Due to the speed of construction and affordable cost, frame houses are becoming popular in Russia. The durability of the building largely depends on the reliability of the foundation. When choosing a foundation, the expected load, the type of soil and the features of the site's relief are taken into account.
Soil characteristics

Before the development of the building project, it is necessary to conduct geological surveys and draw up a topographic plan of the area. Drilling a well or digging a hole allows you to examine the soil. There are several main types of soil:
- Rocky, gravel and sandy soils are the best option for construction. They do not contain voids, are waterproof, and have a low compression ratio. Sandy soil of uniform density does not swell when frozen.
- Clay soil, due to porosity in winter, increases significantly in size. The frozen water causes swelling, which creates pressure on the base of the house. The bearing capacity of the soil is influenced by moisture, with an increase in the parameter, the ability to withstand the load decreases.
- Loam is a type of soil containing sand and clay in a ratio of 3-10% to 30%. In terms of suitability for construction, it is inferior to sandstone, but better than clay.
- Peat, loess and quicksand are soil types characterized by uneven compression and low water resistance. Such soils are not very suitable for the construction of buildings.
If there is weak soil on the purchased site, it is compacted or replaced. In the first case, tamping with surface vibrators and cementation are used. The second method consists in removing soil to a certain depth and replacing it with a sand cushion.
Foundation requirements
The general requirements for the foundation of a house are:
- Strength and resistance to movement and heaving of the soil, which is provided by the material of the structure.
- Durability - the foundation and the building must have the same lifespan.
- Profitability - the optimal consumption of the estimate is based on the purchase of locally produced materials, the appropriateness of the selected type of construction.
As a material, concrete, reinforced concrete are recommended, for sandy soil - brick and cinder block. With a low level of groundwater, it is allowed to use wood after antiseptic treatment.
Ground selection rules
When choosing a foundation for a frame house, its design features and geological data of the site are taken into account. In order to prevent uneven subsidence, high humidity in the basement and other problems, it is necessary to choose a structure that meets the following criteria:
- dimensions, weight, number of storeys and configuration of the building;
- depth of groundwater;
- the level of soil freezing;
- seismic activity in the region;
- basement planning.
The groundwater level and the freezing depth affect the choice of the type of construction. For heaving soil with a high occurrence of groundwater, a fully buried strip foundation is recommended.A shallow structure is suitable in an area where groundwater is far away, and the soil freezes to a shallow depth. The slab is used as a base on mobile or bulk soils. Piles are used as a building support for any soil.
The influence of a frame house on the foundation

Heavy masonry structures with reinforced concrete slabs create a high load on the base. The budget for laying their foundations is 20-30% of the total construction estimate. With lightweight frame buildings, the situation is different. Their weight is much less, therefore, the foundation can also have a lightweight structure.
Knowing the technology of building a cottage, experts calculate the expected load. This will require information about the type of frame (timber, logs or metal guides), insulation, external and internal finishing materials. The foundation for a frame and panel house can have a limited area of support on the ground. These types include pile and columnar structures.
Types of foundations for a frame house
Lightweight buildings can be built on any foundation, but the following types of construction are most commonly used:
- tape;
- pile;
- monolithic;
- columnar.
They have different stiffness and resistance to soil swelling. Detailed information on the pros and cons of structures will help you decide which foundation is best.
Tape

The foundation is a reinforced concrete strip along the perimeter of the entire building. Before the concrete is poured, the formwork is installed. Reinforcement with an iron bar is mandatory. The design is of two types:
- A shallow tape is laid in a trench 40-60 cm, it protrudes 30-40 cm above the ground. For reliability, a continuous reinforcing belt is arranged. The base is erected on a sand cushion.
- Deep-laid - the structure is located below the level of soil freezing. The exact value is taken from the reference book for the region. The base has a high bearing capacity.
Advantages:
- it becomes possible to build a basement;
- high reliability and durability;
- simplicity of the device.
Disadvantages:
- increased material consumption (for a fully buried base);
- long manufacturing period (it is required to wait for the concrete to dry);
- not suitable for areas with high groundwater levels.
Concrete tape is suitable for heavy houses; in private construction, this is the most common base option.
Pile

