Greenhouses and greenhouses protect plants from precipitation, cold and hot air, birds, animals and insects. With a serious approach, they can be used in the cold season as well. In such cases, the structure is made in a capital version, where the foundation for the greenhouse performs the bearing function. The stability and durability of the structure depends on the quality and reliability of the base. Many options have been developed for arranging the base for a greenhouse. Each of them has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
The need for a foundation for a greenhouse

A greenhouse support is not required if it is installed for one season and is lightweight. In such cases, it is enough to anchor the structure in the corners so that it is not overturned by the wind.
The question is different when a greenhouse is made for many years of operation, including in winter. The need to make a foundation is dictated by the following factors:
- It is planned to grow crops in cold weather. Heating is required and can only be installed on a solid base. When installing electrical appliances, reliable waterproofing and grounding are required.
- Stability. Strong and heavy support holds the structure much better, eliminating the chance of it being ripped off the anchorages, knocked over or blown away by the wind. This takes into account the indicator of the mass of the base and the way it is fixed in the ground.
- A well-designed foundation for a greenhouse performs the function of protecting the premises from cold, dampness and parasites. Provided that the ventilation is well organized, it is not necessary to spend energy and money on the treatment of plants from pests.
- Leveling the territory. Completely flat areas are rare. The base will be a kind of box in which the leveled earth will be located. Any equipment can be installed on a horizontal surface without the risk of falling.
- Heavy construction. Even light structures exert significant ground pressure. In the absence of a base, the frame gradually falls into it, and unevenly. As a result, the transparent coating is destroyed and the moving parts of the structure become jammed.
Erection of the foundation is the key to the longevity of the greenhouse and obtaining a high, stable and healthy harvest.
Geological and hydrogeological circumstances

A big mistake is the choice of a support only on the basis of the estimate allocated for the construction. A fragile foundation will not last long, along with it the greenhouse with all its contents will be destroyed. The main criterion when choosing is the soil features on the site. The type of material, type, depth of laying, hydro and thermal insulation depend on its type.
It is advisable to familiarize yourself with the properties of soils that can be found on private estates:
- Sand. Easily permeates moisture, sags under pressure, does not expand when frozen. The best choice is shallow or shallow support.
- Clay. Absorbs and retains water. Leads to heavy weight. Heaps, increasing in volume up to 10%.Deep-buried pile or strip foundations are used.
- Rocky ground. Differs in strength, pressure resistance and volume retention under all conditions. A surface columnar or strip base is suitable.
- Clastic soil. The spiky stones contained in the composition provide stability and prevent deformation. Shallow or surface construction is practiced.
- Quicksand. Differs in mobility and instability due to water-saturated silt. A slab or pile support is recommended. Combinations are possible with particularly low soil static values.
It is rather difficult to repair the base, and it is almost impossible to change it. Therefore, you need to be extremely careful about the choice of technology and materials.
Varieties of foundation for the greenhouse, depending on the material used

