement is used or meshes are used to increase the punching shear and bending strength.
Pile

Such foundations are individual vertical elements connected to each other by a beam or reinforced concrete slab. Varieties of piles are immersed in the ground in special ways, made of durable materials, for example, concrete, reinforced concrete, steel, wood, asbestos cement.
The piles are immersed in the ground with ready-made elements (driven type) or made on site. A funnel is made where the pipe is placed, then the cavity is filled with concrete. Elements in the soil like hanging and pillars work. The first type is used if stable soil is located at great depths. Their strength is determined by summing the friction values along the lateral areas of the pile and under the lower edge. Racks-piles are placed so that their soles rest on a solid layer, for example, rocky. Their length is not more than the depth of stable ground.
Screw piles are buried in the ground by pressing in at the same time as screwing in. The tip is a sharp end with helical blades. The barrel is a combination of a leading part and an extension. The main section is screwed into the ground first, and the extension is used for an extension to reach the load-bearing ground. Diving is carried out manually, mechanically or geared.
Screw dowels are preferably placed on complex hydraulic engineering objects in unstable soils, used to strengthen the slopes of the banks, road and railroad embankments. Various soils do not limit the use of screw pile foundations. Geometrical dimensions, number of blades, pitch, taper angle are taken on an individual basis in each case.
Platen

Solid slabs are poured in the case of construction on soils with uneven expansion with changes in temperature and humidity. Monolithic sites are used on weak, fill-up lands, if the soil water is highly suitable. The foundations are made of reinforced concrete and are made under the entire structure to ensure uniform settlement. Monolithic slabs are arranged on sandy, swampy lands, peat bogs.
Plus a solid base in the ease of manufacture and the possibility of organizing a basement floor. The monolithic slab serves for a long time and has a high bearing capacity; it serves as the basis for the construction of multi-storey buildings in difficult permafrost conditions. The downside is the high cost of metal and concrete.
Fully and shallow foundations
A massive strip foundation of deep laying is made during the construction of apartment buildings, complex technical structures with a high load. A special feature is that the sole is deepened below the freezing point of the soil by 30 - 40 cm. The structure is little subject to temperature destructions and deformations, does not react to the rise of ground moisture. Reinforcement is performed with corrugated reinforcement; for this, the bars are assembled into a frame. Concreting is allowed without metal reinforcement on stony and rocky soils.
The strength and the ability to equip the basement are on the positive side. The disadvantages are manifested in a large amount of work on land excavation and difficulties in removing moisture with a high standing of soil water.
Shallow foundations are suitable for low buildings with wooden, aerated concrete walls, outbuildings in the private sector, gazebos.Concrete tape is used on almost all soils and is preferable on soils with a high moisture content.
The foundation is deepened:
- in the ground with average heaving rates - by 50 cm;
- in soft soils - 50 - 70 cm.
For reliability, sand and gravel bedding is performed by 10 - 15 cm, a blind area with a width of at least 60 cm is made around the structure. Shallow structures have a low cost, but require high-quality reinforcement.
Technology for building a foundation for a house

Preparatory work includes cutting off the vegetation layer, site planning, procurement and delivery of building materials, fixtures, and tools.
Step by step instructions for beginners:
- trenches are dug with an excavator, cleaning the bottom of the excavation is done manually according to the design marks;
- the formwork is arranged from shield elements above ground level by 30 - 50 cm for arranging the basement;
- the reinforcement is tied into a frame inside the formwork or assembled outside, and then installed in blocks;
- concrete is poured into the formwork in layers with mandatory vibration;
- waiting for the strength to develop, removing the formwork.
Covering or coating waterproofing of the surface is done before laying the walls, then backfilling of trenches and unused pockets on the sides is performed.
Insulation and waterproofing of the foundation
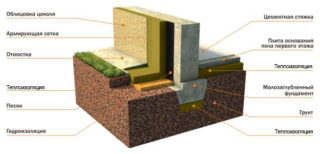
The base of the house is insulated to maintain comfortable conditions in residential and business premises. Heat exchange between the foundation and the soil accounts for a significant part of the heat loss. External insulation protects the building from freezing and increases the service life. The material of the insulating layer is selected taking into account the construction conditions.
Used for insulation:
- expanded clay, sand, slag;
- mineral wool with a waterproofing layer;
- polystyrene, polyurethane, penoplex, expanded polystyrene.
Base waterproofing is used to prevent the foundation from transferring moisture to the walls of the building. Used waterproofing, roofing material in 2 - 3 layers. Materials are glued on molten bitumen or ready-made synthetic mastic is used.