A shallow strip foundation is the most economical base option for low-rise buildings. The simplicity of the design allows you to do it yourself without the involvement of construction organizations. In order for the foundation to provide strength and even distribution of the load, a preliminary calculation is necessary.
- Shallow foundation device
- Calculation parameters
- Reinforcement of the foundation
- The required amount of insulation
- DIY MZLF construction technology
- Preparatory work and markup
- Excavation
- Bulk cushion device
- Formwork installation
- Assembling the reinforcing frame
- Pouring concrete
- Waterproofing and insulation
- Uneven shrinkage on heaving soil
Shallow foundation device
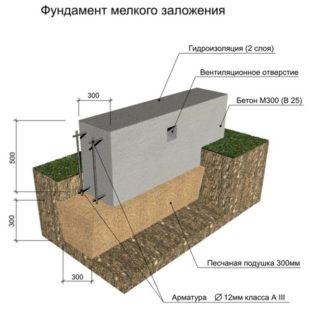
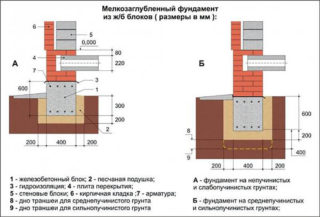
According to the classification, the foundations of buildings with a depth of 30 to 80 cm are referred to shallow strip foundations (MZLF). They are built above the freezing point of the soil, and are recommended for installation on slightly loose soils with good bearing capacity. The strip foundation is chosen with a close location of groundwater.
A feature of the MZLF is the ability to move with the ground, but due to the strength and uniformity of the displacement, it remains intact. The design is recommended for houses with no more than three storeys. Buildings can be of the following materials:
- cellular concrete;
- frame construction;
- timber or logs with wooden floors;
- hollow brick.
In addition to residential buildings, shallow foundations are used in the construction of garages, outbuildings, baths. This type of foundation is difficult to arrange on a site with a strong slope. Also, the design is not recommended for peat bogs and clay soil.

Benefits of MZLF:
- Significant cost savings compared to other types of foundation. Concrete consumption is reduced by 40-70%, labor costs by 50-70%.
- Construction speed - a small amount of work allows you to arrange the foundation in a short period of time.
- The risk of flooding and erosion by groundwater is reduced.
- Foundation work is available for self-fulfillment.
Cons of the foundation:
- limited load;
- difficulties with construction on inclined sections;
- no basement.
When choosing a shallow tape as the base, a water drainage device in the form of drainage ditches with pipes is required. A waterproof blind area with a width of 1 m or more is mounted along the perimeter of the buildings.
Calculation parameters
- Soil type and depth of groundwater. To obtain information, geodetic surveys are carried out.
- The depth of soil freezing - the data is taken from a special table of information by region.
- Difference in elevation on a site - the indicator is calculated by a vertical plan using a theodolite or other devices.
- The weight load on the foundation is the sum of the constant weight of the building and the temporary load (wind, snow, furniture weight, etc.).
Depth of laying is determined based on the data on the freezing point for non-porous soil:
- up to 2 m - 0.5 m;
- up to 3 m - 0.75 m.
for heaving soil:
- up to 1 m - 0.5 m;
- up to 1.5 m - 0.75 m;
- up to 2 m - 1 m.
Belt widthdepends on the total load of the building, including the number of storeys. Average indicator, calculated on materials of walls and ceilings in 1-3 floors:
- MZLF for a house made of aerated concrete or hollow bricks - 0.6-1.2 m;
- frame-panel construction with wooden floors - 0.4-0.6 m;
- logs and wooden floors - 0.3-0.6 m;
- timber with wooden floors - 0.2-0.4 m.
For self-calculation, use the formulaD = q / R:
- D - tape width;
- q is the load of the building on the foundation;
- R is soil resistance.
A shallow foundation rises above the ground, the height of this part of the structure is equal to the size of the underground part or the width multiplied by 4. From the height of the aboveground structure the comfort of living depends. At the maximum distance, the floors will freeze less.
Concrete cost - the main expense item for the construction of an unburied foundation. To ensure the required strength, the solution must be of the M300 grade. To calculate the weight of the concrete, you need to calculate the volume of the base. It is equal to the product of the perimeter by the width and the depth. To determine the total weight of the concrete solution, the mass of 1m3 (for the M300 it is 2389 kg) is multiplied by the calculated volume of the foundation.
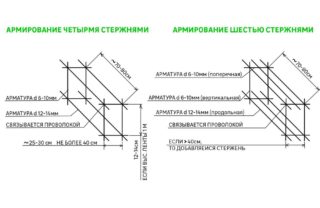
Reinforcement of the foundation
- L - the length of the bars;
- P - the perimeter of the foundation.
When constructing two-story buildings, the amount of reinforcement in the circuit is increased to three rows. When laying, the lower row of reinforcement should not touch the bottom, and the upper contour is located 10 cm below the surface of the foundation.
The required amount of insulation
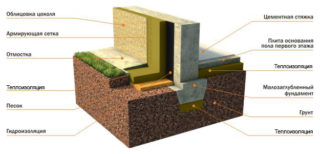
Waterproofing and insulation are mandatory stages in the construction of a foundation on heaving soils. This increases the durability and strength of the structure. The optimal insulation is plates of extruded polystyrene foam (polystyrene foam). The material is resistant to moisture, has minimal thermal conductivity. The amount of insulation depends on the climatic conditions of the region. They determine the thickness of the slabs. It can be 10-15 cm.
Extruded polystyrene foam is used for vertical and horizontal insulation. In the first case, the slabs are laid on the outside of the structure from the sole to the base. To calculate the total amount of foam, it is necessary to divide the area of the foundation walls by the area of one slab (the parameter is specified by the manufacturer).
DIY MZLF construction technology