When planning the construction of a greenhouse, you should not use several types of materials for the foundation. Each of them has its own specific gravity, water absorption, safety margin and service life.
For the manufacture of a base for a greenhouse, the following materials can be used:
- Bar. Working with wood is not particularly difficult, it can even be done with hand tools. Since the timber is afraid of dampness, it is placed at a certain elevation above the ground, filling the gap with a layer of rubble or gravel. Taking into account the operating conditions of wood, it must be prepared for a long stay in an open space. To do this, treat the timber under the greenhouse with an antiseptic and a primer. Outside, you can apply 2-3 layers of drying oil, which is a good protection against moisture. First, the frame is assembled, which is a rectangle divided into compartments. Then the posts are dug into the ground, on which the frame is laid and fixed.
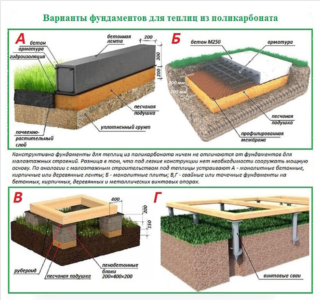
- Concrete. This option is deservedly considered the most durable, reliable and durable. Depending on the type of soil, a monolithic slab or continuous tape with different immersion levels is poured. A sand pillow is mandatory and reinforcement is carried out. The basement level is made up to 50 cm high. The part protruding from the ground serves as a support for the frame and keeps the fertile soil inside the greenhouse.
- Brick. Fired clay brick is characterized by sufficient strength, low thermal conductivity and resistance to dampness. In addition, the masonry fits perfectly into any type of landscape design. The material is laid in a ditch, the bottom of which is pre-rammed, leveled and covered with a sand cushion. Usually 2-3 rows are buried, another 3-5 rows are laid out above the ground. To achieve additional strength, metal rods are laid between the bricks.
- Concrete blocks. The assembly can be carried out using one of the technologies that is best applicable to the characteristics of the site. In the first case, concrete products are laid in a pre-dug pit by analogy with a strip foundation. The depth is determined by the type and level of soil freezing. The joints between the fragments are filled with cement or polymer mortar. The second option provides for the laying of blocks in accordance with the frame scheme, where there will be a support at each angle and rack. The downside of this solution is that you will have to install additional sides to keep the fertile soil. And this is additional forces and means.
- Plastic. It is a quick, effective and inexpensive way to make a base for a light greenhouse. An additional bonus is that such a structure can be collapsible, and this is a valuable quality if you do not plan to use the structure all year round. For assembly, sewer pipes with a diameter of 100-200 mm are used. The products are sold in 2 m long links, complete with corners, tees, couplings and hatches.Thanks to such features, it will not be difficult to assemble structures with sides, the length of which is a multiple of 200 cm. To give the foundation stability, water is poured into the pipes or sand is poured. Anchoring to the ground is carried out using clamps attached to pins or mini-piles driven into it.
When choosing a material, take into account the moisture content of the soil. Wood rots from dampness in 1-2 years, brick will withstand up to 10 years, concrete up to 25-30, and plastic at least 75.
Polycarbonate greenhouse foundation
It is necessary to take into account the following design features:
- Polycarbonate bends only in one direction - in the direction of the inner partitions. Bending across or diagonally will break the slab.
- When the temperature drops, condensation accumulates in the coating cells. This leads to an increase in the weight of the structure by several tens of kilograms. This value must be taken into account when laying the foundation.
- Factory-made greenhouse frame elements can be made of metal or wood. The base material must be selected with appropriate strength, density and hygroscopicity.
- Arched roof structures can collect up to a ton of snow. The foundation must withstand the vertical and horizontal expansion forces that the supports will exert.
- The possibility of dismantling. The polycarbonate greenhouse is assembled with screws and screws. If necessary, it can be dismantled in a few hours. It is advisable to do the same with the base to protect it from dampness, fire, theft or breakage. This applies to prefabricated structures made of timber, concrete blocks and plastic pipes.
When choosing the type of polycarbonate greenhouse foundation, you should remember about the aesthetic side of the issue. Buildings of this type look beautiful and personable. It is desirable that the base correspond to the structure erected on it.
Features of building a foundation for a greenhouse

When building a greenhouse, you should take into account a number of nuances that directly relate to its foundation. It is this part of the structure that determines its reliability and durability. The frame and coating are easy to replace and repair, and the base is almost impossible.
It is necessary to pay attention to the following features of arranging the foundation for greenhouses and greenhouses:
- The right choice of location. Local and public communications should not pass under the structure. Their maintenance, repair or modification involves excavation and removal of all structures along the route.
- Taking into account the relief of the site. Leveling is associated with great physical effort or the involvement of heavy equipment. You can solve this problem with small forces, using piles or pillars as supports.
- The strength of the wind. To exclude the demolition or pulling out of the structure from the ground, it is advisable to use piles, preferably screw. The effect of the hurricane will only be a broken cover, but the foundation and frame will remain in place.
- Soil moisture. Damp soil will only harm concrete and stainless steel. Expensive types of wood will also be able to resist moisture for a long time. However, the cost of such a frame can be much higher than that of concrete. Ferrous iron corrodes upon contact with water, but it can last for more than a dozen years. The downside is that rust disturbs the structure of the soil, and this negatively affects the plants.
- It is advisable to give preference to small foundations.Such structures can be made independently without the involvement of hired labor and means of mechanization.
- Option with an extension. Even at the design stage, you can think about creating a common foundation for a residential building and a greenhouse. This will reduce costs on one side of the foundation, frame and clearcoat. In addition, a convenient passage to the greenhouse will be provided directly from the living quarters.
Taking into account all the nuances will allow you to make the right choice regarding the type of base and materials for its construction. The optimal ratio of price and quality will allow you to achieve the desired result without unnecessary costs.