The foundation accepts the building's bearing load and ground pressure. The foundation of the house must be solid and reliable. His device begins with digging a foundation pit. The process is not limited to earthworks, it is necessary to calculate the dimensions, preparatory measures. Before you start digging a pit with your own hands, you need to soberly assess the possibilities to cope with each stage of work.
Foundation pit construction

The pit construction consists of several stages:
- performing calculations, choosing a form and parameters;
- preparatory work;
- excavation;
- strengthening of slopes if the foundation pit is deeper than 125 cm.
In order to correctly determine the appropriate type of excavation, it is required to conduct a geodetic survey of the site and draw up a building project, calculate the load on the foundation. Based on the information received, the shape and depth of the excavation are selected. Assessing the amount of work, the builders conclude how the digging will take place:
- With the involvement of large or small equipment (excavator) - the option allows you to perform work quickly and without physical effort on digging and loading land.
- Manually - a laborious method, but at a price cheaper than ordering an excavator. It is recommended for the preparation of shallow and pile foundations. It is important to organize the work of people correctly, to observe safety measures.
Even if you dig pits with an excavator, there is a lot of work that will have to be done manually. These are the leveling and strengthening of the walls, tamping the bottom, backfilling.
An important preparation factor is the choice of the time of year to start work. Summer in the first months is the most successful period. The land is dry, excavation is easy, and the vehicles drive up without any problems. In spring and autumn, when the soil is damp, the danger of ground movement increases. In winter, land excavation is complicated by freezing. The prices for work and the general estimate are increasing.
The shape and size of the pit

The pit configuration depends on the type of foundation chosen. Common forms:
- rectangular pit for a monolithic slab;
- square or round pits for posts or piles;
- trenches around the perimeter and for internal walls - under the tape base.
Its size corresponds to the dimensions of the future house. Along the perimeter, the soil is removed at the rate of plus 30-40 cm to the parameters of the building. This distance is required to carry out work on insulation and waterproofing of the base.
When determining the depth of the pit, several factors are taken into account:
Soil type:
- sand or gravel - not less than 1.1 m;
- sandy loam - from 1.3 m;
- loam and clay - from 1.4 m;
- rocky dense rocks - 1.8 m.

The groundwater level affects the permissible depth of the foundation device. The structure should be 40-50 cm above the occurrence of the water layer.
In the reference literature, an indicator of soil freezing is found for a specific region. According to building codes, the depth of the base sole should be 30-40 cm below the specified value.
When installing a shallow foundation of a house, different rules apply. Deepening is carried out by 40-70 cm.
When calculating the parameters of the pit, use the data specified in the building drawing.
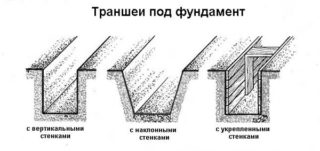
The length and width must exceed the indicated values by 20 cm on each side. The width is also influenced by the depth of the excavation. At a considerable depth, slopes are formed and the profile of the trench takes the form of a trapezoid expanding upward. At the bottom, the dimensions of the pit will correspond to the dimensions of the building, and the upper part will be larger.
Preparatory process
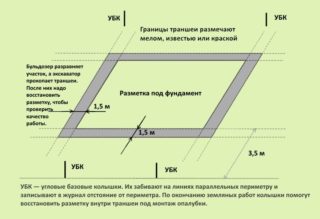
For safety reasons, it is necessary to conduct a survey of the site. Before starting excavation work, make sure that power lines, gas or water pipes will not be damaged. After inspection, a layer of turf up to 20-30 cm is removed, shrubs and other vegetation are removed.
The marking of the directions of soil excavation is applied to the site. The layout must match the master plan. The correctness of the application is checked by measuring the diagonals. The permissible error is 2 cm. On the working site, the marking is done with a construction cord stretched between the pegs. Then chalk paths are poured along it. If necessary, drainage is organized to drain water.
Features of digging for different types of foundations
Certain requirements are imposed on foundation pits for buildings. They must correspond to the size and load of the house, building codes, not to change the set parameters and shape. To fulfill the last point, it is necessary to follow the digging technology. According to the standards, the size of the steps and the angle of inclination of the slopes are selected, the walls of the pit are fastened. Development features depend on the type of foundation of the house.
Tape
At the corners of the perimeter of the house and at the intersection of the internal walls, pegs are driven in and markings are made. The width of the trench is indicated by two parallel lines. Excavation work begins at the highest angle, following the delineated perimeter line. During the digging process, the depth is controlled by the milestones.
If necessary, mount the tape trench from shedding from wooden boards, boards, slate. Spacers are installed between the opposite edges for reliability. After the foundation has solidified, the boards are dismantled. Part of the soil is not removed, but is left for backfilling. Better to use sand. After digging, the bottom of the trench is tamped under the backfill.
Monolithic

A pit for a house with a monolithic slab foundation is dug out with an excavator due to the large volume of earthworks. If the depth is 40-50 cm, then you can dig by hand. The soil is removed in parts, each layer is 50 cm, gradually 25 cm steps are formed. The soil is removed, starting from the center. Then the site is leveled and proceed to the next layer.
Drainage pipes are laid along the perimeter of the pit, below the general level. This is a necessary measure for wet soils. Development is carried out taking into account the characteristics of the soil:
- The sand is well compacted and holds the load, but crumbles when digging. The formation of slopes and strengthening of the side walls will be required.
- Clay and loam as a result of moisture freezing swell in winter. A competent calculation is required when arranging a slab foundation on such soil.
After the work of the technique, the bottom is leveled manually. Often it is necessary to carry out additional excavation in a layer of up to 10 cm. After leveling the bottom, backfilling with clean sand is performed. The layer is spilled with water and compacted.
Columnar

You can dig out the ground under the columnar foundation yourself.Work begins with clearing the site from the top layer of the earth and marking on the ground. You will need to apply a diagram of the perimeter of the house, in the form of two parallel-stretched cords. Places of holes for pillars are outlined in the corners and on spans with a step of 1.6-2.5 m.
To do the work manually, you will need:
- shovels (bayonet and shovel);
- pickaxe or crowbar;
- wheelbarrow for soil removal.
Pits up to 1 m deep can be dug with vertical walls; with increasing depth, slopes are arranged so that the soil does not crumble. The width of the pits is 20-40 cm larger than the pillars in each direction. This distance is necessary for the installation of the formwork. The depth is calculated according to the general rules.
Slope fixing technology

The collapse of the walls of the pits can be caused by various factors: precipitation, low density and high soil moisture, vibration. To prevent collapse, the walls of the pits are strengthened. The method depends on the depth of the excavation and the geodetic data of the site. The walls are fenced around the perimeter with the following materials:
- pipes;
- sheet pile of various types (Larsen, flat);
- piles;
- rolled metal products;
- reinforced concrete structures.
Grooving is more economical than concrete construction. Metal fencing is faster to erect, it can be dismantled and reused. A common option is to install pipes. They are driven around the perimeter with a diesel hammer or a hydraulic kapro installation.
When strengthening the pits with pipes, if necessary, hammering with boards is performed (so that the soil does not spill out). When using sawn timber, less metal products are required, some of the walls are covered with boards. In narrow trenches, the sheet pile is reinforced with struts. The Larsen sheet pile creates an airtight barrier, it is recommended when there is a threat of flooding by groundwater.
For small houses or outbuildings that require a shallow foundation, you can equip a trench on your own. Buildings of several floors with a basement require complex calculations and large-scale work at the stage of soil development. It is better to turn to specialists who know how to properly dig foundation pits.