When arranging the foundations for buildings, their full cost and the ability to carry the mass of the building are taken into account. A variety of columnar bases is a glass-type foundation, which is classified as a pre-fabricated and reliable one.
Application area

Glass-type prefabricated reinforced concrete foundations are made of heavy concrete.
The design is used in multi-storey frame-panel construction of public buildings, in the construction of production and auxiliary premises, industrial enterprises. Bridges, underground parking lots, warehouses, hangars are built on such foundations.
Can be used in non-seismic and seismically hazardous regions. Installation on soils of non-aggressive, slightly or moderately aggressive environment is allowed.
Foundation nozzles are not intended for installation on permafrost, subsidence and bulk (undermined) soils.
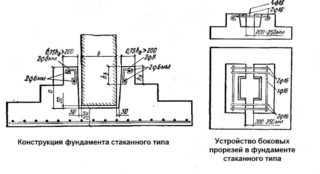
Glass foundation construction
The base plate with a thickness of at least 250 mm can consist of several steps, forming a monolithic structure of a pyramidal or conical shape. The slab absorbs vertical loads from the columns on which the building is assembled.
A pyramidal or square-shaped sub-column has a cavity in which the columns are installed. When assembled, the base looks like a glass, from which the name comes.
The height of the sub-column can be increased depending on the possible load and the configuration of the building.
The entire volume of the glass is reinforced with steel rods and reinforcing mesh.
Pros and cons of glass foundations
The columnar foundation of the glass type has a number of advantages:
- factory-guaranteed compliance with geometric dimensions according to the drawings;
- strength of factory-made concrete, quality control by factory laboratories;
- quick installation of the base;
- a minimum of preparatory earthworks that do not require costly soil development;
- construction begins without waiting for concrete to gain strength;
- installation on most types of soil;
- long service life while protecting against aggressive effects of moisture;
- the ability to create distributed foundations of any size and geometry.
The disadvantages that limit the use of foundation nozzles for a column in private construction include high cost, complexity of transportation and the need for a large free area for installation work.
Manufacturing standards
GOST 24022-80 is applicable for agricultural one-story buildings, where structural reinforcement may be required.
Technical requirements
Foundations are manufactured in steel molds to ensure precise geometry.
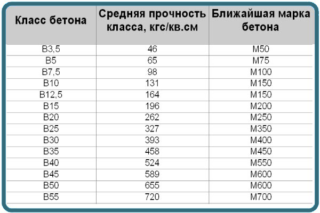
Concrete grade cannot be lower than M200. The M300 brand is used if such a requirement is established by the project. The actual and tempering strength of concrete upon shipment should not be less than 70% of the calculated one, and for the winter period not less than 90%.
Frost resistance is selected based on the climatic conditions of the area of use.
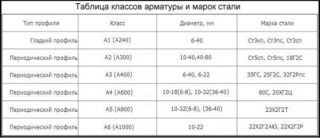
The thickness of the protective layer is 50 mm with a deviation of no more than +10 mm and -5 mm. Cover is the distance from the outer surface of the structure to the closest reinforcement in the mesh.
Each intersection must be connected by welding - twisting with knitting wire is not allowed.
The deviation of the dimensions of the glasses from the drawings should not exceed 16 mm in the horizontal and 10 mm in the vertical plane.
Column and foundation connection
The concrete columns are installed in the cavity and reinforced, leveling in the vertical plane. The gap between the pillar and the walls of the glass is poured with concrete, grade not lower than M200.
Steel columns are welded to the reinforcement released from the walls, free cavities are also filled with cement mortar. Anchoring is possible.
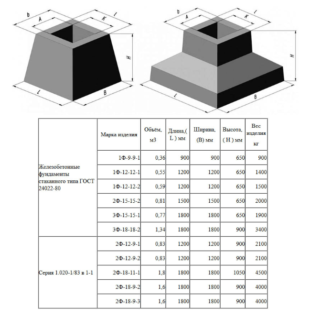
Dimensions (edit)
Standard geometrical dimensions of glasses for columns are indicated in the table in GOST. The dimensions of the sole are critically important, which can be from 1200x1200 to 2100x2100 mm. The bearing capacity of the entire foundation depends on the area.