To build a foundation with your own hands, you will need a step-by-step instruction for the technological process.
Preparatory work and markup
Construction begins with site preparation. It is cleaned of debris and plantings, and the top layer of soil is removed. Pegs, tape measure and cord are required for marking. The scheme of the future building is transferred to the site according to the plan. Pegs are driven in along the perimeter, a cord is pulled between them. The marking runs along the outer wall of the foundation.
Excavation
A trench of the estimated depth is dug under the strip base, plus the height of the bulk cushion. The walls and bottom of the pit are leveled. If necessary, small slopes are made to prevent shedding of the soil.
Bulk cushion device
At the bottom of the trench, a cushion of sand and gravel is arranged. These materials resist heaving of the soil, provide a solid foundation. The layer of filling is 20 cm. The sand cushion is carefully rammed, spilled with water.
Formwork installation
Wooden formwork must hold cubic meters of concrete, therefore, boards or plywood with a thickness of 20-30 mm are used in the manufacture.Boards are fastened with self-tapping screws and bars. The finished shields are installed in the trench. The formwork should rise above the edge of the pit to the height of the aboveground part. For reliability, spacers are installed outside, and opposite parts are connected with transverse bars.
Assembling the reinforcing frame

The metal frame is assembled from corrugated rods. The structure is made in separate parts and lowered into the trench. The main load falls on the corners of the foundation, therefore, special attention is paid to their strength. At the junctions of the contours, additional L-shaped reinforcements are installed, made of reinforcement with a section of 13 mm. The reinforcement should not touch the formwork; supports 7-10 cm high are placed on the bottom.
Pouring concrete
The best option is the simultaneous pouring of the entire volume of concrete. This will ensure the maximum strength of the foundation strip. The concrete solution is prepared from cement, sand and crushed stone in a ratio of 1: 2.5: 4. To remove air bubbles that form when solidifying voids. Use vibrating tools or a drill with a mixer attachment. The concrete is covered with a film for uniform drying, periodically it is moistened with water.
The formwork is removed after 2 weeks. A full set of strength occurs in a month.
Waterproofing and insulation
Installation begins from the bottom, the blocks are tightly pressed against the walls. The best option is plates with interlocks, which prevent the formation of cold bridges. If the material is laid in two layers, the panels are mounted offset by half the width. On top of the insulation, plastering is performed using a reinforcing mesh or roofing material is glued. The last stage is backfilling with soil.
Uneven shrinkage on heaving soil
Soil heaving is an increase in its volume when the water in it freezes. The pressure on the foundation is uneven and can lead to various types of deformation:
- Deflection and deflection - movement of the structure threatens the integrity of the roof.
- Shifts - one side of the base may sag and the other may rise.
- Roll - the problem is typical with a significant height of the house.
To avoid uneven shrinkage of the building before the foundation, part of the heaving soil is replaced with non-heaving soil. 20-30 cm of sand or fine gravel is poured into the trench. Experts advise not to leave an unloaded foundation for the winter. Under the influence of heaving, it can crack and become unsuitable for subsequent construction.