Not a single full-fledged land plot can do without outbuildings (utility blocks). There are many different buildings, the most common of which is the barn. You can keep pets in it, store firewood or tools, you can equip a small workshop or store building materials. The main requirements for this type of outbuildings are the stability of the structure and its durability. These characteristics depend on the correct laying of the foundation, the choice of which is largely determined by the composition of the soil and the characteristics of the future construction.
Soil types

Before you start laying the foundation for the shed, you need to determine the composition of the soil on the allocated land plot. There are several types of soil:
- rocky;
- sandy;
- gravel;
- sandy loam and loam;
- clayey.
A site with rocky or gravel soil is the most optimal option. Rocky soil does not freeze, and gravel can freeze no more than 0.5 meters. These soils do not "float", do not shrink or sink. Their only drawback is heavy handling. However, on such soils, the foundation for the utility block does not require deep deepening.
Clay soil is considered unsuitable for construction. It exerts strong pressure on the base of the structure, is subject to swelling and compression.
The least suitable soil for laying a foundation is sand, sandy loam and loam. Even in light frosts, it freezes to a great depth, and it is also characterized by the formation of "quicksand".
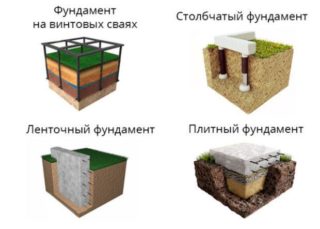
Typical foundations
- tape;
- columnar;
- monolithic (jellied) and its varieties - slab and floating;
- on driven piles (pile);
- pile-screw.
Such structures can be shallow or deeply recessed. The barn is considered a lightweight structure, therefore, during its construction, a shallow foundation is most often laid, the depth of which depends on the depth of soil freezing and averages 0.6 m.
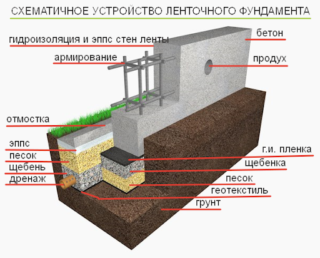
Strip foundation
The strip foundation is most often used in suburban construction. It is a monolithic or prefabricated strip running along the entire perimeter of the structure. All the walls of the structure are then erected along this strip. If the barn is built from heavy materials, a sand and gravel cushion covered with waterproofing must be provided under the foundation. The depth of the laying depends on the composition of the soil and the weight of the structure.
Column foundation
Columnar foundations are used in the construction of lightweight structures (frame, panel, etc.). It is based on massive pillars made of brick, concrete or stone. The pillars are located in places of increased loads and at the corners of the structure. On soft soils, the pillars are made wider to the bottom, which allows distributing and reducing the load on the ground. The pillars are interconnected by a grillage (frame). The space between them is filled with rubble and covered with a layer of concrete. It is not recommended to build a columnar foundation for a barn on heaving soils. In addition, depending on the type of soil, the foundation may need a sand cushion.
Monolithic foundation
The monolithic foundation is a reinforced concrete slab laid on a layer of rubble. The slab is poured under the shed directly on the spot; it is not necessary to deepen it. All load-bearing elements of the erected structure are installed on this slab. It can move with the structure, thereby compensating for the vibrations of the soil (floating foundation). Waterproofing for such a foundation is a prerequisite. The foundation can be used for the construction of structures on heaving and planting soils with weak bearing properties.
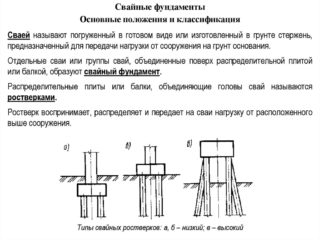
Pile foundation
- unstable and heaving soils;
- high groundwater level;
- swampy terrain;
- uneven landscape.
Pile-screw foundation
A screw pile is a steel pipe with a spiral blade around the barrel. Such a pile is screwed deep into the ground, which makes it possible to compact the soil at its base (underground). The upper part of the piles is cut at one level and poured with concrete. Such structures are laid on marshy, peaty or watered soils. They are used in the construction of lightweight (frame, wooden, etc.) buildings in a complex landscape.
The advantage of the pile-screw foundation is that it can be built at any time of the year.
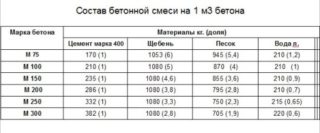
Concrete mortar for pouring the foundation
When preparing the solution, you need to use crushed stone of different fractions - from large to small. Crushed stone, sand and water must be clean, free of debris and any impurities. The cement must be fresh.
Shed foundation construction technology
The laying of the strip foundation begins with digging a trench. Its depth should be 15 cm higher than the depth of soil freezing in the coldest season. The width of the trench should be about 70 cm, which will make it possible to obtain a foundation base (tape) 40 cm wide.Crushed stone is poured at the bottom of the trench, the layer of which, after careful tamping, should be at least 10 cm.After that, the compacted rubble is covered with a 5 cm layer of sand.
Then a formwork is installed in the trench, protruding about 20-30 cm above the edge of the trench, which will raise the building above ground level and protect its walls from getting wet.
To strengthen the entire structure, it is recommended to lay a mesh of reinforcement in the trench. In this case, the diameter of the reinforcement should be about 12 mm, and the size of the mesh cells should be about 30x30 cm.
The prepared mortar is poured into the trench along the upper edge of the formwork and allowed to harden well. Next, the formwork is removed from the trench, the cracks formed are covered with earth and well tamped.
A layer of waterproofing is laid on top of the foundation under the shed, which will separate it from the base of the building.