In some cases, GOST allows a minimum size of the base plate of 900x900 mm.
The height of the entire structure varies from 750 to 1050 mm, of which at least a third is the thickness of the base plate.
Classification methods and product designation
FROM
- 1F is designed for columns-posts with geometric dimensions of 300x300m.
- 2F - foundation for columns 400x400 mm.
Depending on the thickness of the walls and the possible load, the foundations are divided into 3 types.
The first is intended for the construction of walls up to 250 mm thick, and the second for masonry thicker than 250 mm. The third type is intended for especially heavy structures and is provided for by the project.
In addition, two types are distinguished, depending on the operation in aggressive environments: H - normal permeability, P - reduced permeability.
Marking
The foundation designation is carried out with paint on the side surface of the structure. Marking consists of one or two alphanumeric groups separated by a hyphen.
In the first group, according to GOST, the dimensions of the sole and the height of the product are indicated in decimeters, which are rounded to whole numbers.
The second group reveals the bearing capacity, as well as the type of permeability, if the foundation is intended for placement in aggressive environments.
Examples of designations:
- 1F13.8-1. Foundation for a column of 300x300 mm with a foot size of 1300x1300 mm, a height of 800 mm. Bearing capacity of 1 group for walls up to 250 mm thick.
- 2F20.9-2P. The transverse dimension of the column is 400x400 mm, the sole is 2000x2000, the height is 900 mm. It is possible to build walls thicker than 250 mm; concrete with reduced permeability is used.
Installation steps
Glass-type foundations place increased demands on the mechanical composition of the soil. Permafrost, fill and subsiding lands are unsuitable, since subsidence and destruction of the entire structure are possible under the full mass of the building. Movements are also possible on heaving grounds in winter.
Before choosing the type of foundation, geological surveys are carried out, in which, in addition to strength, the hydrological state, the minimum and maximum groundwater levels are determined according to long-term observations.
If necessary, the area is drained, drainage is made. The possibility of deepening into the ground depends on the height of the water.
With a positive decision to use a glass foundation, preliminary measures are started.
Preparing for installation

The construction site is cleared of construction waste and all vegetation, the trees are uprooted. They carry out terrain planning with the help of bulldozers. If a pit is provided for by the project, the soil is excavated with heavy excavators.In addition to the general, a pit can be dug around the perimeter of the building or for each glass separately.
The compacting bed, if provided for by the project, should protrude 300 mm beyond the base plate on each side. Based on this, soil sampling is carried out.
At the end of the sampling of the earth, the bottom of the pit is leveled and tamped using mechanical means.
On soils prone to subsidence, arrange a compacting cushion of fine crushed stone and sand. First, a layer of crushed stone is poured, which is rammed with the help of mechanical devices or attachments on construction mechanisms. The next layer is sand. After spilling with water, the sand cushion is rammed in the same way as a crushed stone.
The next stage is the marking of the places where the foundations are installed. Using the skirting boards, a cord (2 mm wire) and a plumb line, mark the exact point of installation of the blocks. Next, using a dimensional template on the ground, measure the position of the sides of the foundations. For the convenience of installing the foundation, pegs are driven into the ground, which are connected with twine.
The horizontal level of all bases is leveled with a level. The level should be close to ideal - add a pillow if necessary.
Installation work
Workers who have undergone training and have permits to work with lifting mechanisms are allowed to install.
- Check the condition and correct, if necessary, mounting loops. Paint the position of the sides according to the project.
- Slinging is performed with two or four hooks, depending on the weight of the product.
- After lifting, the lower part of the base plate is cleaned of adhering soil.
- The exact orientation of the foundation is carried out manually at a height of 15–20 cm from the ground.
- The final adjustment is made with crowbars after lowering the block to the ground.
- Before backfilling the soil, the foundation is protected from moisture. Use the glue method or coating with special compounds.
- After installing all the glasses, the installation of the columns begins.
Glass-type foundations are actively used in industrial and civil construction. The design allows you to reduce the time for the installation of the bases and immediately after that start construction. Prefabricated blocks guarantee their strength and geometric dimensions, which speeds up installation and contributes to the stability of the structure.