Piles are used for construction in areas with heaving unstable soil. Supports are of several types: rammed, filler, screw. Finished piles are twisted or driven into the ground, rammed piles are made directly on the site. In the construction of light houses, metal screw piles are popular. They can be screwed into the ground by themselves. To connect the supports into a common structure, a grillage is mounted on them.
Advantages:
- erected faster than other types of foundation;
- suitable for all types of soil;
- no excavation required.
Disadvantages:
- significant heat loss;
- metal piles are susceptible to corrosion.
Monolithic slab

A slab foundation for a frame house is a type of monolithic foundation used on soils with high compression. The base is made of concrete and reinforcement and is located under the entire building. A cushion of sand and crushed stone is poured under the slab, insulation and waterproofing are laid. The base can be flat or with additional stiffeners.
Advantages:
- ensures the stability of the house on heaving soils;
- can be used with a close occurrence of groundwater;
- long service life;
- versatility, used in typical projects of country houses.
The disadvantage is the high cost due to the high consumption of materials.
Columnar

For houses of light weight, a columnar base is used. Supports are made of concrete, stone or brick. They are installed in the corners of the building, at intersections of walls, in areas of increased load. The distance between the pillars is 1.2-2.5 m. The lower part of the supports is in the ground, and the upper part protrudes 50-60 cm above it. Beam strapping is laid on top of the pillars.
Advantages:
- differs in the lowest financial costs;
- you can do it yourself;
- quickly being built.
When building on heaving soil, the columnar foundation reduces the service life of the building. Also, there will be no way to make a basement.
Warming and waterproofing
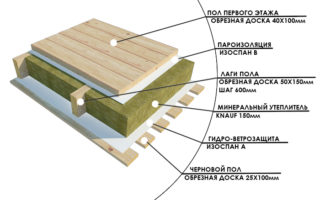
For insulation and protection from moisture, materials are selected that are resistant to the external environment. The strength and durability of the structure depends on the quality of waterproofing. Materials of two types are used:
- liquid mastic;
- roll waterproofing.
Bituminous mastic is the most affordable option for protecting a concrete surface from moisture. It is applied on a clean and primed base in 3-4 layers. The composition penetrates into pores, fills cracks, and prevents the spread of mold. After drying, the mastic is covered with fiberglass or a heater is installed. Another material for waterproofing is bitumen-polymer emulsion or liquid rubber. It forms an elastic, monolithic and durable coating. Lack of material - high cost.
Roll insulation canvases serve as the main or additional protection of a concrete structure. For pasting, roofing material or modern materials based on fiberglass (Isoelast, Technoelast) are used. The material is glued on hot mastic. Sheets of roofing material are laid with an overlap of up to 15 cm, the joints are soldered with a gas burner.
Insulation instructions
Thermal insulation of the foundation occurs at the construction stage. Plate, sprayed or bulk materials are used. Synthetic insulation penoplex and expanded polystyrene do not rot, retain heat well, and are resistant to moisture. The thickness of the insulating layer for them is about 100 mm. Insulation is mounted after waterproofing. Plates are attached with special glue and dowels-fungi. Outside, they are plastered on a fiberglass mesh.
Sprayed polyurethane foam is characterized by low thermal conductivity and the absence of cold bridges. It is an effective insulation that forms a monolithic waterproof layer. It adheres to any surface. The only disadvantage of this option is the payment for the work of the spray specialists.
Thermal insulation of the base of a frame house can be done with gravel or expanded clay. The work begins with digging a trench around the perimeter of the structure and a drainage device. Backfill insulation loses its properties when wet, therefore moisture must be removed. Geotextiles are placed in the drainage ditch, special pipes and covered with crushed stone on top. The expanded clay trench is waterproofed with polyethylene. For effective insulation, its width should be at least 60 cm. A blind area is arranged on top of the bulk material.









